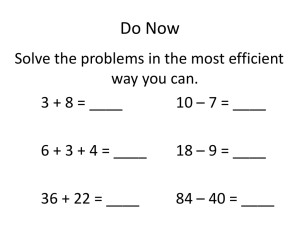Early Number Sense and K-2 problem solving - elementary
advertisement

Goals for today • • • • • Share “what works” with each other Possibly learn some new things about K and 1st grade math Get new resources and do some planning Go inside other’s classrooms Think about how to provide support as needed (“Daily 5”) What about you? • Introductions 3 sessions 1) Early number concepts (today) 2) Adding and subtracting to solve problems (Mar. 13) 3) Describing shapes, measuring length, telling time (Apr. 21) Big Ideas about K-1 Math 1) What children learn in K and 1st grade is a foundation for all other mathematics. 2) Early number concepts lead to addition and subtraction fluency. 3) Common Core is a clear outline of learning expectations. 4) Great resources are available for early numeracy activities. 5) Diagnostic assessments can help students who are behind their classmates. Framework • Counting – More/Less – Number Relationships • Add/Subtract Situations – Strategies – Fluency • Tens and Ones – Place Value – Multi-digit Operations Resources • • • • • Van de Walle and Lovin Kathy Richardson Grayson Wheatley Elementary Math Resources wiki Georgia and New York lesson plans Classroom Visits • Teaching Channel • Number Talks • Eventually your own classrooms?? Sharing and Planning • Always share • Keep track of “What I Want to Try” • Make and take – Daily 5 – Math Work Stations In a first grade class… • Three children successfully solved addition and subtraction tasks for two digit numbers. • Fourteen of the twenty-one children used their fingers to count all or count on as they solved such problems as 6 + 3 = ___ and 8 + 9 = ___. • Three of the children needed cubes to solve such problems and counted all the cubes. • One child had difficulty counting more than seven cubes accurately. Your kindergarten class? • Say the number sequence to 20? higher? • Tell which group of objects has more? which has less? or whether they are equal? • Count a group of objects up to 10? to 20? • Show a set of counters to represent a number? • Recognize dot card groupings and say the number represented, without counting. Look at the math on the diagnostic assessment – what percent have accomplished each task? Your 1st grade class • Start counting at a number other than 1 and continue the sequence? • Count objects up to 20 in a group and write the numeral? • Answer "How many more are needed to make 5 (or 10)?" perhaps using 5- or 10-frame cards. • Answer simple adding or subtracting problems like "Corey has 4 markers. Her sister gives her 3 more markers. Now how many markers does Corey have?" What strategies do they use? Common Core Standards • Take a few minutes to look over the CCSS for K and 1. • Put a check next to those standards that your students learn well. • Put a 0 next to those standards that are introduced but not always learned to mastery. • Put an X next to those standards that you currently don’t address in a meaningful way. It’s important to know the standards inside-out because they guide your planning and teaching. K-1 Number Concepts • • • • More, less, equal Counting objects, “counting on” Number relationships Addition and subtraction problems using strategies based on number relationships • Place value (two digits) Counting & number relationships are the basis for Problem solving which leads to Fluency with whole numbers The End Goal More, less, and same • Entering kindergarten children can most always pick the set that is more. • Although the concept of less is logically equivalent to more, the word “less” is often more difficult for children than “more.” • Whenever you ask “Which is more,” also ask “Which is less.” Elementary Math Resources Activities 1 & 2 Counting • Counting tells how many things are in a set. When counting a set of objects, the last word in the counting sequence names the quantity for that set. • Children will learn how to count before they understand that the last count word indicates the amount of the set. (the cardinality principle) • Resources: Let’s Count: Learning Numbers in Meaningful Ways (T.C.) Illuminations Let’s Count to 10 Activities 3 & 4 Counting on and back • Frequent short practice drills are recommended for children who have difficulty with this. • Number Talks Kindergarten video: Counting Book Activities 5, 6 & 7 Counting on and back • Frequent short practice drills are recommended for children who have difficulty with this. • Number Talks Kindergarten video: Counting Book Activities 5, 6 & 7 • Developing Number Concepts: Kathy Richardson (golden) • Read the section on counting, pp. 2-11 • What difficulties have you found? What works for you? What new activities might you try? • Partner pair/choose one/table talk Number relationships • Numbers are related to each other through a variety of number relationships. The number 7, for example, is • more than 4, less than 9, • composed of 3 and 4 as well as 2 and 5, • is three away from 10, • and can be quickly recognized in several patterned arrangements of dots. • Number relationships for 7 further extend to an understanding of 17, 57 and 370. Starting at 17, how many more are needed to make 20? Simon Says • • • • Simon says, Show six fingers. Janice, tell us about the way you showed six fingers. Peter, yours is different. Tell us about yours. Does anyone have a different way to show six fingers? • Simon says, Show nine fingers. Number relationships 1-10 Activities 8, 9 & 10 See the diagnostic assessment for a few dot patterns Subitizing See the Dot-card packet Quick Images Number Talks Number relationships 1-10 Activities 11, 12 & 13 Frogs on a Log Number relationships 1-10 Activities 14, 15 & 16 Five and ten frame cards • The frame for seven provides a visual model of seven as two more than five and three less than ten. • Working with this model supports the eventual connection to 5 + 2 = 7 and 10 – 3 = 7. • Video • How to Teach a Child Math – Part 1 • How to Teach a Child Math - Part 2 • Packet Number relationships 1-10 Activities 17 – 22 Graphics are from Van de Walle & Lovin, Teaching Student-Centered Mathematics: Grades K-3 Be Patient! • The principal tool that children will use as they construct these relationships is the one number tool they possess: counting. • Initially, then, you will notice a lot of counting, and you may wonder if you are making progress. • Have patience! Counting will become less and less necessary as children construct these new relationships and begin to use the more powerful ideas. Activities 23 – 26 Good basis for assessing Careful observation during number relationship station activities will tell you a lot about where your children are with number concepts. Usually classroom work is sufficient for moving most students along the learning progressions. But when informal observation leads you to believe that a child needs additional support, direct assessment is crucial. Kathy Richardson Assessing Math Concepts Assessing Math Concepts Kathy Richardson’s Assessment Series Concept 1: Counting Objects Concept 2: Beginning Number Relationships Concept 3: Comparing Numbers Concept 4: Identifying and Combining Parts Concept 5: Number Combinations Concept 6: Decomposing Numbers to Ten Concept 7: One Ten and Some More Changing Numbers Assessment Kathy Richardson • Show the numeral 6. What is this numeral? Can you make a pile of 6? • Show the numeral 10. What is this numeral? Can you change this pile (of 6) so there are 10? • Show the numeral 7. What is this numeral? If you change this pile (of 10) so there are 7, do you think you need to get some more or take some away? • Do you know how many you need to add/take away? Go ahead and change the pile to 7. • Show the numeral 9. What is this numeral? If you change this pile (of 7) so there are 9, do you think you need to get some more or take some away? • Do you know how many you need to add/take away? Go ahead and change the pile to 9. • Going Back – to 5: If the child tried to change one number to another but had difficulty, continue with the following numbers: Show me 2. Change 2 to 5. Change 5 to 4. • Going On – to 15: If the child was able to change the numbers with ease, continue with the following: Change 9 to 13. Change 13 to 11. Change 11 to 15. Popsicle Stick Math: Making 10 How could you use this in your class? • Developing Number Concepts: Kathy Richardson (golden) • Read the section on more and less, pp. 129-134 • Dig deeply into More/Less Activities • Read the More/Less Trains assessment (purple p. 3) Number Relationships 10-20 • Very important for basic addition fact families. • Kindergarten and early first grade children should be able to see a set of six with a set of 10 and know that the total is 16 – but they should not be asked to state that the 1 in 16 represents “one ten” or that the 6 represents “six ones.” (what’s a one?) Beyond Fingers: Place Value & the Numbers 11-19 Activities 27, 28 & 29 Double and near-doubles • • • • • • • Double 3 is the bug double Double 4 is the spider double Double 5 is the hand double Double 6 is the egg carton double Double 7 is the two-week double Double 8 is the crayon double Double 9 is the 18-wheeler double Numbers to 100: Intro • The hundreds chart is an essential tool for every K-3 classroom! Counting Collections to 100 Skip Counting with Counting Collections Notice the “Questions to Consider” Coming to Know Number Real world number sense • Estimation and measurement: • Will it be more or less than 10 footprints long? Will the apple weigh more or less than 20 wooden blocks? Are there more or less than 15 unifix cubes in this long bar? • Closer to ______ or to _______? 5 or 20 footprints, 10 or 30 blocks, 10 or 50 cubes? • About _______? … how many footprints? how many blocks? how many unifix cubes? Activities 30 & 31 Make and Take Break Is it reasonable? • • • • Could the teacher be 15 feet tall? Could your living room be 15 feet wide? Can a person jump 15 feet high? Could three children stretch their arms 15 feet? • Number sense is the bridge to mathematical proficiency at all levels. Counting & number relationships are the basis for Problem solving which leads to Fluency with whole numbers Math Talks …to develop basic number concepts After the video, go around your table one at a time and describe one thing you liked or noticed in the teaching episode. Then open up the discussion to responses and further discussion. Benefits Students have the opportunity to: • Clarify their own thinking. • Consider and test other strategies to see if they are mathematically logical. • Investigate and apply mathematical relationships. • Build a repertoire of efficient strategies. • Make decisions about choosing efficient strategies for specific problems. The teacher’s role • Since the heart of number talks is classroom conversations, it is appropriate for the teacher to move into the role of facilitator. “By changing my question from ‘What answer did you get?’ to ‘How did you solve this problem?’ I was able to understand how they were making sense of mathematics.” Procedures and expectations 1. Select a designated location that allows you to maintain close proximity to your students for informal observations and interactions. 2. Provide appropriate wait time for the majority of the students to access the problem. 3. Accept, respect, and consider all answers. 4. Encourage student communication throughout the number talk. Five small steps 1. Start with smaller problems to elicit thinking from multiple perspectives 2. Be prepared to offer a strategy from a previous student. 3. It is all right to put a student’s strategy on the back burner if you’re not following their thinking or can’t think of a good question to help them untangle their reasoning. 4. As a rule, limit your number talks to 5 to 15 minutes. 5. Be patient with yourself and your students as you incorporate number talks into your regular math time. Instructional Resources Our own wiki for sharing teaching ideas, resources, web links http://elementary-math-resources.wiki.inghamisd.org/home • Choose something from today’s session (or a couple things) to try before the next session. Come back with examples of students’ work from what you tried. • Next session March 6, here. • Focus on addition and subtraction. Something to try…