7-4.2 - Food Chains Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
advertisement

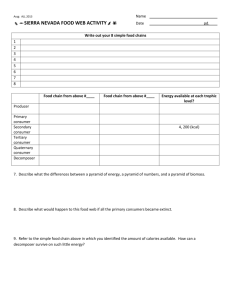
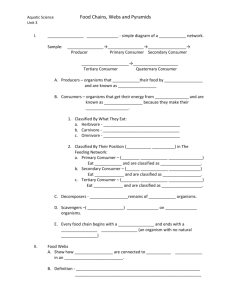
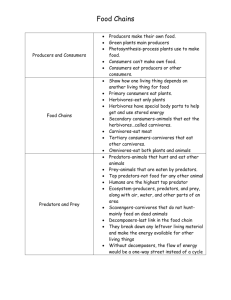
Energy Flow in Food Chains, Food Webs, & Energy Pyramids Mrs. Joelle R. King Science Teacher SC Indicator 7-4.2 Illustrate energy flow in food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. Prior Knowledge • In 3rd grade you learned about simple food chains, including the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers. • In 5th grade you identified the roles of organisms as they interacted and depended on one another through food chains and food webs in an ecosystem. • You learned a lot in 5th grade. Let’s review what you learned. In th 5 Grade… • You learned about producers and consumers like herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. • You learned about decomposers like microorganisms, termites, worms, and fungi. • You learned about the roles of predators and prey. • You also learned about parasites and their hosts. • Wow! You really learned a lot in 5th grade. Future Learning • In high school biology you will learn how to calculate the amount of energy transferred from one level to another in an energy pyramid. • You will also learn the roles that organisms play in the geochemical cycles (such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle). • You will learn more about predation, competition, and symbiotic relationships as well. Essential Question What does a food chain show us? Essential Question How is a food web different from a food chain? Essential Question How is a food chain or food web related to owl pellets? Essential Question How does energy flow through an ecosystem? Essential Question How does the amount of energy change as it moves through an energy pyramid? Food Chains • Food chains use pictures or words and arrows to show the movement of energy through the trophic levels of organisms. • The trophic level of an organism indicates the position that the organism occupies in the food chain. • It shows what it eats and what eats it. Producers & Consumers The levels are numbered according to how far the particular organism is along the chain. • Producers are at level 1. (Plants are producers because they produce their own food.) • Herbivores are at level 2. (consumer) • Predators are at level 3. (consumer) And so on… Anything that cannot make its own food must eat to survive. It must “consume” its food! It is a consumer. Note: There’s something wrong. What is it? Why does this look more like a “cycle” than a chain? Let’s discuss this one in detail. In this food chain, what is the producer? What is the first level consumer? What is the second level consumer? Is the polar bear the 3rd level consumer? Explain. Food Webs • Food webs describe the organisms found in interconnecting food chains using pictures or words and arrows. • In other words, food webs are a bunch of food chains all together! • They describe the complex patterns of energy flow in an ecosystem by modeling who consumes whom or what. Energy Pyramids • An energy pyramid shows the amount of energy that moves from one trophic level to another in a food chain. • The most energy is available at the producer level of the pyramid. • The availability of energy decreases as it moves up the energy pyramid. The Energy Pyramid Awesome Web Site! http://science-class.net/Ecology/energy_transfer.htm • Let’s take a look at the above web site relating to ecology and energy transfer. Another Cool Site http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/food/food_menu.html After we look at the above web site, we’ll go on to view the BrainPop video entitled FOOD CHAINS. The BrainPop videos provide further enrichment of topics discussed in class and are interesting as well as easy to understand! www.brainpop.com Making a Model Let’s make a model of an energy pyramid. The model you will construct will be simple. It will show pictures of the producers and consumers at each level, the names in words, and the trophic levels. The good news is that this model really is perfect for meeting our objectives relating to energy pyramids. Make sure you follow all instructions for proper completion of the model. Acknowledgements • All pictures were obtained from various sources on Google Images. • None of the pictures/illustrations are mine. • Credit is given to all artists/photographers for their work.