Urinalysis BioKit

Carolina Biological
$162.00
This lab will allow the student to test their own urine for color, pH, specific gravity, glucose, and protein.
An addition to the lab will allow studetns to learn how diet, drugs, and disease alter kidney function.
This lab would be used following discussions about the kidneys, kidney function, and the production of urine.
This lab also teaches urine testing methods and use of technology to test urine.
30 Urine specimen containers
2 Urine hyrdometers and jar sets
30 Glass vials
30 Dropping pipets
Jumbo pH stripes, wide range
30 Clinictest tablets with chart
Biuret Reagent
30 Student Guides
10 mL Graduated Cylinder
Access to sinks (for hand washing)
Must be calibrated either before or during the lab. The teacher or the students may complete the calibration.
To calibrate hydrometers
Rinse hyrdrometers and jar throughly
Fill jar ¾ full of water
Place hyrdrometer in the jar without it touching the sides
Read the level of water on the hydrometer scale
Hydrometers measure the specific gravity of a substance
Water has a specific gravity of 1.000
If your hydrometer reading of water is not
1.000 you will need to alter your specific gravity of urine, when it is tested
EXAMPLE 1
The measured specific gravity of water is 1.004
The hydrometer reading is 0.004 too high
That amount (0.004) must be subtracted from the urine measurement to obtain the true specific gravity of the urine
1.025 (measured urine value) - 0.004 (calibration factor) =
1.021 (specific gravity of urine)
EXAMPLE 2
The measured specific gravity of water is 0.996
The hydrometer reading is 0.004 too low
That amount (0.004) must be added to the urine measurement to obtain the true specific gravity of the urine
1.017 (measured urine value) + 0.004 (calibration factor) =
1.021 (specific gravity of urine)
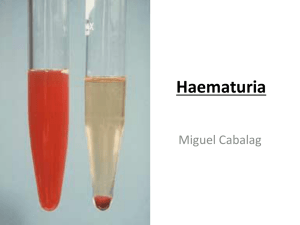
Color
Normal color range is light yellow to amber
Color depends on the amount of urochrome found in the urine
Urochrome is produced as a result of hemoglobin brake down in unused/old red blood cells
Lighter and darker colors can be caused by food, drugs, and disease
Table 2 on the Student Sheet may be useful
pH
pH is the measure of H + ions concentration, which indicates acidity and alkalinity
pH 7 = neutral pH below 7 = acid pH above 7 = base
Normal urine has a pH of 6.0
Food and disease may affect urines pH
Table 3 on the Student Sheet may be useful
Specific gravity
Density of a solution compared to water
Urines specific gravity ranges from 1.010 to 1.025
Varies do to fluid intake and disease
Glucose
Presence indicates diabetes mellitus
Severe metabolic disorder
Due to defective carbohydrate utilization
May be present after a large meal or during times of emotional stress
Protein
Small amounts of proteins are nomrally found in urine
Biuret reagent causes a color change in the presence of excessive protein
Diet and disease can affect protein levels