PPT
advertisement

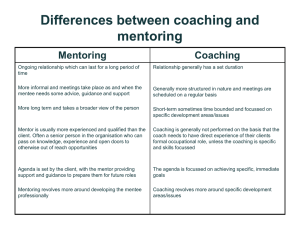
Connections and Actions Utilizing leadership skills to enhance mathematics instruction Laura Maly Bernard Rahming Kim Malacara Cynthia Cuellar Rodriguez Academic Coach-Math Training October 5, 2012 Goals 2012-2013 • To support the ACM when working with colleagues to ensure high expectations and access to meaningful mathematics instruction daily • To strengthen the ACM ability to serve in a coaching capacity in order to increase student achievement in mathematics • To deepen the ACM understanding of the change process to implement district initiatives to move mathematics instruction forward Learning Intention Success Criteria • We are learning to strengthen our ability to serve in a coaching capacity. • We will be successful when we access and implement coaching resources in our daily interactions with teachers. Pitfalls and Potholes From Vision to Action Positively Uplifting Refresh My Memory 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 Activity Time I am so confused! What does an Academic Coach do? In your work as a coach, determine which statements should be a part of your work. Be able to justify your reasoning. What Does an Academic Coach Do? • • • • • • • • • • Work with teachers to improve math achievement Run intervention groups Collaborate at grade level/department meetings Give feedback to teachers on lessons Perform morning, lunch, recess, bus, etc. duties Create CABS or Constructed Response items Provide teachers with resources Create math lessons for CLC Score CABS or Constructed Response items Gather, analyze and interpret data to inform instruction An individual who is well versed in mathematics content and pedagogy and who works directly with classroom teachers to improve student learning in mathematics What is a Math Coach Activity Time Alert! The following question may put a teacher on the defensive and shut down the conversation. Work with a partner to improve the following question: What Might You Say? “As you think about the questions you asked your class, what was the purpose of the questions and do you think they were good questions?” Be prepared to share your revised statement. One possibility As you reflect on the questions you asked the class to move student thinking, how might you describe the differences in what you anticipated and what you heard? Key: Invitation (underline), Cognition, topic, positive presupposition (bold), Plural forms (circle), Exploratory language (dashed line) Personal referencing, personal curiosity, and personal certainty. What are Listening Blocks I don’t have time to have lengthy conversations with teachers. What are Excuses not to Coach What are other excuses we use not to coach? Ensure timely, accurate monitoring of student learning and adjustment of teacher instruction for improved student learning. What is the Assessment Principle Ensure high expectations and access to meaningful mathematics learning for every student. What is the Equity Principle Activity Time Use the focused reading strategy as you read The PRIME Leadership Framework, Teaching and Learning Principle, pg 22-23 Focused Reading.... √ Important idea ! New insight to ponder ? Question Teaching and Learning Principle • Effective Math Leaders… – Are skilled at helping every teacher – Have a dedication to high-quality professional development – View student understanding not as a static, but as emerging from being exposed to interrelated forms of learning – Ensure that teachers are consistently growing in these interrelated forms of learning and actively searching for ways to provide students these experiences – Plan for instruction including well-articulated goals and assessment – Are knowledgeable and promote research-informed teaching practices and effective instructional strategies Activity Time Self-Evaluation Rubric for PRIME Assessment Leadership handout Self Evaluation Rubric 1 Every teacher uses formative assessment processes to inform teacher practice and student learning? 2 3 4 Activity Time As you think of the leadership goals you have set for yourself this year, share with a neighbor…. Stages of Leadership Action Stage 1: Know & Model Leadership of Self Stage 3: Advocate & Systematize Leadership in the Extended Community Stage 2: Collaborate & Implement Leadership of Others NCSM (2008). Principles and Indicators for Mathematics Education Leaders (PRIM Activity Time Acknowledging and Clarifying You’re noticing that… In other words… Summarizing and Organizing For you then, several themes are emerging… There seem to be two key issues here… Shifting Levels of Abstraction A value for you would be… A specific example for you would be… Paraphrase “I’m afraid I will get fired if my students don’t do well on the state assessment, and this decimal place value objective will be tested. The other fourth-grade teachers told me I can’t spend another day on this topic. I must follow a long-range pacing calendar that tells me what to teach each day. Subtraction with decimals is the objective I need to be teaching today, not place value. What should I do? I really need your help. Math is a very difficult subject for me to teach. I am just not very good at math.” Coaching Collaborating Consulting What are the Coaching Stances? Create a quick skit of each stance around a topic of your choice Activity Time A teacher who has many years of experience is reluctant to apply the current district protocols for teaching math. He claims to be satisfied with the instructional repertoire he remembers his own teachers using. “After all”, he says, “it obviously worked for me”. He sees no reason to spend time on what he calls “the latest fads”. There are few disciplinary referrals from his classes. To the casual eye, all is well. What at some of the issues and possible approaches that might apply in this situation. The pace of a conversation affects both the emotional and intellectual climate. The fast pace of our world tends to support the belief that there is a relationship between speed and intelligence. However, complex thinking takes and requires time. Lipton & Wellman, 2003 What is Wait Time When having a coaching conversation with a teacher, I ask a lot of questions without any paraphrases to get to the heart of the issue. What is Interrogation Acting with the intention of making a positive difference in the lives of students. What is Moral Purpose Activity Time As a table group, quickly sketch Michael Fullan’s Five Components in his Framework for Leadership. A Framework for Leadership Michael Fullan, Leading in a Culture of Change, 2004 Activity Time As you reflect on your accomplishments this month with teachers in your building, list things you have done to establish relationships that may have contributed to those accomplishments. DO’s and Don’ts of Building Relationships Do’s Make relationships a priority Show personal regard Make daily deposits Be a committed listener Keep your promises Use reflective feedback Promote thinking rather than advice giving Articulate expectations and standards Trust others Celebrate success Don’t Break commitments Breach confidentiality Act as a supervisor/evaluator Work with only those similar to you Be too quick to offer your suggestions or opinions “We are more likely to learn something from people who disagree with us than we are from people who agree. But we tend to hang around with and listen to people who agree with us, and we prefer to avoid and not listen to those who do not. This may be a good strategy for getting through the day, but it is a lousy one for getting through the implementation dip.” Leading in a Culture of Change, M. Fullan, What is Redefining Resistance Who is the Peanuts Gang Learning Intention Success Criteria • We are learning to strengthen our ability to serve in a coaching capacity. • We will be successful when we access and implement coaching resources in our daily interactions with teachers. “The question for educators is not whether all humans can learn but what conditions can we devise so that they will learn.” Roland Barth, Learning By Heart