PhD Candidate: Hamideh Khanbareh
advertisement
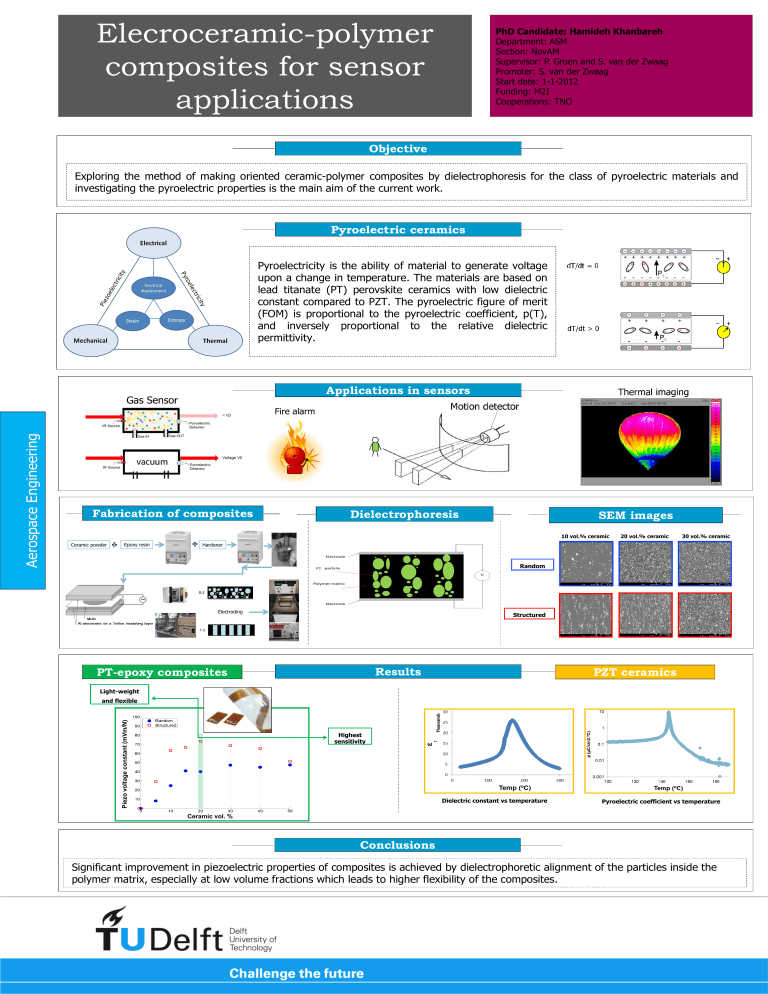
Elecroceramic-polymer composites for sensor applications PhD Candidate: Hamideh Khanbareh Department: ASM Section: NovAM Supervisor: P. Groen and S. van der Zwaag Promoter: S. van der Zwaag Start date: 1-1-2012 Funding: M2I Cooperations: TNO Objective Exploring the method of making oriented ceramic-polymer composites by dielectrophoresis for the class of pyroelectric materials and investigating the pyroelectric properties is the main aim of the current work. Pyroelectric ceramics Pyroelectricity is the ability of material to generate voltage upon a change in temperature. The materials are based on lead titanate (PT) perovskite ceramics with low dielectric constant compared to PZT. The pyroelectric figure of merit (FOM) is proportional to the pyroelectric coefficient, p(T), and inversely proportional to the relative dielectric permittivity. Fabrication of composites Dielectrophoresis SEM images 10 vol.% ceramic Ceramic powder Epoxy resin 20 vol.% ceramic 30 vol.% ceramic Hardener Random Electroding Structured Results PT-epoxy composites PZT ceramics Light-weight and flexible Piezo voltage constant (mVm/N) Aerospace Engineering Applications in sensors Highest sensitivity Dielectric constant vs temperature Pyroelectric coefficient vs temperature Ceramic vol. % Conclusions Significant improvement in piezoelectric properties of composites is achieved by dielectrophoretic alignment of the particles inside the polymer matrix, especially at low volume fractions which leads to higher flexibility of the composites.