MFIP Sanctions
advertisement

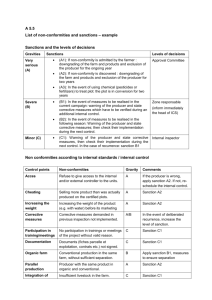
Ellen Smart, Mid-Minnesota Legal Aid eesmart@mylegalaid.org What is a sanction? A client’s MFIP grant is reduced by 10% to 100% because the client is not doing something that is required. Two types of sanctions: Child support sanctions (implemented by the child support worker) MFIP sanctions implemented by the employment counselor or a financial worker Sanction Reductions First sanction: 10% reduction. (Child support sanctions start at 30% even if it’s the first one.) Second through sixth sanction: 30% reduction. Seventh+ sanction: 100% case closure. Client must cure the sanction and reapply before the case will open again. A grant cannot be sanctioned more than once each month. Effect on Grant A family of four with no other income receives $621 in cash and $604 in SNAP($1225 total). At 10%, the family’s cash drops to $498.50 (SNAP stays at $604). At 30%, the family’s cash drops to $253.50 (SNAP stays at $604). SNAP can also be reduced if there is not enough cash to cover the sanction. Child Support Sanctions Clients can be sanctioned for noncooperation with child support. Child support sanctions start at 30% . Minn. Stat. § 256J.246, subd. 2. During the sanction, the client is also cut off Medical Assistance (MA). Minn. Stat. § 256.741, subd. 8(b)(3). Written notification to the client is required. Child Support Good Cause Available to clients who can demonstrate that they or their children may be harmed if a child support case is pursued. After the client alleges good cause, child support collection efforts must stop while the client works on her good cause application. Clients are automatically given 20 days, but that time may be extended. MFIP Sanctions Sanctions are implemented by the financial worker or employment counselor. Sanctions can only be implemented by the financial worker if the client misses the initial benefits overview. Client must be sent a Notice of Intent to Sanction (NOITS) before the sanction is implemented. Reasons for MFIP Sanctions Not attending an MFIP or employment services overview. Failing to create/renew/follow an employment plan. Refusal to complete questionnaires or assessments re: chemical health, mental health, or learning needs. Quitting or not accepting suitable employment. Not attending school. (Parents must attend school if under 18 and can choose between school and work if under 20.) Notice of Intent to Sanction (NOITS) A NOITS is the notice your client must receive before an MFIP sanction is imposed. Things that must be on the NOITS: date, reason for the sanction, what the client has to do to make it right before the sanction is imposed, a deadline, a language block, and appeal rights (including the client’s right to a conciliation conference with the job counselor). The client must be given at least 10 days to comply. Watch the reason for the sanction closely. Is it for failure to do an activity on the plan? If not, is the reason valid? Implementing a Sanction Once a NOITS has expired, the job counselor sends a status update to the county imposing the sanction. The client receives a notice from the county that they are in sanction. If the status update is not received or processed towards the end of the month (usually after the 22nd), it will not be implemented until the following month. If your client “cures” a sanction at the end of the month, the next month’s grant will be reduced at first. In a couple of weeks, a supplement will be issued for the difference. Your Client Gets a NOITS What is the date on the NOITS? Appeal and/or request a conciliation conference. Is the NOITS adequate? Did your client fail to do the activity specified on the NOITS? What is going on with your client? Why didn’t s/he comply? Sanction Defenses 60 or over Client or household member ill or disabled Domestic violence Personal or family crisis Lack of transportation or child care and other good cause reasons Child under 12 months (Minn. Stat. § 256J.561, subd. 3) Employment plan was not appropriate or was asking the client to do too much Be creative Client meets a Family Stabilization Services (FSS) category Employment Plan Issues Are the hours requirements valid? No matter how many hours are on the plan, clients cannot be sanctioned for doing at least this (Minn. Stat. § 256J.55, subd. 1(c)): 87 hours/month in a one-parent household with a child under 6 130 hours/month in a one-parent household with no children under 6 55 hours/week total for two-parent households Does the plan meet the needs of your client? Is your client capable of what the plan requires? Good Cause Reasons Lack of transportation Lack of child care Quit because employment was unsuitable Client or child has to go to court Client has to go to child’s school because of a problem (or client has to stay home with child who is suspended) Client is already in suitable work activities Other emergencies like funerals Creativity Common-sense reasons which may or may not resonate with the job counselor. Client is 37 weeks pregnant, and her plan calls for 35 hours of job search per week. Client is the victim of identity theft, so job search is useless. Child Under 12 Months Not an exemption or good cause but useful in avoiding sanctions. A household can be exempt from cooperating with employment services for up to one year if there is a child under 12 months in the household. Only one parent at a time can use this. 12 months total, not 12 months per child. Client Ill or Disabled Is your client unable to participate in activities for less than 30 days? Over 30 days? Less than 30: A doctor’s note should excuse your client from activities for those days. Over 30: Clients need a more detailed form from their doctor. Other: Low IQ, learning disabilities, etc. Household Member Ill or Disabled Needed in the home (30 days or more) Severe & Persistent Mental Illness (adults) and Severe Emotional Disorder (children)* Home care/waivered services* Temporary illnesses * Banked months! Domestic Violence If violence can explain noncompliance, the client should develop a family violence waiver (FVW), and the sanction should be cured. FVW Benefits: FVW clients cannot be sanctioned for failure to attend group employment services overviews. The months an FVW is in place do not count towards the 60-month limit. Employment plan requirements can be relaxed in terms of activities and hours. Extension basis! Family Violence Waivers Part of the employment plan. Must be written with the client, the employment counselor, and a person trained in domestic violence (advocate). Each county must have an advocate available. Requires proof. See Minn. Stat. § 256J.545. Clients cannot be required to get an OFP/HRO, participate with court proceedings, call the police go to counseling, or take their children to counseling. Family Violence Waivers and Sanctions Once a client tells the employment counselor about domestic violence, a referral to an advocate should be made. If a client has a FVW, they should not be required to attend a group employment services overview.b If domestic violence can explain noncompliance, the sanction should be lifted for prior months, too. Problems with Family Violence Waivers Client tells her job counselor about violence, and the job counselor does nothing. Job counselor tells the client she have to have an OFP to qualify or cannot live with the abuser. Job counselor singlehandedly makes the determination that the violence isn’t serious, recent, or believable. Renewal issues (job counselor wants additional proof or thinks the client should be “over it by now”). Seventh Sanction Issues Before implementing a 100% sanction, the job counselor must follow certain procedures, including attempting to meet with the client. Minn. Stat. § 256J.246, sub. 1(d). This is the only time job counselors must go back and review prior sanctions even though the appeal time has run, so use this to your advantage! Minn. Stat. § 256J.246, subd. 1(d)(3). Other Sanction Issues If a client is in sanction during her 60th month, s/he is not eligible for extensions, so it is important to identify these cases quickly. Get the sanctions panel from a financial worker if you do not know how many times your client has been sanctioned and a time panel if your client does not know what month s/he is in. Family Stabilization Services (FSS) If the client receives FSS, there are extra steps the employment counselor must take before imposing a sanction in Minn. Stat. § 256J.575, subd. 7(d). These are things like attempting a face-to-face meeting and reviewing the file. Many of the “sanction defenses” are FSS criteria. If the employment counselor should know or suspects your client qualifies for FSS before it’s been proven, your client should still get FSS’s heightened sanction protection. In some cases, your client will be moved to an FSS-only employment service provider. FSS Criteria Parent applying for Social Security benefits Clients with family violence waivers Parents 60 or over Non-citizen who has been in the U.S. for under a year Client ill/incapacitated for over 30 days Household member who meets SED/SPMI standards or gets waivered services Needed in the home Client is developmentally disabled/mentally ill/has an IQ under 80 and has been assessed to be severely limited in ability to find or maintain employment Client is considered unemployable Further information Minn. Stat. § 256J DHS Website (http://mn.gov/dhs/) Combined Manual Employment Service Manuals Bulletins Appeals & Regulations Division (for appeals forms, fax number, etc.) Forms www.lawhelpmn.org (links to fact sheets and other legal services info) Hennepin County’s employment services website (information about job counselors and has links to DHS forms and manuals) (http://www.hennepin.us/portal/site/HennepinUS/menuitem.b1 ab75471750e40fa01dfb47ccf06498/?vgnextoid=a68891a45c2f 3210VgnVCM20000048114689RCRD)