Written Assignment 4 by Ewing Coleman Green EDD 9100L CRN
advertisement

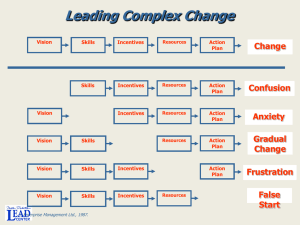
The Authors Richard DuFour Long-time educational administrator, author Professional Learning Community (PLC) expert Co-authored primary text in EDD 8111 Communities of Practice (DuFour & Eaker, 1998) www.allthingsplc.info Robert Marzano Long-time educational researcher and author www.marzanoresearch.com Similarities to EDD 9100 Kouzes and Posner (2007) extensively cited Five practices of exemplary leadership (Model the way, Inspire a shared vision, Challenge the process, Enable others to act, and Encourage the heart) Staying in love; leadership is an affair of the heart Northouse (2012): leadership is an influence process to achieve common goals, and leadership is about relationships and results Clawson (2012): importance of emotion; VABEs Vision is essential Similarities (cont’d) Principalship is key to creating culture and building capacity (self-efficacy) Distributed leadership Principal’s Actions Collaborative Teams Actions Student Achievement Teacher Professional development is embedded (learn from work versus taken away from work to learn) Importance of communication (clear, inspiring) Importance of celebration of milestones Dissimilarities to EDD 9100 Focused primarily on leading educational systemic change and improving student achievement through PLCs Less on interpersonal aspects of leadership No discussion of ethics and integrity Learnings/Reinforcements Every great leader is teaching and every great teacher is leading Power of PLC to align resources to measurably improve student learning Three Big Ideas All students learn at high levels Collaborative effort to meet student needs Results orientation (use SMART goals: Strategically aligned, Measurable, Attainable, Results focused, Time-bound) Evidence of impact Administrivia Focus on Student Learning Learnings (cont’d) Collaborative practice, sharing, and observation Learning from peers, mutual accountability Shift from principals vertically ‘supervising’ teachers to educators horizontally building collaborative capacity Transformation from culture of isolation to culture of collaboration Recurring cycle of collective inquiry Curriculum Learning engagement design Monitoring student learning Individual student differentiation Job Relevance My role as 8Red PLC leader Essential to gain shared vision and ownership of direction My role on Middle School Leadership Team Help us improve PLC effectiveness My role on upcoming Differentiation Task Force TBD, student learning enrichment My role as Algebra 1 teacher Individual student learning needs Agreements Senior leadership must ensure organization has the capacity to deliver against coherent initiatives Avoid initiative fatigue Focus on the critical few Sustained, patient, continual effort Provide time and resources Collaborative time (i.e., common planning time) Role of effective educator is a calling, a work of love, because it is fundamentally about serving others The people; passion for a moral purpose The process; must be a lifelong learner Agreements (cont’d) Beware the Dark Side Clawson (2012): “Be aware that when people work on something they believe in deeply, they can work so hard that they begin to do damage to themselves and others” (p.232) Be mindful of sphere of influence Move to standards-based reporting including learning behaviors (O’Connor, 2007) Disagreements Including traditional letter or numeric grading schemes on standards-based report cards (O’Connor, 2013) Discussion on formative assessment omitted importance of student self-assessment (McMillan & Hearn, 2008) Who Should Read and Why? Constituents in education at all levels From Board of Directors to teachers Alignment of organization on initiatives key to student learning Professional Learning Community model is a paradigm shift in pedagogy References Clawson, J. G. (2012). Level three leadership: Getting below the surface (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. DuFour, R., & Eaker, R. (1998). Professional learning communities at work: Best practices for enhancing student achievement. Bloomington, IN: National Educational Service. DuFour, R., & Marzano, R. J. (2011). Leaders of learning: How district, school, and classroom leaders improve student achievement. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree. Kouzes, J., & Posner, B. (2007). The leadership challenge (4th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass. References (cont’d) McMillan J. H., & Hearn, J. (2008). Student self-assessment: The key to stronger student motivation and higher achievement. Educational Horizons (87)1, 40-49. Retrieved from http://www.eric.ed.gov/ezproxylocal.library.nova.edu/PDFS/EJ815370. pdf Northouse, P. G. (2012). Introduction to leadership (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. O’Connor, K. (2007). A repair kit for grading: Fifteen fixes for broken grades. Portland, OR: ETS Assessment Training Institute. O’Connor, K. (2013). Essentials for principals: The school leader’s guide to grading. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree. Image URLs Slide 9. SAS logo. Retrieved from http//:www.saschina.org Slide 13. Board of Directors. Retrieved from http://ts4.mm.bing.net/th?id=H.4604759954425579&pid=15.1 Slide 13. Teacher. Retrieved from http://ts2.mm.bing.net/th?id=H.4535250221531749&pid=15.1