cental problems in the management of innovation
advertisement

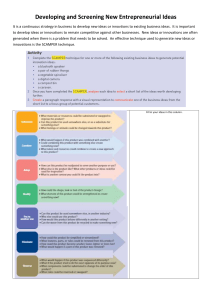
Andrew H. Van de Ven is a Professor of Organizational Innovation in the Carlson School of Management of the University of Minnesota. In his paper called “ CENTRAL PROBLEMS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INNOVATION”. He Is discussing about how innovation plays an important role in social and economic development. It also discuss about what managerial problems any idea faces before turning into an innovation. He has discussed four central problems in the management of innovation as The human problem of managing attentionIt talks about about physiological limits on humans, group limitations, and literature on ways of managing attention. The process problem is managing ideas into good currencyIt says basic concept or an idea of innovation may be an individual activity but implementing that idea/ innovation is a collective achievement of pushing those ideas into good currency. The structural problem of managing part-whole relationshipIt says that great innovations happens because of the variety of ideas and for that matter multiple functions, resources and disciplines are needed to transform innovative idea into reality. The strategic problem of institutional leadershipIt is about the strategic problem of creating a leadership that is helpful for an innovation and how an organization can become committed to seeing that innovation under that leadership. An innovation is a new idea, which may be a recombination of old ideas. Successful innovation enquires both technical innovations ( new technologies, producs and services) and administrative innovations (new procedures, policies and organizational forms). Learning to understand the close connection bet technical and administrative innovations is part of innovation management. It is said that an innovative idea without a champion gets nowhere. People try to contribute to the process of innovation as per their backgrounds, experiences and activities that occupy their attention. People become attached to ideas over a time. Project management and program planning technologies like PERT, CPM and PPM can help in managing innovation process to avoid individual and organizational problems. Management of attention- people have basic physiological limitations of not being able to handle complexity , of adapting to gradually changing conditions. Physiological limitations of human beings Most people have very short span of attention. Average person can retain raw data in short term memory for only a few seconds. Dissatisfaction with existing conditions stimulates people to search for improved conditions, and they will cease searching when a satisfactory result is found. People unconsciously adapt to slowly changing environments. Group and organizational limitations- In the group or an organization the problems of individual’s inertia, behavior and incompatibility preferences are added to the limitations of human beings in managing attention. Group plays strong pressure of working together on the individual members. Innovation is an intra- and extra organizational network building effort that revolves around the creation, adoption, and sustained implementation of a set of ideas among people who, through transactions , become fully committed to these ideas to transform them into a regular practice or implemented reality. From a managerial perspective, Innovation can be answered by understanding 3 basic questions ; 1. How do innovations develop over time? 2. What problems are encountered? 3. What responses are appropriate in managing these e problems ? 3. Partwhole Relationships 1.To develop ideas INNOVATION 2. Managing People 4. Institutional Leadership Lodahl and mitchell point of view for innovation is : It is a phenomena of institutional success to a certain degree that exhibits three basic charateristics, • AUTHENTICITY : To embody an organization’s idea • FUNCTIONALITY : To work in line with the purpose • FLEXIBLITY : To incorporate inputs/ suggestions from its members The process of innovation involving the building up of intra- & extraorganizational networks leads to a critical point of creating institutional leadership. In an organization, Institutional leadership is of prime importance for building a cultural belt which help foster innovation. It’s the measure of reflection of the amount of support an organization can draw from its members/community to pursue an IDEA, also creating a social, economic and political setup needed for a community to sustain it’s members. •Institutional leadership is needed for an organizational innovation during the key period of development and transition, in situations when an organization is forced or open to consider alternative ways of doing things. •It defines the “character of culture” of an organization. •This responsibility is carried out through four key functions : 1. Defining the institution’s mission 2. Embodying purpose into the organization’s structure and system. 3. Defending the institution’s integrity. 4. Ordering internal conflict. INSTITUTIONAL PROCESS Creation, Elaboration of Ideology Use of personal network; selection based on values Face-to-face contact, sharing, rituals Charismatic, mythic Ideals paramount: Structure tentative IDEA Founding Ideals TECHNICAL PROCESS Statement of organizational goals Recruitment Broad search : Use of universalistic criteria Socialization Rules & procedures learned from colleagues Leadership Problem solving/ consensus making Formalization Early routinization/ uncertainty reduction "Creativity is thinking up new things. Innovation is doing new things." — Theodore Levitt Thank you….