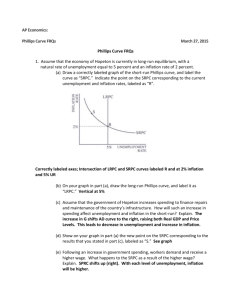
Inflation and Unemployment
advertisement
AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Module 34: Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve April 3, 2014 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve Objectives - Understand each of the following: • What the Phillips curve is and the nature of the short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment • Why there is no long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment • Why expansionary policies are limited due to the effects of expected inflation • Why even moderate levels of inflation can be hard to end • Why deflation is a problem for economic policy and leads policy makers to prefer a low but positive inflation rate 2 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein The Short-Run Phillips Curve • Review: AD/AS model and tradeoff between inflation and unemployment • SRPC displays the downward sloping relationship • Can extend below X axis but not to the Left of Y axis…why? 3 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein The Short-Run Phillips Curve • When SRAS curve slides down the AD curve, ie technology breakthrough, SRPC shifts downward 4 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Inflation Expectations and the Short-Run Phillips Curve • Changes in the expected inflation rate cause an upward shift in SRPC • Expected p translates into higher actual p for each level of unemployment • Believed to be 1-for-1 5 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein The Long Run Phillips Curve • NAIRU: Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment • Keeping unemployment below NAIRU leads to ever-accelerating p • NAIRU implies there is no long-term trade-off between p and UR 6 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein The Costs of Disinflation • What if the government tried to reduce inflation? • Keep UR > NAIRU, create recession until p subsides • Painful in that it creates higher UR • Example: Voelker 7 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Deflation • Debt Deflation – debts paid with dollars worth more • So borrowers cut back on projects, causing further deflation • Zero Bound - expected deflation causes real interest rates to approach zero and lenders stop lending • Liquidity Trap – Fed can’t cut rates below zero, so Monetary Policy becomes ineffective 8