Information on BEP-RTI
advertisement
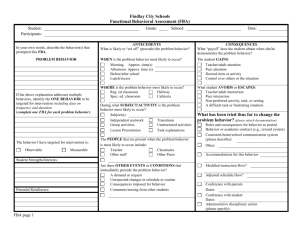
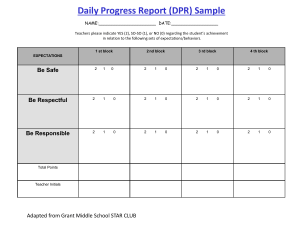
Information on BEP-RTI By: Ms. Amy Evans Behavior Educational Program-Response to Intervention (BEP-RTI) • • • • • Agreeing on and establishing school rules Teach these rules to the students Gathering and recording behavior through observation Receiving positive incentives for appropriate behavior Providing the set of established rules to parents and encouraging them to reinforce them at the home environment Behavior Support Team • • • • Usually includes coordinator, teacher, parent, and students Receive behavioral referrals Helps map out plan for behavioral change Teacher, parent, and teacher are interviewed using a form called the Functional Behavioral Assessment-Behavior Support Plan Protocol (F-BSP) • Focused primarily in the Tertiary Prevention BEP-RTI Coupon • • • • • Teacher gives to student privately A positive reinforcement Given when goals are being met Worth double if signed by teacher Can be redeemed at coordinators office “Check in, Check out” System • • • • • Tertiary Prevention active procedure Goals from Behavior Support Plan Form called Daily Progress Report (DPR) Responsible for form between school and home Parent signs form and Student brings it back to the school coordinator Daily Progress Report (DPR) • • • • • A form used on daily bases Teacher encourages student to self-score Communicates why and on what behavior needs changing Form used on “Check in, Check out” System Provides Behavior Support Team information on the progress of the student Data Based Decisions • • • • • Classroom management based on Finding the targeted behaviors Gathering and recording observations Charted and monitored for progress Used with the help of ABC (Antecedent, Behavior, and Consequence) establishment Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) • Tertiary intervention plan for needed support • Behavior Support Team decided that the primary and secondary prevention levels were unsuccessful • Detailed observations need to be recorded • Development of an Individualized Behavior Plan (IBP) • Consists mainly of a three step process (Step 1: Request for Assistance Form, Step 2: Teacher/Parent/Student Interviews, and Step 3: Establishing a Testable Hypotheses Functional Behavior Support Plan Protocol (FBSP) • Type of interview by the Behavioral Support Team (BST) to help figure out the underlying problem • • • • Establish a hypothesis that may be causing the behavior Modify old plans and make new ones as necessary Obtain specific, measurable, and objective information about student Record frequency, intensity, and context of the behavioral problem High-5 Ticket • • • • • Receive as an award for showing improvement on a behavior goal Can be redeemed at later time for a desired award Used as a motivator Teacher gives ticket in an “high Five” way May, however, be deemed more beneficial to some students to give in private setting Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEA) • • • • • Federal Law Reauthorized in 2004 Guidelines for school Special Education Program Defines thirteen possible disabilities Heavier emphasis on effective scientific based instruction are given to students Motivational Goal: Relational • • • • Stems from a theoretical view Behavioral problems relating to wanting attention Used for creating testable hypothesis Solutions: could give more feedback and attention, provide more interaction, or use the attention as a stronger reward • Motivational incentive for goals to become met Motivational Goal: Avoidance • • • • Stems from a theoretical view Behavioral problems relating to escaping from people or events Used for creating testable hypothesis Use gathered data based information to see if there may be an underlying cause • Use the information to try to avoid another behavior episode No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB) • • • • • Federal law Scientific based instruction used by classroom teachers Prove through data that students are learning Required the three tiered model to be implemented in schools Mission of providing student’s individual needs so they won’t fail Primary Prevention • • • • • First level of three tier model in the Positive Behavior Support (PBS) “Check in and check out” with school coordinator Uses daily progress report form Receives feedback from teacher Establishes up to five positive school wide rules Request for Assistance Form (RAF) • Forms available to all teachers in school • Completes form on student with a behavior problems by teacher or other educator with direct contact • Takes filled form to (BEP) committee • Committee responds within three days • Form indicates the methods tried within the classroom Rewards • • • • • BEP-RTI coupon High 5 ticket Used to help motivate student to behave appropriately Show students that someone is paying attention to them Helps students to achieve the goals that have been set for them Secondary Prevention • • • • • Second level of the tier model in the Positive Behavior Support (PBS) Increased attention and support from the first level About fifteen percent of students are represented in this level Referred to as students who are “at risk” for behavioral problems Goal is to stop the behavior from getting out of hand Self-Scoring • • • • • Shown improvement in their Daily Progress Report (DPR) Teacher stops scoring and allows the student to take the responsibility It is a process Teacher reviews the scores students give themselves Teacher gives feedback and encouragement as needed Tertiary Prevention • • • • Third level of the tier model in the Positive Behavior Support (PBS) Most extreme behavior problems About five percent of the students Most needed support using a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) and an Individualized Behavior Plan (IBP) • Begins with a Request for Assistance Form (RAF) and develops into a Daily Progress Report (DPR) Testable Hypotheses • Done at the tertiary level • Behavior Support Team (BST) tries to figure out during the Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) • Determined cause of behavior • In order to prevent worsening of behavior in the future • Reasons and motivations behind behavior problem Three-Tiered Positive Behavior Support • • • • • A school-wide program Levels include primary, secondary, and tertiary Requires various amount of support from teachers and parents Categorizes the students behavior Similar to Response to Intervention (RTI) for academic model