GE Brown Bag Presentation: Common Core
advertisement

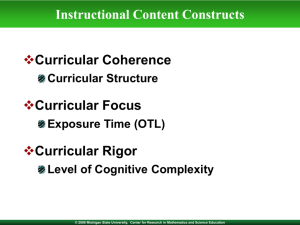
Understanding the Common Core State Standards The education landscape is shifting and your child will need different skills to be poised for success The US economy and our education system are directly linked U.S. workers lack the education and skills needed to compete successfully in the U.S. economy. • By 2020, 80% of jobs will require post-secondary education • 53% of business leaders reported difficulties in recruiting employees with the needed skills, technical training, and education;1 • The U.S. now ranks 12th out of 36 OECD countries in the number of 25-34 year-olds with a college degree;2 • By 2018 there will be 3 million fewer college graduates than required by the labor market.3 The recent U.S. economic downturn will only worsen if the deficit of high-skilled, educated workers continues. How can we improve the U.S education and economic situation? Common, globally competitive academic standards will strengthen the knowledge and skill set of U.S students. Students will leave school fully prepared to engage in college and the workforce. A high-skilled and educated workforce will increase U.S economic competitiveness on the local and national level. The Common Core State Standards are an effort to ensure that all U.S students receive the quality education needed to succeed in future endeavors. What are the Common Core State Standards? • The Common Core State Standards Initiative (the “Standards”) is a state-led effort coordinated by the National Governors Association (NGA) and the Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO). www.corestandards.org • The Standards are benchmarked to those of the most highly competitive nations globally • As of January 2012, forty-six states and the District of Columbia have adopted the Common Core State Standards (CCSS), a consistent set of English language arts (ELA) and mathematics expectations for grades K-12 that students need to meet to succeed in college and careers • States have committed to implement the new standards by the 2014-15 school year • This is an aggressive timeline that will require a strategy that draws on state policymakers, district and school officials, and classroom teachers to ensure a successful and efficient implementation and transition States that have adopted the Common Core * Minnesota adopted the CCSS in ELA only The Common Core State Standards include teaching, assessment and curriculum At the local level, formative assessments will take place on an regular basis, weekly to monthly. Formative Assessments Common Assessments At a state level, Common Assessments will be based on the new CCSS and administered throughout the year. Common Core State Standards CCSS serve as the foundation for ongoing national improvements by ensuring rigorous curriculum, assessments, and teaching. Benefits of the Common Core Standards Consistency • Previously, every state had its own set of standards and set of expectations for student performance Equity • Common standards can help create more equal access to an excellent education Competition • All students must be prepared to compete with not only their American peers, but also with students from around the world Clarity • Clear and coherent standards will help students (and parents and teachers) understand what is expected of them Collaboration • Common standards create a foundation for districts and states to work collaboratively The GE Foundation is investing in the Standards The GE Foundation will serve as a leader in supporting the implementation of the Standards District • Investing in 7 school districts across the country and providing support to schools and district offices for implementation of the Standards State • The GE Foundation is working to align district and state Standards implementation National • Convening local, regional, & national businesses to build private sector support for the Standards • Investing in the national leaders and organizations in support of the Standards • Informing education policies for the Jobs and Competitiveness Council The US Education System is not globally competitive Typical US State World Leading Countries Topics Whole Number Meaning Whole Number Operations Measurement Units Topics G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l Common Fractions Equations & Formulas Data Representation & Analysis 2-D Geometry: Basics Polygons & Circles Perimeter, Area & Volume Rounding & Significant Figures Estimating Computations Properties of Whole Number Operations Estimating Quantity & Size Decimal Fractions Relationship of Common & Decimal Fractions Properties of Common & Decimal Fractions Percentages Proportionality Concepts Proportionality Problems 2-D Coordinate Geometry Geometry: Transformations Negative Numbers, Integers & Their Properties Number Theory Exponents, Roots & Radicals Exponents & Orders of Magnitude Measurement Estimation & Errors Constructions w/ Straightedge & Compass 3-D Geometry Congruence & Similarity Rational Numbers & Their Properties Patterns, Relations & Functions Slope & Trigonometry G6 l l l l l l l G7 G8 Compared to a world standards, the US Education System does not measure up l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 G7 G8 l l l l Measurement Units l l Common Fractions l l Equations & Formulas l l Data Representation & Analysis l l 2-D Geometry: Basics l l Polygons & Circles l l Perimeter, Area & Volume l l Rounding & Significant Figures l l Estimating Computations l l Properties of Whole Number Operations l l Estimating Quantity & Size l l Decimal Fractions l l Relationship of Common & Decimal Fractions l l Properties of Common & Decimal Fractions l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l Whole Number Meaning l l l l l l l Whole Number Operations Percentages l l l l l l Geometry: Transformations l l Negative Numbers, Integers & Their Properties l l Number Theory l l Exponents, Roots & Radicals l l Exponents & Orders of Magnitude l l Measurement Estimation & Errors l l Constructions w/ Straightedge & Compass l l 3-D Geometry l l l l Congruence & Similarity l Rational Numbers & Their Properties l Patterns, Relations & Functions l l Slope & Trigonometry l l Proportionality Concepts Proportionality Problems 2-D Coordinate Geometry l l l l l l Math Science 100% 100% 80% 80% 60% 60% 40% 40% 20% 20% US 0% 0% 4th Grade 8th Grade 12th Grade 4th Grade 8th Grade 12th Grade *Third International Math & Science Study A Map of What Top-Performing Countries are Teaching Grade Topic Whole Number: Meaning Whole Number: Operations Measurement Units Common Fractions Equations & Formulas Data Representation & Analysis 2-D Geometry: Basics 2-D Geometry: Polygons & Circles Measurement: Perimeter, Area & Volume Rounding & Significant Figures Estimating Computations Whole Numbers: Properties of Operations Estimating Quantity & Size Decimal Fractions Relation of Common & Decimal Fractions Properties of Common & Decimal Fractions Percentages Proportionality Concepts Proportionality Problems 2-D Geometry: Coordinate Geometry Geometry: Transformations Negative Numbers, Integers, & Their Properties Number Theory Exponents, Roots & Radicals Exponents & Orders of Magnitude Measurement: Estimation & Errors Constructions Using Straightedge & Compass 3-D Geometry Geometry: Congruence & Similarity Rational Numbers & Their Properties Patterns, Relations & Functions Proportionality: Slope & Trigonometry Real Numbers, Their Subsets & Properties 1 2 3 4 5 n n s n n n n n n s s s s l n n n l s l s l l l l s l s l l n n l l l l l l l l s n n l l l l s 6 7 n l l l l l l l n n n l 8 9 10 11 12 n s n n s n s l n s n s n s n s l Intended by 4 out of the 6 topachieving counties l l Intended by all but one of the topachieving countries (5 out of 6) l l l l l l s l s n l n l l l l l s s n l Intended by all of the top-achieving countries s n l l s n s s l s s l s s n s l s n n s s s n l s n l l l s l n s n l n n A Map of What the US is Teaching for the Addition of Whole Numbers 7 6 4 3 2 1 VT LA NH/R I DoD EA IN MO NV OH OK OR SD WA NJ AZ CA DC FL MI NM NY TX MD MN UT VA CO ME WY TN AL KS MS ND AR ID AK HI 0 SC GA NC WV Grade Level 5 States Culminating Learning Expectation Intermediate Expectations Initial Learning Expectation Repeated Expectation 9 Addition and Subtraction of Fractions 8 7 Grade Level 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 States Culminating Learning Expectation Intermediate Expectations Initial Learning Expectation Repeat and/or Extension Expectations Major Changes in Literacy Instruction as a result of the CCSS From… To… Majority of what students read is literature. Very little time available for science and social studies instruction. Building knowledge through content-rich nonfiction Students spend most of the time writing about personal experiences, opinions not grounded in evidence. Reading, writing and speaking grounded in evidence from text, both literary and informational Students read text, without consideration of complexity to prepare for postsecondary expectations and vocabulary instruction is often focused on literary terminology, rather than “academic vocabulary” (alliteration vs. ignite) Regular practice with complex text and its academic language The Common Core Standards provide coherent organization and clear student expectations Major Changes in Math Instruction as a result of the Standards From… To… A mile-wide, inch-deep curriculum that speeds through topics, rather than building strong foundation Focus: Focus strongly where the standards focus Scattered, isolated topics that don’t build on student understanding Coherence: Think across grades, and link to major topics Math curricula that emphasize either fluency or understanding in mathematics and that application is often seen as just “extra” Rigor: In major topics, pursue conceptual understanding, procedural skill and fluency, and application The Common Core Standards provide coherent organization and clear student expectations How will my child be assessed on the new Standards? • The new assessments are being developed by 2 consortia of states • The new assessments that are aligned to the Standards will be launched in 2014 • Students in grades 3-12 will be assessed each spring • Assessments will, in full operation, be implemented online Sample Assessment Question Pre-Standards: Math (3rd grade item) • A lunch menu has 3 beverages selections: water, juice, and milk. The menu also offers 2 sandwich selections: turkey and peanut butter. How many different meals on one beverage and one sandwich are possible? Sample Assessment Question Common Core Standards: Math Sample Literacy Question: Pre-Common Core Standards Most people have a special activity or hobby that they enjoy. Some people collect things while others like to read or play games. What activity do you like to do? Write a composition describing what you enjoy doing. Explain why that activity is special to you. Sample Assessment Question Common Core Standards: Literacy (Text-dependent question) The Adventures of Tom Sawyer • Why does Tom hesitate to allow Ben to paint the fence? How are his sentences constructed to reflect that hesitation? What effect do Tom’s hesitations have on Ben? How Can I Support my Child’s Learning? • Refer to the PTA guide on the Standards: http://www.pta.org/common_core_state_standards.asp • Talk with your child and ask questions about what he/she is learning • Communicate actively with your child’s teachers about how he/she is integrating the new Standards into the classroom • Be patient: the new standards (are more rigorous, will introduce a new way of teaching, assessment results will reflect higher expectations) • Explore Resources: 1. Commonstandards.org 2. Commoncore.org 3. PTA.org