How to optimize comfort in stereoscopic displays
advertisement

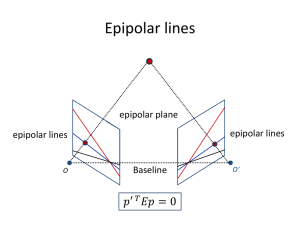
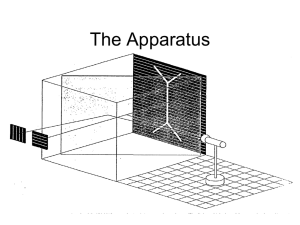
How to optimize comfort in stereoscopic displays Martina Rasch, Manuel Wyss and Florian Zoubek Motivation [1] 2 Vergence-Accommodation Conflict [2] 3 Vergence/Accommodation-Coupling [3] 4 How to measure comfort? [4] [5] 5 Random Dot Stereograms [6] vs. 6 Disparity Disparity Manipulation Depth Range 7 Disparity Disparity Manipulation Comfort Zone Depth Range 8 Disparity Disparity Manipulation Comfort Zone Depth Range 9 Disparity Disparity Manipulation Comfort Zone Depth Range 10 Creating a Metric vs. 11 Quality Model 12 Disparity Frequency Model *Different for each frequency Response [JND] 5 4 3 2 1 Disparity [arcmin] [7] 13 Pipeline [8] 14 Further Applications Standard stereo Backward-compatible stereo [9] 15 Disparity Mapping in Post-Production [10] 16 Algorithms View-interpolation [11] Multi-rigging [12] 17 Method Disparity map extraction Disparity map optimization Computing Correspondence Features Minimize error and maximize comfort 18 Disparity manipulation Warping Disparity map extraction [13] 19 Disparity optimization [14] 20 Disparity manipulation with warping 21 [15] Temporal constraints [16] 22 Applications [17] 23 Thank you for your attention! List of Figures [1] Oculus Rift: http://pixelvolt.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Oculus-Rift-GDC-2013.jpg [2] Figure 1, Hoffman, David M., et al. "Vergence–accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue." Journal of vision 8.3 (2008). [3] Adaptation of Figure 1, Lambooij, Marc, et al. "Visual discomfort and visual fatigue of stereoscopic displays: a review." Journal of Imaging Science and Technology 53.3 (2009): 30201-1. [4] Questionaire: selfmade (Shown questionnaire created by David M. Hoffman et. al) [5] Stopwatch: http://www.flickr.com/photos/purplemattfish/3020016417/ [6] Random dot stereogram: http://www.jrg3.net/presentations/random_dot.jpg [7] Slide 10, http://people.csail.mit.edu/pdidyk/projects/LuminanceDisparityModel/LuminanceDisparityModel.pptx [8] Figure 4, Didyk, Piotr, et al. "A perceptual model for disparity." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG). Vol. 30. No. 4. ACM, 2011. [9] Figure 11, Didyk, Piotr, et al. "A perceptual model for disparity." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG). Vol. 30. No. 4. ACM, 2011. [10] Adaptation of Figure 10, Lang, Manuel, et al. "Nonlinear disparity mapping for stereoscopic 3D." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29.4 (2010): 75. [11] View interpolation: http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/larryz/ZitnickSig04.pdf [12] Multi-rig: http://www.3dfocus.co.uk/3d-news-2/3d-technology/mio3d-push-for-stereo-rigs-with-3-or-more-cameras/6282 [13] SIFT: http://groups.csail.mit.edu/graphics/classes/CompPhoto07/PPT/12_Phototourism.key/SIFT_fade.png [14] Adaptation of Figure 1, Lang, Manuel, et al. "Nonlinear disparity mapping for stereoscopic 3D." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29.4 (2010): 75. [15] Adaptation of Figure 14, Lang, Manuel, et al. "Nonlinear disparity mapping for stereoscopic 3D." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29.4 (2010): 75. [16] Figure 9, Lang, Manuel, et al. "Nonlinear disparity mapping for stereoscopic 3D." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29.4 (2010): 75. [17] Adaptation of Figures 11 and 12, Lang, Manuel, et al. "Nonlinear disparity mapping for stereoscopic 3D." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29.4 (2010): 75. 25