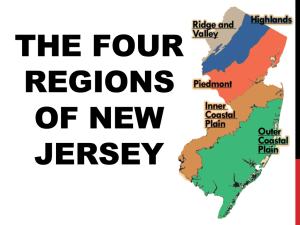
Georgia's Physiographic Regions: Piedmont, Blue Ridge & More
advertisement

Welcome to the Piedmont Region of Georgia!!! General information Located just north of the Fall Line and south of the mountain regions of north Georgia, the Piedmont is often referred to as the “heartland” of the state. The name for this region is based on its location and means “foot of the mountains.” The Piedmont region is the second largest physiographic region in the state and contains about half of the state’s population. Land Use Land use in the Piedmont includes manufacturing, cropland, forestry, grazing and woodland as well as some mining. Rivers Chattahoochee River Flint River Ocmulgee River Oconee River Lakes in the Piedmont Description Lake Lanier Looking out across the Piedmont there are sloping hills and valleys in the north. While in the southern part of the region flatlands can be found. This region was known as the cotton belt of antebellum days Lake Sinclair Underneath the surface in the Piedmont, areas of bedrock (solid rock) consisting of granite, gneiss, & marble can be found . The soil in this region is clay. Chattahoochee River West Point Lake Strom Thurmond Lake Hartwell Lake J. Strom Thurmond Lake Lake Oconee Lake Russell Hartwell Lake Crops Wheat Corn Livestock Raised in Piedmont Cattle Climate Soybeans Poultry The Piedmont region has hot summers and mild winters. It is usually hot and humid during the summer months. The growing season is from 210 to 240 days. The annual rainfall in the Piedmont ranges from 48 to 56 inches. Festivals Natural Resources Granite Feldspar Oconee National Forest Dogwood Festival in Atlanta Yellow Daisy Festival at St. Mountain Industry Many industries have been founded in the Piedmont Region including the following: Chick-fil-a Coca-Cola Home Depot Rich’s Department Store Land Use Welcome to the Blue Ridge Region of Georgia!!! General information Located in the northeastern corner of the state, the Blue Ridge Region is known for its rugged beauty. This region contains Georgia’s highest and largest group of mountains and Georgia’s highest peak, Brasstown Bald. The beginning of the Appalachian Trail is found in Blue Ridge. The Blue Ridge Mountains form the first barrier to warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico. Therefore, the highest annual rainfall in the state can be found here as well as Georgia’s highest erosion rate. Description The bluish tint of the mountain range is the first defining characteristic of this region. The mountains are heavily forested and filled with hardwoods such as hickory and oak trees. Many tourist landmarks can be found here. The Blue Ridge Region contains less than one percent of Georgia’s prime farmland. Most land is used for forestry, grazing, and woodland. Rivers Chattahoochee River Chattooga River Savannah River Toccoa River Toccoa River Lakes for Recreation Blue Ridge Lake Chattuge Lake Lake Burton Lake Rabun Nottely Lake Skiing Crops Apples Climate Corn Natural Resources Hardwood Timber Gold The Blue Ridge Region has warm summers and moderately cold winters. The growing season is from less than 180 days to 210 days in some portions of the region. The annual rainfall in the Blue Ridge is over 56 inches. Marble Festivals Alpine Helen Apple Festival in Ellijay Georgia Mountain Festival in Hiawassee Gold Rush Days in Dahlonega Industry Cabbage Patch Kids founded in Cleveland Land Use Welcome to the Ridge & Valley Region of Georgia!!! Land use in the Ridge and Valley includes manufacturing, cropland, forestry, grazing and woodland. General information Located between the Blue Ridge Region and the Appalachian Plateau in Region in north Georgia, the Ridge and Valley is known for its carpeting industry. The city of Dalton is found here and is known as “The Carpet Capital of the World.” Description The parallel ridges and open valleys of this region give rise to its name . Small farms can be seen on the valley floors while the ridges remain forest-covered. The ridges are composed of sandstone. The valley floors were formed from limestone, shale, and other sedimentary deposits. Rivers Coosa River Etowah River Oostanaula River Etowah River Lakes in the Ridge & Valley Allatoona Lake Carters Lake Allatoona Lake Etowah Indian Mounds Crops Corn Soybeans Wheat Cotton Livestock Raised in Ridge and Valley Cattle Poultry Climate The Ridge and Valley Region has warm summers and moderately cold winters. The growing season is from less than 180 to 210 days. The annual rainfall in the Ridge and Valley ranges from 52 to 56 inches. Festivals Prater’s Mill in Varnell Natural Resources Limestone Barite Chattahoochee National Forest Wagon Train in Chatsworth Chief Vann House The Chief Vann House is known as the “Showplace of the Cherokee Nation.” The home was the first brick home built within the Cherokee Nation in 1804. Industry Carpet Manufacturing Welcome to the Appalachian Plateau Region of Georgia!!! General information Located in the northwestern corner of the state, the Appalachian Plateau is the smallest physiographic region in Georgia. It is known as the Cumberland Plateau. The TAG Corner can be found in this region and is where Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia meet. Description Limestone caves, deep canyons, and unique rock formations can easily be seen in this region. Waterfalls over layers of sandstone and shale millions of years old can be viewed here. Land Use Land use in the Appalachian Plateau consists of forestry and grazing and woodland. Mountains & Canyons Lookout Mountain Sand Mountain Cloudland Canyon Cloudland Canyon Crops Corn Climate Soybeans Natural Resources Coal (Ga.’s only known source) The Appalachian Plateau Region has warm summers and moderately cold winters. The growing season is less than 180 days. The annual rainfall in the Appalachian Plateau ranges from 52 to 56 inches. Chickamauga & Chattanooga National Military Park Attractions The oldest and largest National Military Park in the country, Chickamauga & Chattanooga was the site of the second bloodiest battle during the Civil War. Rock City Anna Ruby Falls Welcome to the Coastal Plain (Inner) Region of Georgia!!! General information Located in the southern part of the state, the Coastal Plain is the largest physiographic region in the state. During prehistoric times, it was completely covered by the ocean. The beginning of this region is marked by the Fall Line. It is divided into the Inner Coastal Plain and the Outer Coastal Plain. Land Use Land use in the Inner Coastal Plain includes manufacturing, mining, cropland, grazing, and woodland. Rivers Alapaha River Altamaha River Flint River Description Ogeechee River Flat land with low relief and flat to gentle slopes is the first noticeable difference in this region. Rivers flow more slowly in this region and generally become wider as they flow toward the coasts due to the flat land. Ocmulgee River This is the major agricultural region in the state and contains the Vidalia Upland (where ideal soil for growing Vidalia onions is found) and the Dougherty Plain (where ideal soil for growing peanuts, pecans, and corn is found). St. Mary’s River Ocmulgee River Oconee River Satila River Savannah River Savannah River Lakes in the Inner Coastal Plain Lake Seminole Walter F. George Reservoir Climate Crops Peanuts Pecans Peaches Corn The Inner Coastal Plain has hot summers and mild winters. It is usually hot and humid during the summer months. The growing season is from 240 to 270 days. The annual rainfall in the Inner Coastal Plain ranges from less than 48 inches to 56 inches in the southwestern corner. Festivals Onions Cotton Big Pig Jig in Vienna Cherry Blossom Festival in Macon Watermelon Georgia Peach Festival in Fort Valley Livestock Raised in Coastal Plain (Inner) Cattle Poultry Mossy Creek Barnyard Festival in Perry Industry Founded in Inner Coastal Plain Natural Resources Sand and Gravel Kaolin (clay) Fuller’s Earth (clay) Limestone Bauxite Welcome to the Coastal Plain (Outer) Region of Georgia!!! General information Located on the Atlantic Coast, the Outer Coastal Plain is the center of naval stores and pulp production in the state. The Okefenokee Swamp can be found here and is the home for hundreds of varies plant and animal species. Description Large swamplands, marshy areas, interlocking rivers and tributaries, and sandy beaches are primary features in the Outer Coastal Plain. It is the home to many endangered species and much of the land is used as wilderness sanctuaries. Major shipyard ports can be found along the coast along with seafood gathering and processing. Many tourist come for the scenery and relaxation the Outer Coastal Plain has to offer. Land Use Most of the land in the Outer Coastal Plain is poorly suited for agriculture The land is used for pasture and growing pine tress for timber, pulp, turpentine, & other products. There is some pulp manufacturing located here. Rivers & and the Ocean • Atlantic Ocean • Altamaha River • Savannah River • Satilla River • St. Mary’s River Okefenokee Swamp Animals Alligator Egret Gopher Tortoise Coastal Wetland Georgia’s Coastal Wetland is an are of lowlying land that is covered by water all or part of the time. It is home to many species of animal and plant life. These wetlands also serve as a buffer for the mainland during storms as well as a filter of pollutants from some of Georgia’s rivers. Barrier Islands: The islands that block the wind and sand and help protect the mainland from erosion are known as barrier islands. These are found off of the coast of the Outer Coastal Plain. These islands were once referred to as the “Islands of Gold” by Spanish explorers. The islands include Cumberland Island Jekyll Island St. Simons Island Tybee Island Natural Resources Sand and Gravel Forestry Climate The Outer Coastal Plain has hot summers and mild winters. It is usually hot and humid during the summer months. The growing season is over 270 days. The annual rainfall in the Outer Coastal Plain ranges from 48 to 56 inches. Festivals St. Patrick’s Day Festival in Savannah