11.1 Atmosphere
advertisement

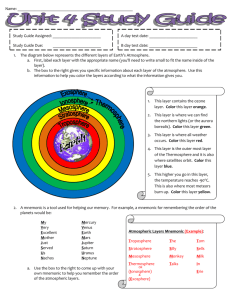
Atmosphere What is the Atmosphere • Thin layer of air that regulates global temperature, and filters out dangerous solar radiation. • Looks like a thin halo of blue light around the earth. Composition of the Atmosphere • 78% is nitrogen (N2) • 21% is oxygen (O2) • 1% are trace gasses nitrogen oxygen trace gasses The Layers from Space to Earth • Thermosphere • Ionosphere • Mesosphere • Stratosphere • Troposphere TIM ST. • An easy way to remember the layers is to use the mnemonic device TIM St. • T hermo sphere • I ono sphere • M eso sphere • S trato sphere • T ropo sphere Troposphere • Almost all weather occurs in this layer • Most clouds, wind, rain, snow are in this layer • As you go higher in the Troposphere it gets cooler. Temperature Inversions • Hot air is usually closer to the earth because the sun heats the surface of the earth. • Temperature inversions- when cool air gets trapped beneath hot air. • This happens in Los Angeles and causes smog = smoke (from cars) + fog (moisture in air) Stratosphere • The layer of the atmosphere that extends upward from the troposphere to an altitude of 50 km. • Contains the ozone layer O3 (Found in the Stratosphere) Ozone • Ozone comes from the greek ozein “to smell” • Ionizers make ozone from oxygen O2 Oxygen O3 Ozone Naturally the Sun’s Rays make ozone from oxygen O2 Oxygen O3 Ozone Depletion of the Ozone Layer • Occurring over Antarctica Ozone Depletion • Caused by some chemicals such as CFC’s Who cares if the ozone is thinning? • Ozone provides protection from solar radiation which can cause skin cancers. Mesosphere The mesosphere is 50-80 km This is the coldest layer of the atmosphere -80°C Noctilucent or "night-shining" clouds (NLCs). Occur in the mesosphere Ionosphere • The area of the earths atmosphere where electrically charged IONS are found • Used in radio communications • Closer to earth during the day • Farther from the earth at night Auroras occur in the Ionosphere Excited ions release light in the polar regions of the globe Thermosphere • The hottest layer of the atmosphere • Thermo = heat • This is where meteorites can burn up upon entry into the atmosphere. The Greenhouse Effect The causes of the greenhouse effect • The burning of fossil fuels to produce carbon dioxide gas • Any process that releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere Atmosphere Poster • • • • • Label the Layers of the atmosphere Elevations of the layers Temperatures of the layers 2 interesting facts about the layers Draw the two interesting facts in the appropriate layers