Chapter 35 Section 4 Changes in Central and Eastern Europe
advertisement

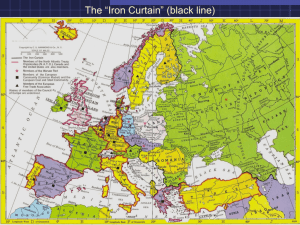
Chapter 35 Section 4 Changes in Central and Eastern Europe Changes in the Soviet Union lead to changes throughout Central and Eastern Europe Do Now: What caused the downfall of the Soviet Union? End of Cold War • Polish leader Lech Walesa organized Solidarity (independent trade union), elected 1st non-communist government in Eastern Europe. • Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989), Helmut Kohl led to the reunification of Germany in 1990. Collapse of the Soviet Union (1991) Collapse of the Soviet Union (1991) • Attempted coup to overthrow Gorbachev failed in 1991. • Communist support for coup forced Gorbachev to recognized independence of several satellites. • Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine formed Commonwealth of Independent States in December 1991. • Soviet Union now fully broken apart, Gorbachev resigned at the end of 1991, COLD WAR FINISHED. • Yeltsin replaced Gorbachev, said to move too fast. • Putin took power in 1999. Poland Reforms The Rise of Solidarity • Workers strike to win recognition of Solidarity- Polish labor union • Lech Walesa- leader of the unionbecomes national hero Solidarity Defeats Communists • Communist government banned solidarity but can not solve economic problems • In 1988, workers rebel to force recognition of Solidarity • Elections in 1989 and 1990 make Walesa president of Poland Poland Reforms continued Votes out Walesa Poland under Kwasniewski • Walesa tries to build a free market economy • Alexander quickly Kwasniewski was elected President in • Though some 1995 progress made, many Poles unhappy • Brings Poland into NATO • Walesa votes out • Tries to build a strong market economy Hungarian Communists Disband • In 1990, voters elect non-Communist government in Hungary • Democracy thrives • Hungary joins NATO in 1999 Germany Reunifies • East Germany’s leaders resists reforms as in Poland and Hungary • Thousands of East Germans try to escape through Hungary to Austria • East Germany closes its borders which sparks massive protests • In late 1989, new East German leader opens Berlin Wall • By end of year, communist government there collapses Germany’s Challenges • Reunification- merging of two Germanysachieved in 1990 • East Germany in poor shape, needs rebuilding • This costly effort forces German leader Helmut Kohl to raise taxes • In 1998, Kohl voted out of office • New leader-Gerhard Schroeder- has difficulty reviving economy • Angela Merkel elected chancellor in 2006; economy begins to stabilize Democracy Spreads Czech breaks up in Czechoslovakia • Economic reforms hurt Czech Reforms • In 1989 large crowds protest in Prague, demand democracy • Harsh government cracks down- more protests • By 1989, Communists gone • Vaclav Havel elected President people of eastern partSlovakia • In 1993, Czechoslovakia splits into two separate countries • Both economies grow – Slow in Czech Republic – Faster in Slovakia • In 2004 Slovakia elected Ivan Gasparovic president and join NATO and EU Overthrow in Romania A Popular Uprising • In 1989, Romania leader has army shoot protesters • This action prompts major revolt and collapse of communist rule • Dictator Nicolae Ceausescu and wife executed Christmas Day 1989 Romanian Economy • Corruption and crime prevalent through 1990s • Economy lags • Much of economy still owned by government, not in private hands • Government begins moving towards market economy Breakup of Yugoslavia • Yugoslavia has 8 ethnic groups in a federation of 6 republics • Milosevic, Serbian leader, tries to impose control over the whole country • Slovenia and Croatia fight off Serbian army, win independence • In 1992, Bosnia-Herzegovina declares independence; war breaks out • Serbs forces participate in ethnic cleansinggetting rid of Bosnian Muslims • In 1995, UN, US establish peace setting up multiethnic government Rebellion in Kosovo • In 1998 fighting starts in Kosovo, Serb province of ethnic Albanians • Serbian army invades to put down Albanian rebel with harsh force • In 1999, NATO bombs Serbia – Forces Serbia to withdraw Region faces challenges • • • • Serbia has a new leader Milosevic faces war crime trials Montenegro declared independent in 2006 Serbia accepted peacefully