Fall Protection Part 2.
advertisement
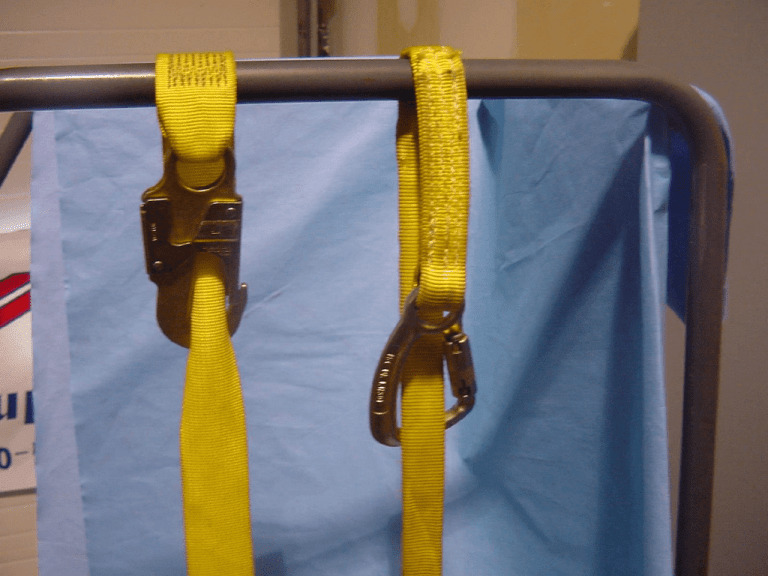
8183 CROSS-ARM STRAP 9186 LOOPED CROSSARM STRAP WITH SHOCK ABSORBER ALWAYS INSPECT YOUR FALL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT!!! Calculating Forces Calculating Total Fall Distance Freefall = 6 feet maximum Deceleration Distance = 3.5 feet maximum Lifeline elongation = 2 feet maximum Total fall before stopping = 11.5 feet Portion of body landing below attachment point approximately 5 feet minimum Harness effect = 1 ft Total clearance below attachment point required to avoid contacting lower level may be as great as 18.5 feet or more! When Utilizing Vertical Lifelines Anchorage Devices – – Vertical Lifelines – – – – Size and construction shall be compatible with lifeline Shall be positioned over head to minimize free fall distance (maximum of six feet) Shall be positioned in the proper direction – they only work in one direction Lanyards – – Shall never be wrapped around itself, or secured with knots Shall be long enough to reach the lowest level and protected against sharp edges Regular 5/8” rope is not a lifeline, use lifeline rope with a 5,000 lbs. Minimum breaking strength Rope Grabs – – Connected to a structure capable of supporting 5,000 pounds Protected against damage from sharp edges Shall have built-in shock absorber limiting force to 900 lbs. Should be limited to 3 feet in length Full-body Harness – Properly adjusted to the individual SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Steep Slope Roofs (Greater than 4 and 12) Sloped Roofing – Roofing Brackets & Slide Guards Steep Slope Commercial Roofing Guardrails Scaffold Catch Platforms Fall Arrest System Scaffold Catch Platform Scaffolding erected at the perimeter of the roof to limit a fall to less than six feet Addition fall protection may be required at the rake or gable end of the building Guardrails would be required to prevent an employee from rolling off of the scaffolding Scaffolding must be erected under a trained supervisor and inspected daily by a competent person. SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Sloped Roof - Guardrail Systems Protection Before You Start Fascia Rail Platform Rail SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Sloped Roof – Guardrail Systems Another version - Guardrail installed after roof edge is finished. Standing Seam Roof Anchors Pictured above are standing seam roof anchors. There are now many types of anchors available for difficult applications. Should you come across a situation where you feel the fall protection provided will not work, or have difficulty locating a suitable anchor location, notify your foreman who should contact Management or the Safety Department immediately. SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Requirements for PFAS (1926.502(d)) – Maximum “Free Fall” distance- 6 feet. – Interps allow larger fall distance as long as other criteria are met. – Maximum force on your body when you come to a stop is 1800 pounds. • Force depends on your weight, fall distance, and deceleration device (e.g., shock absorbing lanyard). • The shorter the fall the better. – Maximum deceleration distance is 3.5 feet. • Stopping distance after your lanyard becomes tight & the shock absorber begins to stretch. (one reason why you can’t tie two lanyards together) – No impacting of objects during fall – Prompt rescue (10 min. max) SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Making the PFAS Work for You Think before you tie! Will you stop? – What are you attached to? Making the connection – Make sure the lock on your hook is working. – Do not wrap around & hook back to lanyard. – Do not shorten the lanyard with a knot. – If possible, always hook up at ‘D’ ring height or higher. – Do not hook lanyards together. – Take out of service any PFAS component previously loaded by a fall SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Making the PFAS Work for You Other requirements? – Clearance distance – will you hit anything? • Typically minimum of 10 ft- 6 ft for free fall + 3.5 ft for deceleration and 0.5 ft for clearance. – Swing fall hazard - will you be a pendulum? • Are you anchored directly overhead? • Extremely important for retractable lanyard due to ratcheting effect – RESCUE! • If PFAS is your protection, then your employer’s fall protection program must have a way to promptly get you down (typically 10 minutes max). SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Warning Lines Must be functional, not just visual. – Minimum 500 pounds tensile strength. – Stanchions resist 16 lbs. tipping force. – Must be 34” to 39” above the roof surface. – Safety monitor or PFAS if outside lines. – Secured at each stanchion so line doesn’t pull through when contacted. – Install line and stanchions according to the manufacturer. – Adjust as necessary – lines may stretch as the day gets hotter. SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Warning Lines Manual work: place line >6’ from edge. Mechanical work: place line >6’ from edge parallel to equipment direction and >10’ from edge perpendicular to equipment direction. • Competent in recognizing fall hazards • • • • Able to see, communicate orally with, and be on the same roof as, the employee monitored Avoid responsibilities which could distract their attention Must wear an orange vest A safety monitor is a competent person who monitors the safety of employees working outside the warning lines • Can be used for edge Fall Protection when applying a hot asphalt roof, spraying acrylic, or foam applications. Hose attendant must serve as Safety Monitor for trigger man only! NOTE: Roofs smaller than fifty feet in their least dimension can use just a safety monitor. What are OSHA’s requirements? The Safety Monitor shall be competent to recognize fall hazards The Safety Monitor shall warn the employees when it appears that the employee is unaware of a fall hazard or is acting in an unsafe manner The Safety Monitor shall be on the same working/walking surface and be within visual sighting distance of the employees being monitored The Safety Monitor shall be close enough to communicate orally with all the employees. What are the fall hazards I should be warning employees about? Backing up to close to the edge Any unprotected roof opening Tangled extension cords Airborne debris Bees, Wasps, Hornets Water, ice, or other slippery conditions Any change in walking/working conditions SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Low-Slope Roofs Barrier tape is not an adequate warning line as it provides no resistance to a person contacting it. SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Low-Slope Roofs – Perimeter Guarding Parapet Walls less than 39” SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Low-Slope Roofs – Perimeter Guarding Extending the parapet wall SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Low-Slope Roofs – Perimeter Guarding Guardrail for parapet walls SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Low-Slope Roofs – Perimeter Guarding Wall-Mounted Guardrail Systems SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Residential Construction- alternative procedures based on feasibility/greater hazard of using conventional fall protection May follow the alternative procedures in STD 03-00001 (formerly 3-0.1A) provided the structure meets its definition of “residential construction”. “Residential construction” means same materials and methods as a typical single family home – Includes ‘discrete parts” of commercial buildings, such as shingled entranceways Otherwise employer must demonstrate infeasibility or greater hazard to follow alternative procedures developed in a written alternative fall protection plan (502(k)) maintained on site SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing STD 03-00-001- Alternative procedures for residential roofing Allowed only for areas where slope is < 8:12 and < 25 ft eave to ground height – Specially trained workers only – Inspect roof surface for slip hazards and eliminate such hazards or take other effective measures. Have workers wear appropriate footwear. – Suspend work when hazardous conditions exist due to adverse weather – Holes/openings effectively guarded or covered – Ladders/scaffolds meet Subparts X and L. – No ascending/descending roof within 6 ft of the rake edge – Locate supplies/materials more than 6 ft from rake edge or 3 ft for tile roof installations – No impalement hazards below the eaves/rakes SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing STD 03-00-001- Alternative procedures for residential roofing Low slope roofs (< 4:12) safety monitor or slide guards >4:12 and < 8:12 (not tile or metal roof) slide guards tile or metal roof < 8:12 safety monitor or slide guards SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing STD 03-00-001- Alternative procedures for residential roofing Slide guard requirements – 2”x6” nominal stock minimum (90 degrees) – No more than 3 rows of roofing material installed before installing slide guard – Installed continuously along eave – For >6:12, install additional slide guards at intervals of 8 ft maximum – Remove guards on way down the slope SUBPART M Fall Protection for Roofing Q&A What are the fall protection requirements when installing fall protection systems, including guardrails? Can a roofing contractor use warning lines to demarcate a roof opening, specifically a skylight or series of skylights? Isn’t the goal to prevent employees from going within 6 ft of the skylight? What is the minimum height of a warning line? What do I have to consider before tying myself off, or allowing an employee to tie off?