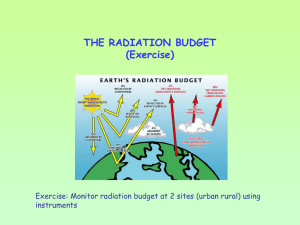
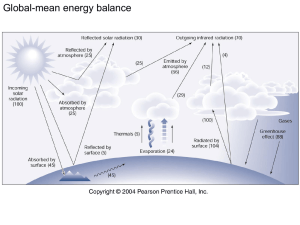
Radiation (higher) - Tasker Milward Physics Website
advertisement

Radiation Infra-red radiation transfers heat between all objects. Infra-red radiation is an electromagnetic wave and can travel through a vacuum. Heat from the Sun reaches us through the vacuum of space by travelling as infra-red radiation. These heaters emit radiant heat energy. They are useful for heating large areas from above, especially outdoors where hot air would be blown away easily. An object can absorb (take in), emit (give out) and reflect radiation. A hot object will emit more infra-red radiation than it absorbs. A cold object will absorb more infra-red radiation than it emits. In this way heat is transferred from hotter to colder objects. An object whose temperature does not change will emit infra-red radiation at the same rate as it is absorbed. Objects which are at the same temperature as each other will absorb, emit and reflect infra-red radiation at different rates depending on the type of surface which the object has. Why is it hotter inside a black car in sunshine, than inside a white car? Radiation - Surfaces - Absorption and Emission. An object with a matt (dull) surface will absorb and emit infra-red radiation at a faster rate than an object with a shiny surface. An object with a dark surface will absorb and emit infra-red radiation at a faster rate than an object with a light surface. Radiation is also reflected at the surface. Matt, black objects ABSORB and EMIT more heat than light-coloured, shiny ones. Imagine a hot piece of metal which has a matt black surface and a shiny white surface. A thermometer is placed at the same distance from both surfaces. The thermometer next to the matt black surface shows a higher temperature because it emits radiation at a faster rate. Heat leaves the metal more quickly through the matt black surface than the shiny white surface. Part of the space shuttle is covered in matt black tiles. These help the craft to lose heat from its surface when it re-enters the Earth's atmosphere on returning from space. The space shuttle gets very hot in the Earth's atmosphere in the same way that meteors do. The pipes of solar heaters are painted black to absorb most heat. …and “solar cookers” have reflective shiny parabolic dishes to concentrate the sun’s heat onto a small spot. Infra-red imaging cameras show us a very different picture of things – “Seeing by Heat” IR imaging can be used in diagnosing illness – and also for surveillance at night. IR imaging from space shows details of storms and other weather patterns that can’t be seen in visible light Pulses of IR can be used in remote control mechanisms NOW ANSWER THE QUESTIONS 1. What form of radiation is given out by a warm object? 2. What “spectrum” does this radiation belong to? 3. What is it easy for heat radiation to travel through? (Give an example of this) 4. What kind of places are suitable for radiant heaters to be used in? 5. Why does a black car get hotter than a silver car on a sunny day? 6. Why does a satellite have “radiator”, and what is it “getting rid” of? What colour is the radiator Copy and complete: A h___ object will e______ more infra-r___radiation than it absorbs. A cold o_______ will absorb m______ infra-red r________ than it emits. In this way h_______ is transferred from hotter to c__________ objects. An object whose t_________ does n____ change will e_____ infra-red r_______ at the same rate as it is a_____________.