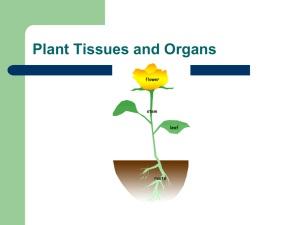
plant anatomy
advertisement

THE IMPORTANCE OF PLANTS 20th Century Med. Man Video (30 min) Walk on Campus to identify (sheet in binder) 1.flowers,cones, ferns and mosses 2. flower parts 3.common trees and plants (locust, oak, pear, hemlock, dandelion, violet, grass, poison ivy, dogwood, pine, black cherry) Info on seeds was covered for quarter long project Flower parts were covered when we did genetics MOSS- non-vascular, reproduce with spores FERN vascular, reproduce with spores CONIFERS vascular, reproduce with pollen and seed in cones FLOWERING PLANTS Vocabulary • • • • • • Cereal Legumes root crops fruit grain vegetative part root hairs, root cap, herbaceous plant, vascular bundle transpiration Read (570-579, 534-541) FLOWER ANATOMY POLLEN Apple seeds CASHEW Fruit and seed The importance of plants • A. • 275,000to 400,000 – SPECIES OF FLOWERING PLANTS • 3,000 • 200 • 12 USED FOR HUMAN FOOD DOMESTICATED MAIN FOODS DOMESTICATION • - REQUIRE HUMAN INTERVENTION TO MAINTAIN CURRENT FORM Activity! • Name the major food crop plants that are harvest. • This is based on amount harvested list is by weight harvested 1. 7. 13. 2. 8. 14. 3 9. 15. 4. 10. 16. 5. 11. 17. 6. 12. list is by weight harvested 1. SUGAR CANE* 2. WHEAT* 3. CORN* 4. RICE* 5. POTATO 6. SUGAR BEET 7. BARLEY* 8. MANIOC 9. SWEET POTATO 10. SOY BEAN 11. SORGHUM* 12. BANANA 13. GRAPE 14. TOMATO 15. OAT* 16. ORANGE 17. APPLE What do all the * have in common? * MAJOR plant family Grass family SUGAR CANE RICE BARLEY SORGHUM POTATO SUGAR BEET manioc SWEET POTATO BANANA C. HUMAN EXISTENCE • 200,000 TO 100,000 may have been humans in an early form H. sapiens var. sapiens and H. sapiens var. neaderthalensis • 25,000 to 35,000 years ago substantial archeological and fossil evidence of H. sapiens (us) EARLY HUMAN LIFESTYLE? • • Man Hunter/gatherer herd food season • Change in human behavior approximately 9,000 years ago • Domestication/agriculture develops simultaneously in several places in the world GOOD EVIDENCE OF FARMING • 7,000 B.C. • " • 5,000 • 7,000-5,000 • 5,000 Fertile Crescent, Near East Wheat , Barley Thailand bean and pea Asia rice Mexico near Texas gourds, chili, beans Mexico City squash, beans, avacado, Maize Current foods in an area reflect heritage D. NOTES ON 20TH CENTURY MED MAN. (video in library) • • • • • • • Botany Ethnobotany Dr. Mark Plotkin (Harvard) Jaguar Shaman Rainforest Destruction and Old age of Shaman 25% of modern meds have their origin in plants examples poppy (opium, morphine) periwinkle (vincristine) willow (aspirin) PLANT ANATOMY Part II of Plants Read 569-582 I. GROSS ANATOMY • ROOTS (functions?) – – – – Anchor absorb water and nutrients asexual reproduction (ex. Raspberry) storage ex. Yam, carrot , beet LEAVES – Photosynthesis – Enzymes, sunlight, chlorophyll – Transpiration – release of water through the leaf surface. The plant is like a straw. Roots have the opening and the leaves have the exit – asexual reproduction ex. African violet Kalanchoe – storage ex. Cabbage, onion, lettuce STEM support the leaves and flowers asexual reproduction ex. Potato, strawberry storage ex. Potato, broccoli, cauliflower , asparagus II. CELLULAR ANATOMY • transport • xylem • phloem • Active Cell division • absorption • Water up • Sugars down • Meristem • Root tip • • support- wood dating activity with growth rings How old is this stem? 12 years old cell division Adding to length at root and stem tips by apical meristem cell division Adding to the width of stem -lateral meristem Vascular bundle Looks vaguely like an ice cream cone Photosynthesis • • from work sheet • • • • leaf anatomy- stomata chromatography- pigments chlorophyll carotene xanthophylls Photosynthesis 1. Leaf Anatomy – stomata and guard cells (from worksheet) 2. Chromatography- pigment mixtures are separated and analyzed • Chlorophyll – green pigment • Carotene – orange pigment • Xanthophylls – yellow pigment III. PLANT RESPONSES (tropisms) • Controlled by hormones that stimulate specific cells to grow • Thigmotropism – response to touch (vines, venus fly traps) • Phototropism – response to light (seedlings) • Gravitropism – up and down growth • Chemotropism – response to a chemical stimulus (ex. fertilizer) Thigmotropism • The turning or bending response of an organism upon direct contact with a solid surface or object. Phototropism Gravitropism Chemotropism Legumes • • • • Simple dry fruit Common name for fruit is a pod Peas, beans, lentils, and peanuts High in protein Quiz on plants MONDAY • • • • • Video Med Man, Human uses of plants, Text Notes, Vocab LABS Tree Ring, Chromotography, Campus Walk and Plant identification, • Cross word • Plant anatomy 4th Quarter NOTEBOOK CONTENTS • Cover Sheet • Assignment Sheet • Grade Sheet • Vocabulary (96 - 133) • Notes THIS IS 10% OF YOUR QUARTER GRADE!!! • Daily Work – – – – – – Pg 149 Theory of Evol WS Pg 157 Theory of Evol WS History of Life WS Pg 161 Evolution WS Plant Puzzle Virus Paragraph (living or nonliving) • Labs – – – – Amino Acid Lab Viral Lab Plant Walk Dendrochronology Notebook check WEDNESDAY…. Here’s another option… Plant Test Topics • Video Med. Man • Human Uses of plants, Text • Notes – gross anatomy, cell anatomy, list of food crops and numbers of species of plants, photosynthesis • Vocab • Labs – chromotography, campus walk, plant identification • Crossword with stuff on back • Plant anatomy Plant Jeopardy – Easy questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Products of photosynthesis? This transports water in a plant - _______ Define ethnobotany. What is causing loss of knowledge in rainforest ecosystems? 5. Release of water through leaf surface is called ________. 6. Square stem…strong smell = ________ 7. Trees can either be flower producing or _____ producing. Plant Jeopardy – Easy questions 1. Products of photosynthesis? Sugar and O2 2. This transports water in a plant – xylem 3. Define ethnobotany. Study of how plants are used in a community 4. What is causing loss of knowledge in rainforest ecosystems? Old age of Shaman and forest destruction 5. Release of water through leaf surface is called _transpiration_______. 6. Square stem…strong smell = _Mints_ 7. Trees can either be flower producing or _cone___ producing. Medium Level 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What does chromotography do? What is the stomata of a leaf? What controls the stomata? Functions of the roots? Name two things that we eat that are roots….stems….and leaves. Where does cell division occur in plants? What plants are cultivated in Mexico? Contrast phloem and xylem cells. Contrast wind vs. insect pollinated flowers. Medium Level 1. What does chromotography do? Separates pigments by mass 2. What is the stomata of a leaf? Pore to release water 3. What controls the stomata? Guard cells 4. Functions of the roots? Anchor, food storage, asexual reproduction, absorb water and nuts. 5. Name two things that we eat that are roots….stems….and leaves. Carrot, beet, turnip asparagus, broccoli, cauliflower, potato cabbage, lettuce, onion Medium Level 6. Where does cell division occur in plants? Apical meristem and lateral meristem 7. What plants are cultivated in Mexico? Maize, chilis, gourds, beans, avocado 8. Contrast xylem and phloemcells. Carries water up the plant, carries sugars from the leaves to other parts of the plant 9. Contrast wind vs. insect pollinated flowers. Small, dull with no scent, larger, showy and fragrant Difficult Questions… 1. What was the evidence of farming 7000-5000 BC? 2. What does domestication mean? 3. What do tree rings tell us? 4. What are the functions of the leaf? 5. Give the basic chemical reaction of photosynthesis. 6. The fruit of a maple tree is called a ___. 7. Name three grains that are on the list of top food crops harvested by weight. Difficult Questions… 1. What was the evidence of farming 7000-5000 BC? Permanent shelters and cultivated fields 2. What does domestication mean? Plant or animal requires human involvement to maintain its current form 3. What do tree rings tell us? Past weather conditions, Age 4. What are the functions of the leaf? Photosynthesis, asexual reproduction, food storage Difficult Questions… 1. Give the basic chemical reaction of photosynthesis. CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 2. The fruit of a maple tree is called a samara___. 3. Name three grains that are on the list of top food crops harvested by weight. Maize, rice, wheat, sugar cane TEST QUESTIONS #3. Fill In A #4