JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE - European Soil Portal
advertisement
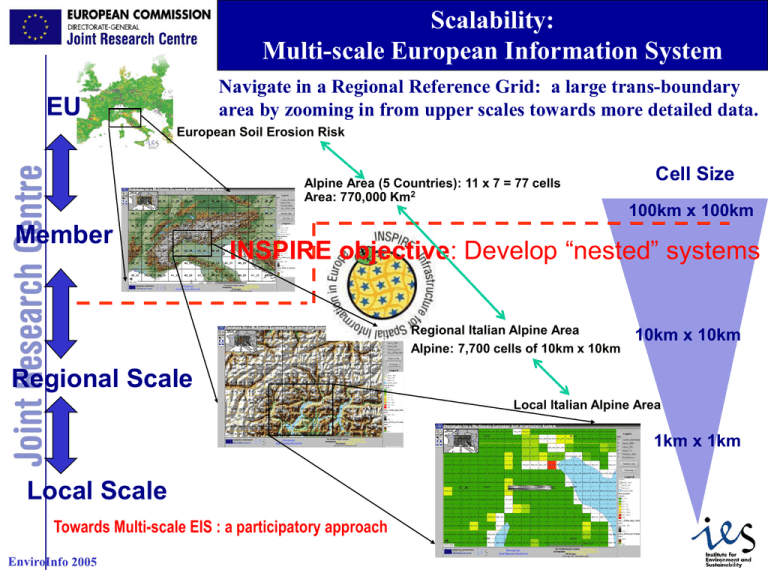
Scalability: Multi-scale European Information System Navigate in a Regional Reference Grid: a large trans-boundary area by zooming in from upper scales towards more detailed data. EU European Soil Erosion Risk Alpine Area (5 Countries): 11 x 7 = 77 cells Area: 770,000 Km2 Member Cell Size 100km x 100km INSPIRE objective: Develop “nested” systems Regional Italian Alpine Area Alpine: 7,700 cells of 10km x 10km 10km x 10km Regional Scale Local Italian Alpine Area 1km x 1km Local Scale Towards Multi-scale EIS : a participatory approach 1 Regional Environmental projects: Exchange of harmonised information Create a useful network among regional and national institutions which own and manage environmental data Give an overview of available information on regional environmental themes Exchange of knowledge and experience among different regions, different countries Set up and update of shared environmental databases in regional level (themes: Air quality, Water, Soil, etc) Use of participatory approach, according to the principles of INSPIRE (local ->Regional -> Country -> E.U) Develop common procedures to allow data exchange Definition of a common format for data exchange Testing of the exchange format in sample areas Filling in the exchange format and updating databases 2 Interoperability: importance of standards Use of Mapping Internet Services: Stand-Alone web based application for the navigation of environmental maps (Web mapping services) Towards web instead of desktop applications Use Inspire principles and OGC Standards for the creation of spatial data infrastructures Importance of Metadata: Standard ISO 19115 Public users should have access to environmental and may be able to discover available spatial data Use of standards Use of the same co-ordinate systems: • LAEA_ERTS INSPIRE Reference Grid: Lambert Azimuthal Equal Area Metadata Standards: ISO 19115 Use of WMS interoperability Mapping unit: Raster cell or Polygon? Pixel size: multiply by 1km (100 km, 10km, 1km, 100m…etc) 3