File - the bgr`s world of science
advertisement

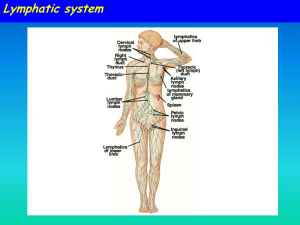
BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION BY Smt.G.K.VINAYAGAM PGT(BIO) K.V,DHARWAD. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Living organisms are made up of cells . This cells need oxygen and nutrients for their growth. These are supplied through circulatory system. In lower organisms like sponges and hydra circulation is through water but in higher organisms it through blood and lymph. BLOOD COMPONENTS (a) (b) (c) Plasma Formed Elements; Erythrocytes Leucocytes Thrombocytes It has 90_92% of water,6_8% of proteins. There are 3 types of proteins. Fibrinogen –Helps in coagulation of blood. Globulin-Involved in defense mechanism. Albumin- Helps in osmotic balance. It has minerals. Plasma without fibrinogen is called serum. ERYTHROCYTES • Human RBC Is devoid of nucleus • Biconcave in shape. • RBC contains Hemoglobin. • Life span is 120 days. • Total count of RBC is 55.5 millions/mm3 • Transport of respiratory gases. Leucocytes Colorless. Nucleated. Total count 6000 to 8000mm3. Short lived. TYPES OF LEUCOCYTES Granulocytes Agranulocytes TYPES OF GRANULOCYTES • • • • Eosinophils; 2-3% of Leucocytes. Resist infections. Associated with allergic reactions. NEUTROPHILS • 60-65% of Leucocytes. • Phagocytic in nature. BASOPHIL It secretes histomine,serotonin& heparin. Involved in inflammatory reactions. AGRANULOCYTES Lymphocytes; It forms 20-25 % of formed element. It is of 2 types B-Lymphocytes &TLymphocytes. Both are responsible for immune responses of the body. Agranulocytes Monocytes;These are phagocyte in nature.It forms 6 –8% of formed element. BLOOD CLOTTING Thrombokinase Prothrombin Thrombin Calcium Fibrinogen Thrombin Fibrin Fibrin +Formed Elements Bloodclot BLOOD GROUPING Blood group Antigens Antibody DONATE BLOOD TO A A anti-B A,AB B B anti-A B,AB AB A,B -------- AB O ------- AntiA,B ALL RH GROUPING Another surface antigen is also present in RBC. This surface antigen was first reported in Rhesus Monkey. So it is called Rhesus factor or RH factor. 80% of people are Rh+ve ,they have Rh factor. RH INCOMPATIBILIITY FEMALE Rh-ve Anti Rh antibody * FOETUS (Rh+ve) safe At child birth Destroy the 2nd foetus Second Foetus MALE Rh+ve LYMPH As the blood passes through the capillaries in tissues, some water along with many small water soluble substances move out into the spaces between the cells of tissues leaving the larger proteins and most of the formed elements in the blood vessels. This fluid released out is called the interstitial fluid or tissue fluid. This fluid present in the lymphatic system is called the lymph. It has lymphocytes. It is colourless. Fats are absorbed through lymph. CIRCULATORY PATHWAY OPEN CIRCULATION • In this blood pumped by the heart enters into the open spaces called sinuses. • Blood flow is not regulated Closed circulation • In this blood is confined to the blood vessels. • Blood flow is regulated. Structure of human heart It is located in thoracic cavity in between 2 lungs. It is protected by pericardium. It has 4 chambers (2 Atria& 2 ventricles) INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN HEART Heart is made up of cardiac muscle. Right auricle is separated from Right ventricle by means of a septum with 3 flaps called tricuspid valve. Left auricle is separated from left ventricle by means of a septum with 2flaps called bicuspid valve/mitral valve. Conducting system of human heart Cardiac cycle initiates from SA node( Pace maker). It also maintains the rhythm of heart beat. It is located in the right upper corner of right atrium. From SA node the electrical impulses reach the AV node. AV node is located in the lower left corner of the right atrium. From AV node it reaches the Bundle of His. Finally it reaches the ventricles through Purkinjee fibres. Human heart is myogenic in nature. CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF HUMAN HEART Cardiac cycle CARDIAC CYCLE CARDIAC OUTPUT • It is the amount of blood pumped by heart per minute is called heart output or cardiac output. • Cardiac output =72*70 ml • =5040 ml. TYPES OF BLOOD VESSELS ARTERIES • Carry blood from heart to different parts of the body. • Carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary pulmonary artery. • Deeply seated. • Valves are absent. • Have thick walls VEINS • Carry blood from different parts of the body to heart. • Carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein. • Superficialy seated. • Valves are present. • Have thin walls. DOUBLE CIRCULATION Deoxygenated blood Right Atria Deoxygenated blood Right ventricle Pulmonary artery Deoxygenated blood Deoxygenated blood PULMONARY CIRCULATION Lungs oxygenated blood Body parts SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION Pulmonary vein oxygenated blood Systemic arota oxygenated blood Left ventricle oxygenated blood Left atria oxygenated blood DOUBLE CIRCULATION Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH (ECG) ECG; It is the graphical repersentation of electrical activity of cardiac chambers. P wave-Depolarisation of atria QRS _Depolarisation of ventricles. TwAVE_Repolarisation of cardiac chambers. DISORDER OF CIRCULATORY SYSTEM High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Angina Pectoris Heart Failure SPHYGMOMANOMETER HYPER TENSION A persistant rise in diastolic pressure above 90 mmHg and or systolic pressure above 140mmHg is termed as hypertension. ATHEROSCLEROSIS • It is due to the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of arteries leading to narrowing of arteries. • This also causes hypertension. • Blood supply to the cardiac muscle is reduced. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Loss of elasticity of the walls of arteries due to ageing. MYOCARDIAL INFRACTION Very low blood flow to the cardiac muscle. As a result cardiac muscle cannot sustain its function. ANGINA PECTORIS Acute pain in the chest due to very less supply of oxygen to the heart muscle.