Mon
advertisement

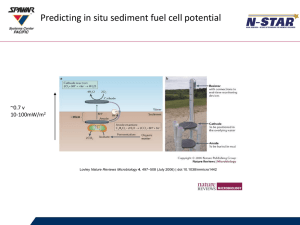
Reminder: HW3 Part II due Wednesday! Midterm Thursday Aquatic Ecosystems Monday, August 22nd Ecotone: the transition zone between two diverse communities WHAT DID YOU FIND?????? Kelp Effect on Waves Kelp forest ecosystem Otters eat sea urchins Kelp provides otter habitat Sea urchins eat kelp Kelp forest ecosystem & human values Kelp Effect on Waves Impact of Kelp on Low Productivity Terrestrial Env’ts Example: Channel Islands •Kelp detritus = nutrient input to intertidal communities •Marine bird and mammals feed on intertidal organisms •Feces/guano provide nutrients to terrestrial organisms •Biggest impact where ratio of shoreline to area is high Kelp forest ecosystem •30-40 m water depth •Determined by light availability •Require high concentrations of nutrients •Occur mostly in areas of upwelling •Provide primary production (food) and habitat! Selective Pressures in Intertidal Zones Tides Salinity Waves Rocky Intertidal Zonation Where to snorkel, rocky shore or sandy beach? Why? Aquatic Ecosystems Oceans • Lakes Streams and Rivers • Estuaries Freshwater wetlands • • • Some General Questions: Where does the energy to support aquatic life come from? How productive are each of the aquatic environments? What is the limiting factor in each aquatic environments? How are nutrients cycled? How have humans changed these environments? The open ocean is most like… A) B) C) D) a tropical rain forest the boreal forest the desert chaparral …with regard to productivity. Where is the ocean most productive? Where sunlight is available: Top 100 meters (euphotic zone) Where nutrients are available: near the coast From upwelling rivers bring nutrients Polar upwelling – Short, intense productivity Net Primary Productivity (NPP) by Biome Atmospheric/Ocean Coupling surface currents are driven by wind Ocean: surface currents Ocean Primary Productivity Coastal Upwelling •Most upwelling occurs in response to longshore winds. •Upwelling: increased nutrients, increased primary production good fishing! •El Nino brings warm water, shuts down upwelling, bad for fisheries Coastal Upwelling Is Primary Production always good for upper trophic levels? Red tide Harmful algal blooms: toxicity or increase in BOD suffocation, starvation LA Times: Altered Oceans Pulitzer Prize The open ocean is most like… A) B) C) D) a tropical rain forest the boreal forest the desert chaparral …with regard to productivity. Coral reefs Coral reefs are extremely productive Visibility is great! But we know that nutrient-rich water is murky How is this possible? Where are the nutrients? What terrestrial biome does this remind you of? Coral reefs Efficient cycling of nutrients Complex relationships between organisms • • • Corals: plants or animals? zooxanthellae in coral intricate food webs Freshwater Ecosystems Lakes, streams and rivers Light Penetration in Lakes Euphotic zone Aphotic zone Sediment Secchi disk eu: well or good a: without Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Lakes Thermal Stratification of Lakes Summer Epilimnion Hypolimnion Sediment Thermocline Thermal Stratification of Lakes (wind) Summer Fall Epilimnion Hypolimnion Sediment Thermocline Well-mixed profile Sediment Thermal Stratification of Lakes (wind) Cooling Fall Summer Epilimnion Hypolimnion Sediment Thermocline Well-mixed profile Sediment Cooling Winter Frozen Warmer Well-mixed Hypolimnion profile Well-mixed Sediment Thermal Stratification of Lakes (wind) Cooling Fall Summer Epilimnion Hypolimnion Sediment Thermocline Well-mixed profile Sediment Warming Cooling Winter Spring Well-mixed profile Sediment Frozen Warming Well-mixed Hypolimnion profile (4°C) Sediment Summary Aquatic Ecosystems Limiting factors (light, nutrients, dissolved oxygen) and Temperature Rocky Intertidal Zonation and adaptations Oceans Productivity: euphotic zone/thermocline/nutrients/BOD/algal blooms Open ocean vs. coast – Nutrients: upwelling and coastal inputs Coral Reefs (zooanthellae, coral bleaching, ocean acidification, dynamite fishing) Lakes… seasonality of: Light penetration (euphotic vs. aphotic zones) Temperature (epilimnion vs. hypolimnion) Oxygen (aerobic vs. anaerobic/anoxic) Nutrients (oligotrophic vs. eutrophic)