Lean Production Systems
advertisement

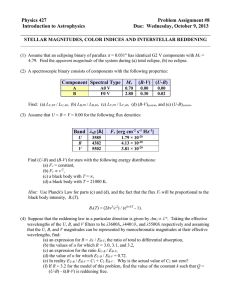
Lean Production System SKB Simulation 1 & 2 SKB 2-2 Lean Transformation Focus on lead-time reduction to: Increase customer loyalty and market share Achieve growth in sales & earnings Sustain the competitive advantages Improve stakeholder value Lean Production System Six Sigma Process Capability Kaizen Breakthrough Methodology SKB 2-3 Lean Production System Lean Production System Efficient Use of: Just in Time People Equipment Materials Space Improve process capability Minimize variation Manage abnormality Jidoka Production Smoothing Drives cost reduction SKB 2-4 Just-In-Time Is... A manufacturing system which produces: What the customer wants In the quantity the customer wants When the customer wants it While using the minimum: Raw materials Equipment Labor Space SKB 2-5 Lean Production System Key Concepts and Tools Pace to Takt time One-piece flow Pull system SKB 2-6 Importance of Takt Time Synchronizes operations to customer demand Prevents overproduction Tool for creating flow Determines optimal staffing Net operating time Customer requirements SKB Drives capacity analysis & equipment utilization Must be updated periodically as demand changes 2-7 Batch Fake Flow 1-Piece Flow SKB 2-8 “A Sea of WIP” “Now You See It!” SKB 2-9 One-Piece Flow Supermarket Operation I H G F E A I SKB H G F E D C B B A C D Aisle 2 - 10 Pull System Produce to Actual Customer Demand SKB 2 - 11 Implement Pull System Supplier Production kanban Water Spider RM Pick-up kanban Drop production kanban LSS FG LSS Supermarket Schedule board SKB 2 - 12 JIT Elements Small, inexpensive machines in process order One-piece flow production, counterclockwise Ergonomically-correct operations Standing operations, moving while working Pull system discipline “Standard operations” defined and implemented SKB 2 - 13 Simulation 3 & 4 SKB 2 - 14 JIT Benefits Creates a system which is intolerant of production abnormalities Eliminates waste in production processes Reduces lead times Quality… Cost… Delivery! SKB 2 - 15 Lean Production System Efficient Use of: Just in Time People Equipment Materials Space Improve process capability Minimize variation Manage abnormality Jidoka Production Smoothing SKB 2 - 16 Jidoka is… A. A method for reducing defects B. Equipment autonomation to improve productivity SKB 2 - 17 Jidoka A. Tools or Methods to Reduce Defects Detect defects when they occur Prevent defects from passing to next operation Identify root causes of defects Eliminate root causes Reduce or eliminate defects SKB 2 - 18 Jidoka Elements Visual Control Mistake-proofing (Poke-Yoke) 5S Manual Work Andon Automatic machine work Abnormality Response/Reaction Roles and responsibilities Line stop guidelines Sigma Kaizen (DMAIC) Basic QC Tools New Standard Operations and training Skill matrix and performance Autonomation Separate person from machine Advanced Statistical Tools Countermeasures SKB 2 - 19 Jidoka Elements Visual Control 5S Andon Parts presentation Standard work Tool presentation Andon Pack line SKB 2 - 20 Abnormality Response Process Q C D S React to problem Measure impact MAN MACHINE EFFECT METHOD Alert team Develop and test improvement MATERIAL Find root cause Gauge 4 Check 2B Train affected associates in new standard operations SKB Update standard operations with tested improvement 2 - 21 Jidoka B. Equipment autonomation Separate operator work from machine work Before: Operator watches machine run After: Operator loads and moves Auto shut-off “Hanedashi” auto unload Operator moves to next operation Question: Do you watch your dishwasher run? SKB 2 - 22 Jidoka Benefits Increases production quality Increases productivity Ensures on-time delivery Quality ... Cost ... Delivery! SKB 2 - 23 Lean Production System Just in Time Efficient Use of People Equipment Materials Improve process capability Minimize variation Manage abnormality Jidoka Space Production Smoothing SKB 2 - 24 Production Smoothing Is... Adapting production rates to variations in customer demand Variation in volume Variation in product mix SKB 2 - 25 Production Smoothing Variation in Volume Customer Demand Average Daily Demand = Target Production Quantity Time SKB 2 - 26 Production Smoothing Variation in Mix Monthly Schedule (3200 units) Model A Model B Model C 1600 units 800 units 800 units 5 10 15 20 Day Daily Schedule (160 units) Production pattern AABCAABC 80 80 40 40 1 80 40 40 2 80 40 40 3 40 40 20 Day SKB 2 - 27 Production Smoothing Benefits Maintains a consistent, high product quality Reduces the requirements for capital investment Reduces staffing costs Ensures on-time delivery Quality ... Cost ... Delivery! SKB 2 - 28 Lean Production System Efficient Use of: Just in Time People Equipment Materials Space Improve process capability Minimize variation Manage abnormality Jidoka Production Smoothing Drives cost reduction SKB 2 - 29