Spread Spectrum Techniques for Wireless Communication
advertisement

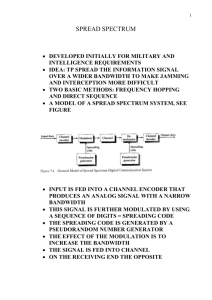
Spread Spectrum Techniques for Wireless Communication Axel Acuna Spread Spectrum Methods by which a signal generated with a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth. These techniques are used for a variety of reasons: Establishment of secure communications Increasing resistance to natural interference, noise and jamming Prevent detection Limit power flux density How It Works? Spread spectrum uses wideband, noise-like signals that are hard to detect, intercept, or demodulate. Spread-spectrum signals are harder to jam (interfere with) than narrow band signals. This technique: decreases the potential interference to other receivers (anti-jam, or AJ). while achieving privacy low probability of intercept (LPI). Spread spectrum generally makes use of a sequential noiselike signal structure to spread the normally narrowband information signal over a relatively wideband (radio) band of frequencies. The receiver correlates the received signals to retrieve the original information signal. Direct sequence and frequency hopping are the most commonly used methods for the spread spectrum technology. DSSS: Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum FHSS: Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum DSSS The carrier of the direct-sequence radio stays at a fixed frequency. Narrowband information is spread out into a much larger (at least 10 times) bandwidth by using a pseudo-random chip sequence. Uses the same amount of transmit power and carry the same information as narrowband The power density of the DSSS signal is much lower than the narrowband signal, making it more difficult to detect. FHSS FHSS achieves the same results provided by DSSS by using different carrier frequency at different time. The receiver and the transmitter must be synchronized in time and frequency in order to ensure proper transmission and reception of signals. FHSS is better than DSSS radio when dealing with multipath. Since the FHSS does not stay at the same frequency. Questions?