KAPIL
advertisement

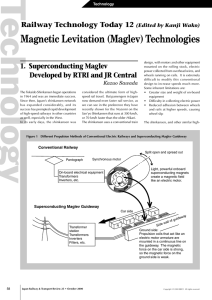
INNOVATIVE TRAINTECHNOLOGY MAGLEV INNOVATIVE TRAIN TECHNOLOGY MAGLEV TERMINOLOGY TYPES OF MAGLEV COMPARISON SAFETY FUTURE UTILITY The principal of a Magnet train is that floats on a magnetic field and is propelled by a linear induction motor. They follow guidance tracks with magnets. These trains are often referred to as Magnetically Levitated trains which is abbreviated to Maglev MAGNETIC +LEVITATION= MAGLEV OPPOSITE ATTRACT LIKE REPEL LEVITATION is derived from ‘levis’ means light. A small (~6mm) piece of pyrolytic graphite levitating over a permanent neodymium magnet array (5mm cubes on a piece of steel). RAIL GUN MAGNETIC FLOATERS PROPULSION OF ROCKETS MAGLEV TRAINS INNOVATIVE TRAIN TECHNOLOGY FRICTION FREE TRAVEL. HIGH SPEED ACCELERATION CARRIES NO ENGINE SAFETY & COMFORT Comparison of Systems Railroad / MAGLEV Titel Wheel-on-rail Electromagnetic Levitation Guidance Propulsion Propulsion Support Support ATTRACTION TYPE EMS-Electro-magnetic Suspension (Developed By Transrapid Germany) REPULSION TYPE EDS-Electro-dynamic Suspension (Developed By Japan) INDUCTRACK (Developed by USA) Vehicle Chasis Guidance Magnet Guideway Magnet Support Magnet Guideway System Components of EMS Electromagnetic Levitation Stator Pack Support Magnet Linear Generator Guidance Magnet Eddy Current Brake Guidance Rail A simple motor’s Stator is when Cut open and flattened it becomes a Linear Motor. Instead of producing a Rotational Torque it produces a Linear force and thus is practically suited to MAGLEV operation. Speed control is achieved by Frequency control or by varying the field Excitation by changing the current direction. There is reaction plate in which the current is induced, thus producing Horizontal motion LINEAR SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR Propulsion Principle of EMS Magnetic Traveling Field GUIDEWAY TYPES At-grade guideway Typ III 1,25-3,5 m Elevated guideway Typ II 49,536 m Elevated guideway Type I 25 m SHANGHAI MAGLEV, Top speed: 400 Km/Hr. Developed by TRANSRAPID, Germany Built by RTRI,Japan Uses a Super conducting Magnet. Linear Synchronous Motor Application. Repulsion Type. Guideway clearance is up to 10 cm. Expensive system A repulsive force and an attractive force induced between the magnets are used to propel the vehicle (superconducting magnet). The propulsion coils located on the sidewalls on both sides of the guideway are energized by a three-phase alternating current from a substation, creating a shifting magnetic field on the guideway. The on-board superconducting magnets are attracted and pushed by the shifting field, propelling the Maglev vehicle. At one end of the tank is the integrallyattached on-board refrigerator, which serves to re-liquefy the helium gas once vaporized by regular heat absorption and external disturbances during running. Developed by RTRI, Japan. TOP SPEED: 581 Km/Hr, REPULSION Type EMS is Attraction type whereas EDS is Repulsion type. Guideway clearance: EMS- Upto 3/8” and EDS-Upto 4”. Control Circuitry : EMS-on board (Power Ec. Control) EDS-External Control. Guideway Structure: EDS has much Complex and expensive construction than EMS. Magnets : EMS-electromagnets powered by continuously charged Batteries, EDS-Superconducting Magnets which need cooling arrangement. TOP SPEED: EMS-450 Km/Hr, EDS-581 Km/Hr EDS needs wheels at start but the EMS doesn’t. Developed by USA. Based on Halbach array concept. REPULSION TYPE. Permanent Magnets Rests on wheel when stationary. Permanent magnets lift upto 50 times weight. Currently under R & D. LONGSTATOR PROPULSION SWITCHING Motor Section Switched Off Activated Motor Section Energy Supply Motor Section Switched Off ADVANTAGES OF MAGLEV OVER CONVENTIONAL RAIL COMPARISON PROPULSION SYSTEMS Transrapid (Track-mounted drive) Railroad (Vehicle-mounted drive) Gradient (max. 10%) Gradient (max. 4%) Transrapid/ICE Acceleration distance to 300 km/h (185 mph) LAND CONSUMPTION (m2/m) 14 HST 12 TR at grade 2 TR elevated (under identical conditions) 51 34 200 km/h 125 mph MAGLEV BULLET TRAIN 22 MAGLEV BULLET TRAIN 29 300 km/h 185 mph 52 MAGLEV Wh/seat-km cannot be achieved by Bullet trains SPECIFIC ENERGY CONSUMPTION 400 km/h 250 mph SPECIFIC CO2 EMISSIONS Values in grams per seat-km 190 33 300 km/h 185 mph 400 km/h 250 mph Car MAGLEV 23 MAGLEV BULLET TR. 30 Short-haul Flight 60 Transrapid 08 THANK YOU