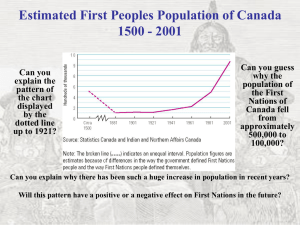
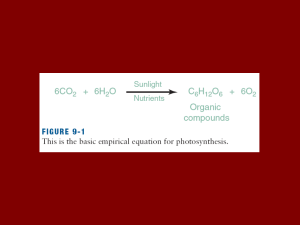
Tropical Dry Forests: Distribution, Climate, and Human Impact
advertisement

Tropical Dry Forest Global Distribution • • • • India Africa South America Northern Australia Major Climate Characteristics • Climate: Seasonal Climate (Wet and Dry Seasons), but Long Dry Seasons. • Elevation: 200 - 1000 m above sea level • Temperature Range: 20 ºC - 30 ºC; • 24 ºC average • Precipitation: October - May Peak Seasons (60-370 mm). Peak Month is January (370 mm = 14 in.) A Few Representative Species • Not as diverse as a Tropical Rainforest • Deciduous Plants (Let leaves fall in dry periods. Leaves conserve water which sustain plants during periods of drought.) • Monkeys, Deer, Large Cats, Rodents, Ground Dwelling Birds Indigenous Peoples • South America: Columbian and Brazilian indigenous peoples. Mato Grosso tropical dry forests (in Brazil) sixteen indigenous tribes (Auetí, Meináco, Waurá, etc.) • Pygmy peoples in central Africa (location of dry forests) • Adivasi (collective term for indigenous peoples of India) • Aborigines in northern Australia Two Major Human Impacts • Deforestation (many effects, loss in biodiversity, contributes to global warming) • Overgrazing (many effects; leads to soil erosion which impairs growth) Solutions (Actual or Proposed) • Actual - Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) (various int’l organizations that seek to curb deforestation) • Actual/Proposed - Improved Farming Methods (Cyclic Agriculture) • Actual/Proposed - Assessments of carrying capacities of rangelands to prevent overgrazing. Natural Resources • Relatively High Net Primary Product (NPP) • 1200 NPP, ranges between Desert (100 NPP) and Tropical Rainforest (2200 NPP)