Microeconomics: Absolute & Comparative Advantage Presentation
advertisement
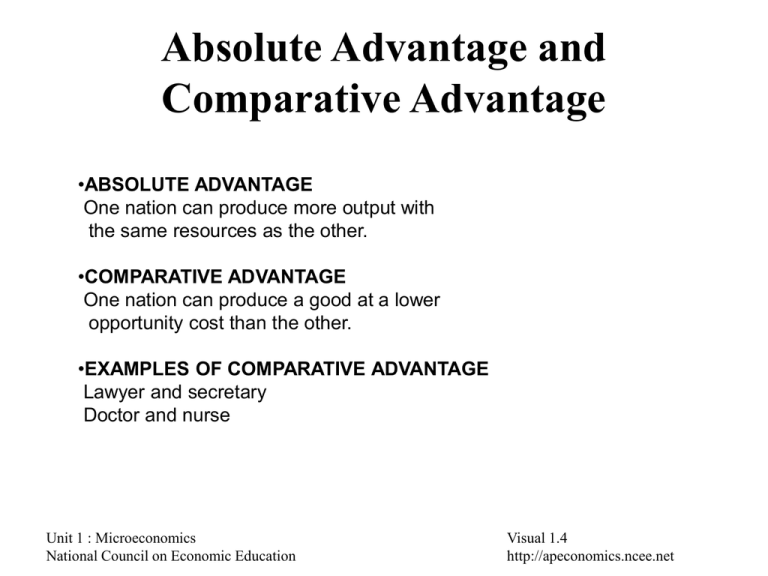
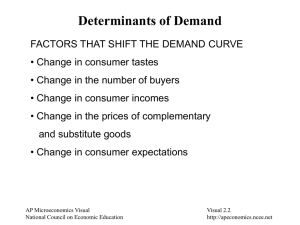
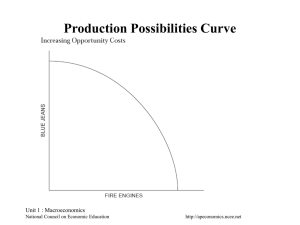
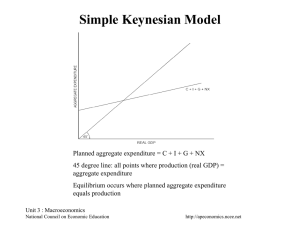
Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage •ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE One nation can produce more output with the same resources as the other. •COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE One nation can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than the other. •EXAMPLES OF COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE Lawyer and secretary Doctor and nurse Unit 1 : Microeconomics National Council on Economic Education Visual 1.4 http://apeconomics.ncee.net The Circular Flow of Resources, Goods, Services and Money Payments Unit 1 : Microeconomics National Council on Economic Education Visual 1.3 http://apeconomics.ncee.net Possibilities Curve Production Unit 1 : Microeconomics National Council on Economic Education Visual 1.2 http://apeconomics.ncee.net The Economic Way of Thinking • • • • • • • • • • • • Everything has a cost. People choose for good reasons. Incentives matter. People create economic systems to influence choices and incentives. People gain from voluntary trade. Economic thinking is marginal thinking. The value of a good or service is affected by people’s choices. Economic actions create secondary effects. The test of a theory is its ability to predict correctly. Unit 1 : Microeconomics National Council on Economic Education Visual 1.1 http://apeconomics.ncee.net Determining Comparative Advantage (Output Method) 1. Which nation has an absolute advantage in producing CDs? 2. Which nation has an absolute advantage in producing beef? 3. Which nation has a comparative advantage in producing CDs? 4. Which nation has a comparative advantage in producing beef? 5. Should Japan specialize in CDs or beef? 6. Should Canada specialize in CDs or beef? Unit 1 : Microeconomics National Council on Economic Education Visual 1.5 http://apeconomics.ncee.net Changes in Demand and Quantity Demanded Unit 1 : Microeconomics National Council on Economic Education Visual 2.1 http://apeconomics.ncee.net