longshore drift
advertisement

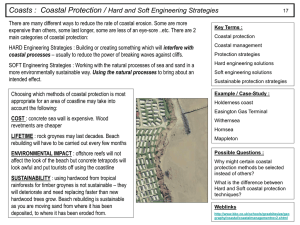
YOU SHOULD MAKE SURE YOU KNOW THE CONTENT OF ALL THESE SLIDES AND COMPLETE ALL ACTIVITIES You need to know the words below, check you have them in your books. SWASH – movement of water up the beach as a wave breaks. BACKWASH – movement of water down the beach as water from wave returns to the sea. FETCH – the length of the stretch of water that the waves have travelled across to reach the coast. PREVAILING WIND – the direction the wind usually blows from. You need to be able to describe the differences between constructive CONSTRUCTIVE DESTRUCTIVE WAVES WAVES ERODE BUILD THE BEACH BECAUSE SWASH BACKWASH IS STRONGER IS STRONGER THAN THAN BACKWASH SWASH And destructive waves. • HYDRAULIC POWER – The force of water and air pushed into cracks and shattering the cliff. • CORRASION – The force of pebbles and rocks thrown against the cliff, breaking pieces off. • ATTRITION – Pebbles rubbing together in the water and making smooth rocks. • CORROSION – A chemical reaction that is particularly good at wearing away limestone. YOU MUST MAKE CERTAIN THAT YOU UNDERSTAND WHAT THE PROCESSES DO. THEY ARE THE KEY TO SCORING HIGH MARKS ON MANY SIX MARK QUESTIONS. IF YOU DON’T UNDERSTAND THEM, YOU CANNOT SCORE MORE THAN TWO OUT OF SIX! METHODS OF TRANSPORT How material is carried in the water SOME ROCKS WILL DISSOLVE IN THE SEA. TINY MATERIAL IS CARRIED ALONG IN THE WATER PEBBLES BOUNCE ALONG THE BOTTOM. LARGE ROCKS ARE DRAGGED ALONG THE BOTTOM. Look at the diagram carefully. You can see that the prevailing wind is blowing at an angle to the coast. This affects the direction of the swash. The backwash is affected by gravity and moves back towards the sea at right-angles to the coast. This is a really important idea for the coats unit. You need to practise remembering the diagram so that you could draw it in an exam. Remember that a diagram with no labels is no good. Without looking at the previous slide. Draw a diagram to explain longshore dirft. Underneath it, explain how longshore drift happens. Use all the words below. ANGLE PREVAILING WIND BREAK GRAVITY BACKWASH RIGHT-ANGLES TRANSPORTATION WAVES SWASH THE WORDS ON THE PREVIOUS SLIDE ARE GREAT WORDS TO WRITEANGLE IN THE MARGIN IN THE PREVAILING WIND EXAM WAVES BEFORE STARTING AN BREAK ANSWER. CAN YOU REMEMBER GRAVITY THEM SWASH ALL? CLICK TO CHECK. BACKWASH THERE RIGHT-ANGLES WERE 9 TO REMEMBER! TRANSPORTATION WHAT DO THE FOLLOWING WORDS MEAN? CLICK TO CHECK YOUR ANSWERS. CORROSION SALTATION A chemical reaction that wears away rocks such as limestone. Material bounces along to seafloor. CORRASION TRACTION Cliffs are eroded by the force of rocks thrown in the water breaking pieces off. Large rocks are dragged along the seafloor. ATTRITION SUSPENSION The smoothing of rocks and pebbles as they bash against each other in the sea. Small material is carried along in the water. HYDRAULIC POWER SOLUTION Rocks are forced apart and shattered as air and water are pushed into cracks. Some rocks slowly dissolve in the water and are carried in solution. As the notch gets deeper the overhang unsupported Corrasion attacksbecomes the cliff between theseand falls under the force of gravity. This leaves a “shelf” two marks the most. Hydraulic power between high andforce low tide called a wave cut forces air and water into small gaps platform. pieces of rock to break off. The notch gets deeper into the headland, leaving an overhang. Original cliff position HIGH TIDE MARK LOW TIDE MARK Draw a diagram to show how wave cut notches and platforms are formed. Write a description of what happens making sure you explain how the processes work. Include the words below….. High Tide Low Tide Corrasion Hydraulic Power Overhang Notch Deeper Retreat Weathering makes the top of the arch thinner. Eventually it will collapse. Weaknesses in the rock are attacked by corrosion (dissolving the rock around the weakness) and hydraulic power which The weakness grows into a cave over time shatters pieces of rock around the crack as asthe hydraulic power and corrasion the force of water and air pushes into continue to act on the cliff. Eventually the cliff. cave will cut through the headland leaving an arch. Draw a diagram to show caves, arches and stacks are formed. Write a description of what happens making sure you explain how the processes work. Include the words below….. Weakness Corrosion Corrasion Hydraulic Power Cave Deeper Weathering Arch Collapse Stack A spit is a deposition feature. For a spit to form three factors are needed. You will need to remember these and label them on any diagram about spits. 3. An area where longshore drift occurs. 1. Shallow Water 2. A sudden change in the direction of the coastline 3. As the water gets deeper and the river current stronger deposition stops. Wind blowing from a different direction may curve the end of the spit. 2. At the sudden change in coastline the longshore drift continues in the same direction through the shallow water. 1. Waves break on the beach at an angle. Material is washed up the beach in swash whilst gravity carries the material back down the beach in backwash. The is called longshore drift. LONGSHORE DRIFT DEEP WATER PREVAILING WIND RIVER CURRENT SECONDARY WIND HOOKED END SHALLOW WATER CHANGE IN DIRECTION OF THE COASTLINE CAVE HYDRAULIC POWER CORRASION HEADLAND HARD ROCK LONGSHORE DRIFT DIRECTION OF COAST HIGH & LOW TIDE SHALLOW WATER CORROSION DEEP WATER CORRASION RIVER CURRENT HYDRAILIC POWER HOOKED END NOTCH PREVAILING WIND OVERHANG COLLAPSE PREVAILING WIND STRONG BACKWASH WEATHERING ANGLE WEAK SWASH ARCH SWASH BEACH DESTROYER HYDRAULIC POWER BACKWASH TALL WEAK GRAVITY SHORT WAVE LENGTH CORROSION TRANSPORTATION FREQUENT Reflecting Many Rip Rap of the is energy anGroynes expensive mayin the way UK to are victorian. protect cause scouring the coast Eventually at asthe largethe The beach is built up by wood of amounts base rots the ofand wall. rock they are This need needed. the extra sand and this replacing. may result in damage to helps keep waves away the foundations of the from the coastline. wall. BEACH GROYNES RIP SEA RAP NOURISMENT WALLS are–are large wooden built rocks isalong fences a softthe engineering that are at dumped coastline. along approach The rightare the angles huge coast. to protecting to They the the concrete coast. They absorb Sand wave walls. trap isenergy added They material and reflect to the beach carried prevent wave to help energy by thelongshore maintain force backofout natural waves drift. to sea. protection reaching against the coast. the sea. Direction of longshore drift Rip Rap There may is seen be problems by manyfurther to be downwalls very ugly the and coast because affect to the Sea are may expensive beach tourism there in thewill area have if the lesscoast build, costing approx £10,000 sand. is not attractive. per metre Sea Groynes Rip Walls Rap A constant can can canbe be beseen seen supply seenin ininof sand Bridlington Blackpool. Morecambe is required. Name of defence Groynes Seawall Rip Rap Beach Nourishment Description of what it looks like How it works? Disadvantages Where it can be seen? Landscaped cliff to a more Mappleton is ongentle the Holderness Coast in slope. Water would East Yorkshire. roll up the cliff base rather than eat into it. The cliff are made of glacial till (boulder clay) and are very soft. Grass at base of cliff helps bind the soil The Holderness coast has one of the fastest erosion rates in the world – an average of 2m per year. Sand trapped by rock armour. The threat to the main road (B1242) through the village prompted the council to protect the coast. Great Cowden is down coast of Mappleton. The beach has almost disappeared here bacause of the sand trapped at Mappleton. Erosion increased from 2 metres per year up to 20 metres lost in one year as waves bashed the cliff 24/7. Sue Earl had to pay for the demolition of her farm here. Healthy beach at Mappleton as sand is trapped by the rock armour which keeps the waves from the cliff base. Which coastline is Mappleton on? What is the cliff made of at Mappleton? Why did the council decide to protect Mappleton? How does planting grass at the base of the cliff help? What has been used to trap sand from longshore drift? Holderness M.G.Q. Boulder Clay (Glacial Till) M.G.Q. M.G.Q. To protect the B1242 RootsM.G.Q. grip the soil Rock Armour M.G.Q. What was the average erosion rate along the Mappleton coast? 2 metres per year M.G.Q. Name the place where erosion increased after Mappleton was protected? Great Cowden M.G.Q. How much did the erosion rate increase here? 20 metresM.G.Q. lost in one year How often did the waves reach the cliff here? 24/7 M.G.Q. Name the farmer who had her farm demolished? Sue Earl M.G.Q. Holbeck Hall in Scarborough fell into the sea in 1997 when the cliff slumped at the base causing mass movement. Mudflow- occurs when the cliff become so saturated with rainwater that the cliff collapses and is mobile enough to flow quite quickly on to the beach. Blackpool became popular during the industrial revolution with holiday makers from the north of England. Today it faces problems of coping with visitors and keeping its business against an increasingly competitive global market. Solutions: Problems include: •Investment in street cleaning equipment and •Unemployment in winter months when attractions maintaining a clean beach – earning an EU Blue are closed. Flag. •Overcrowding and congestion at peak times. •Extending the season into winter months by •Competition from resorts abroad more the becoming a conference centre andwith marketing reliable weather. illuminations. •Keeping the beach clean. •Providing new facilities, some of which are indoor – e.g. Pepsi Max.






![PERSONAL COMPUTERS CMPE 3 [Class # 20524]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005319327_1-bc28b45eaf5c481cf19c91f412881c12-300x300.png)