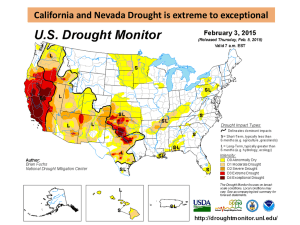
Week 12: Climate change and the cryosphere
advertisement

Climate change and the cryosphere 1 Outline • • • • • Background, climatology & variability Role of snow in the global climate system Contemporary observations of climate change Cryospheric indicators of climate change Future global & regional projections & 2 implications of climate change Background, climatology & variability 3 20th Century Climatology Observed Ref: Masuda GFDL 4 Current snow coverage 5 1 April 2013 Departure from average 6 1 April 2013 Seasonal climatology 7 Observed & GFDL Northern Hemisphere Snow Extent (x106 km2), 1973-2000 Season OBS GFDL MAE RMSE Winter 44 42 2.4 0.55 Spring 30 35 4.8 1.00 Summer 6 4 2.3 0.51 Fall 19 20 1.7 0.40 Annual 25 25 0.9 0.22 8 Mean annual maximum monthly snow water equivalent (mm) in Canada, 19801997 (Brown et al. 2003) 9 Current SWE in the Prairies 10 Monthly Eurasian standardized snow cover extent anomalies 11 Interannual variability 12 Source: Karl et al. (1993). Role of snow in the global climate system 13 Annual cycle of daily discharge in Skeena River (1955-2004) freshet 14 Contribution of snow to river runoff 15 Source: Barnett et al. (2005). Teleconnections Definition: Atmospheric interactions between widely separated regions that have been identified through statistical correlations (in space and time). For example, the El Niño teleconnection with the Southwest United States involves large-scale changes in climatic conditions that are linked to increased winter rainfall. 16 17 Correlation coefficient between annual Eurasian snow extent anomalies & discharge anomalies the following year in 64 rivers of northern Canada Source: Déry et al. (2005), JGR. 18 Observed 20th century climate change 19 Warming air temperatures Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia, http://www.cru.uea.ac.uk/ 20 20th century climate & trends Reference: Déry and Wood (2005) 21 Trends in global surface air temperature 22 Trends in global surface precipitation 23 Cryospheric indicators of global change • Snow depth, swe, density, albedo & temperature (heat content) • Duration of snow cover & growing season • Snowmelt/spring freshet date • Soil moisture 24 Snow depth Source: Curtis et al. (1998), Int. J. Climatology 25 26 Se p. 1 Oc t. 1 Oc t. 31 No v. 30 De c. 30 Ja n. 29 Fe b. 28 Ma r. 29 Ap r. 28 Ma y. 28 Ju n. 27 Ju l. 27 Au g. 26 Average annual cycle of daily SWE (mm) Annual cycle of daily snow accumulation (SWE) at Barkerville 1971-1977 1996-2005 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 Date 27 28 Trend (%) in April 1st swe, 19501997 Source: Mote et al. (2005), BAMS 29 Albedo Source: Stone et al. (2002), JGR. 30 Trend (days/year) in snow cover duration, 1972-2000 31 32 Snowmelt Date Source: Stone et al. (2002), JGR. 33 Reference: Déry and Brown (2007) 34 Annual cycle of daily runoff for the Little Swift River near Barkerville 35 Trend in centre of volume in river discharge across western N. America 36 Source: Stewart et al. (2005), J. Climate. Future projections & implications of global change 37 Components of the climate system 38 IPCC 4th Assessment 39 40 IPCC 4th Assessment Expected indicators of climate change IPCC 3rd Assessment 41 42 IPCC 4th Assessment 43 IPCC 4th Assessment IPCC 4th Assessment Runs 44 Trends in Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent Source: Déry et al. (2006), JGR. 45 Projected change in seasonal snow cover frequency based on GFDL CM2 simulations (21st - 20th century) 46 -0 Projected change in frequency Trends in Northern Hemisphere snow mass 47 Projected change in seasonal snow water equivalent (swe) based on GFDL CM2 simulations (21st - 20th century) -1 48 Projected change in swe (mm) 49 Regional climate (baseline) • Source: PCIC (http://www.pcic.uvic.ca) 50 Temperature Projections 51 Precipitation projections 52 Regional Projections for snow 53 Implications of global change • Increase in planetary albedo (positive feedback on global warming) • Decreasing water resources, including soil moisture • Longer growing season • Impacts on recreational activities • Ecological implications 54 Further reading: 55 Points of Discussion: • Which component of the cryosphere is most vulnerable to climate change? • What are the possible environmental impacts of climate change in Prince George, B.C., Canada? • Will there be any jobs for cryospheric scientists in the 21st century? 56