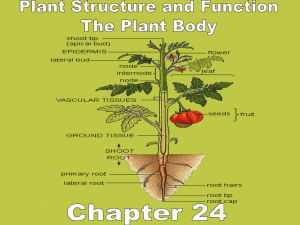
Plant Growth
advertisement

Plant Growth Way too much information for a single presentation… Plant Growth Outline • • • • • • • Indeterminate growth Determinate growth Plant Hormones Shoot apical meristem (and shoot tip), hormones Root apical meristem (and root tip), hormones Lateral Buds / Nodes Cambium ring/Secondary growth Two types of growth Indeterminate and Determinate Indeterminate Growth • Animals = maximum size & shape • Plants = no maximum size or shape • Able to keep growing all their lives • Limited by resources Indeterminate Growth • If injured, plants can grow more: – Branches – Leaves – Roots • Being bigger means being more susceptible to: – Disease – Pests – Weather & Gravity Determinate Growth • Maximum size and shape • Certain parts of the plant have determinate growth: – Leaves – Flowers – Fruit • Cannot heal/fix these when injured Indeterminate vs. Determinate Growth Hormones All growth is influenced by hormones Hormones Influence Growth • Auxin – – – – Associated with (root) growth Cell elongation Keeps leaves from dropping Apical meristem (not lateral buds) Hormones Influence Growth • Cytokinin – Associated with (stem) growth – Cell division – Lateral bud growth Hormones Influence Growth • Ethylene – Gas that encourages fruiting/ripening Hormones Influence Growth • Abscisic Acid – Shoot dormancy Hormones Influence Growth • Gibberellic Acid – Stem elongation and division Meristems The tips of the root and the shoot Shoot Apical Meristem • At the tip of the shoot • Growing tip can turn into any type of tissue • Hormone-controlled • Makes hormones that keep lateral buds from growing Shoot Tip Anatomy • Cell Division • Elongation • Differentiation – Dermal tissue – Ground tissue – Vascular tissue Getting plants to fill out… Root Apical Meristem • At the tip of the root • Growing tip can turn into any type of tissue • Hormone-controlled Root Tip Anatomy • • • • Root Cap (protection) Cell Division Elongation Differentiation – Dermal tissue – Ground tissue – Vascular tissue Growth is Hormone Controlled Growth is Hormone Controlled Cytokinin Auxin • What’s in the rooting powder we use in the greenhouse? – Auxin – Cytokinin Growth is Hormone-Controlled Lateral Bud/Nodes • Next to leaf • Could become meristem • Hormone-Controlled Lateral Bud/Node Secondary Growth Plants getting wider Secondary Growth • Stems getting fatter – Woody tissue • Only some plants can do this! Vascular Bundles • Scattered in the stem • In a ring in the stem If the stem gets fatter… • It needs more xylem and phloem to support the new tissue • Vascular Bundles in a RING only! Vascular Cambium Also called the Lateral Meristem • Between the Xylem and Phloem • Xylem is ALWAYS on the inside • Phloem is ALWAYS on the outside Secondary Growth • Cambium produces more xylem on the inside (DEAD thick walled-cells) • More phloem on the outside (slightly alive) • Tree bark is actually old, dead PHLOEM • Neato! Tree rings • In the spring/summer cambium makes big cells since it is growing fast • In the fall cambium makes smaller cells since it is growing slowly • Change in cell size throughout time is seen as a ring… Tree rings Size of Rings • You can tell the climate of an area using tree rings… • “Good” years are really wide because the tree grew fast in the spring and summer. • When plants grow at a steady rate all year there are NO TREE RINGS! Plant Growth Outline • • • • • • • Indeterminate growth Determinate growth Plant Hormones Shoot apical meristem (and shoot tip), hormones Root apical meristem (and root tip), hormones Lateral Buds / Nodes Cambium ring/Secondary growth The End