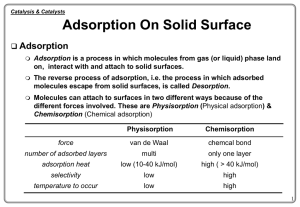
adsorption refrigerator - IQ
advertisement
CHEMICAL ENGINEER University of Valladolid Chemical Engineering Laboratory II CHILLING ADSORPTION Ana Celina Gondim Santos Sara Pérez Nieto (Group B - 22) Valladolid, 20 de Octubre de 2011 2/27 1. INTRODUCTION 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 3. RESEARCHS 4. APLICATIONS 5. CONCLUSIONS 3/27 1. INTRODUCTION Cooling adsorption systems Oil crisis (1970) Ecological problems (1990) Advantages: ● environmentally friendly refrigerants ● can recover waste heat at low temperature levels ● low operation costs Evaluation of an Adsorption cooling system: ● coefficient of performance (COP) ● specific cooling power (SCP) 4/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.1 System configuration and operation ADSORBENT ADSORBATE Figure 1. General basis system layout of the adsorption chiller. Adsorbent cooling: Adsorbent heating: adsorption process + refrigerant evaporation desorption process + refrigerant condensation 5/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.1 System configuration and operation Figure 2. Photograph of the silica gel-water adsorption chiller. 6/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.1 System configuration and operation Figure 3. The adsorption icemaker during ice production. Figure 4. Solar-powered icemaker without valves. 7/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.2 Parameters of work Parameters that influence in the performance of the system: ● Temperature of cooling water ● Adsorption temperature ● Heating source temperature ● Desorption temperature ● Cycle time load control tool T↑ and madsorbed ↓ (Pconst) T↑ and P↑ (madsorbed-const) to get more cooling. 8/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.3 Key issues for the development of adsorption systems ● The hight cost of production is a drawback for adsorption systems. ● To become more commercially attractive, it is necessary to make a cost and size reduction: Increasing the SCP throught enhancement of the internal and external heat transfer of the adsorber; ● Increasing the COP throught the improvement of the heat management. ● 9/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.3 Key issues for the development of adsorption systems The main technologies to enhance the external heat transfer are related to: extended surfaces: to increase of the heat exchange area; ● coated adsorbers: to increase the wall heat transfer coefficient; ● heat pipe technology: to have a high heat flux density and less intermediate elements. ● 10/27 2. ADSORPTION REFRIGERATOR 2.3 Key issues for the development of adsorption systems The main technologies to enhance the internal heat transfer are related to: consolidated adsorbents: because consolidated adsorbents have lower mass transfer properties than granular adsorbents, which could lead to very low adsorption rates. ● 11/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.1 Researches tendency Increase in adsorption cooling systems performance → compete with electric compression machines. ● Adsorbents ● R&D develop performing Components Sistems Harmonization of thermodynamic cycle. ● the adsorbent with the 12/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.1 Researches tendency Investigation in adsorbing materials: silica gel/water ● zeolite/water ● activated carbon ● activated carbon fibres/ammonia ● Methanol ● R134a ● 13/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.1 Researches tendency Adsorption refrigeration systems modelling: Many modelling techniques; ● Simulate the adsorption refrigeration systems; ● Simulation techniques: ● lumped-parameter ; ● lumped analytical ; ● dynamic ; ● distributed . ● 14/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.1 Researches tendency Simulation constant values: Overall heat transfer coefficient for adsorbent beds; ● Evaporator; ● Condenser. ● 15/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.1 Researches tendency Researches about adsorption cooling: Divided into some specifics ways to improve adsorption cooling systems. evaluation of adsorption and physical-chemical properties of the working-pairs; ● development of predictive models of their behaviour in different working conditions. ● study of the different kinds of cycles. ● 16/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.1 Researches tendency Figura 5. Design drawing and a frontal view of the adsorption chiler test facility. 17/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.2 Read Researches Development and test of two heat regenerative adsorption systems: ● ice making and air conditioning; ● activated carbon-methanol adsorption pair; ● cycle time was short → good heat transfer. 18/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.2 Read Researches Synthesis and characterization of a new composite sorbent: Improve the adsorbent; ● Make the isobars of ads-/desorption steeper; ● Increase the mass of water exchanged at the same boundary conditions; ● Improve the hydrothermal stability. ● 19/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.2 Read Researches Testing of the lab scale adsorption chiller: Study the influence of the cycle time; ● Study the relative duration of the isobaric steps; ● Relative duration of the isobaric steps on the performance of an adsorption cooling system. ● 20/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.2 Read Researches Design and performance prediction of a new generation adsorption chiller: (Mathematical model) ● Describe the heat and mass transfer process ● Adsorbent bed the composite adsorbent ● the metal of the tube ● the working fluids ● ● Condenser cooling water ● the metal of the tube ● refrigerant ● 21/27 3. RESEARCHS 3.2 Read Researches Optimization the operation strategy : ● Different temperatures of hot water inlet, cooling water inlet and chilling water inlet → different COP and cooling capacity; ● Conventional chiller; ● Composite adsorbent higher cooling capacity COP slightly higher 22/27 4 . APLICATIONS ● Jiagsu Province, China cool a grain depot during hot summers ; ● silica-gel adsorption chiller driven by a low temperature heat source . ● ● Shanghai Research Institute of Building Science ● chillers being used in the air conditioning system of a “green” building. 23/27 4 . APLICATIONS (a) (b) Figure 6. (a) Shanghai ‘‘Green’’ Building; (b) equipment room. 24/27 4 . APLICATIONS ● European project Climasol ● examples of buildings that already use solar-powered sorption air conditioners ● System located in the cosmetic company ● adsorption chillers powered by hot water in the summer ● Chinese ● small policy for energy exploitation power adsorption chillers ● suitable for combined cooling, heating and power systems or heating and power system 25/27 5 . CONCLUSIONS We tried to synthesize the four articles, taking the best that each had. It was observed that: • Adsorption cooling systems are becoming increasingly considered for applications where cooling is required and low grade heat is available. • Adsorption refrigerating machines consist essentially of an evaporator, a condenser, valves, and an adsorber-reactor containing a porous medium as adsorbent. • Some parameters influence in the performance of the system and there are drawbacks in these systems that don’t make them so commercially attractive. • Researches about adsorption cooling are divided into some specifics ways to improve adsorption cooling systems. • Looking for real application for the cooling adsorption, some buildings and grain depot were found in Asia and Europe. 26/27 Thank you! CHEMICAL ENGINEER University of Valladolid Chemical Engineering Laboratory II CHILLING ADSORPTION Ana Celina Gondim Santos Sara Pérez Nieto (Group B - 22) Valladolid, 20 de Octubre de 2011