Surface albedo measurements
advertisement

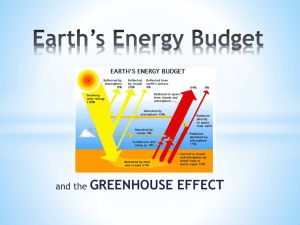
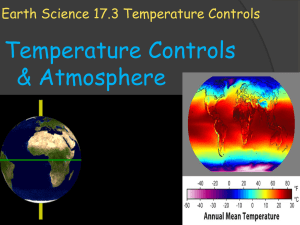
Introduction Surface Albedo Albedo on different surfaces Seasonal change in albedo Aerosol radiative forcing Spectrometer (measure the surface albedo) Measurement of the albedo on gray concrete. Measurement of the albedo on black surfaces. Measurement of the albedo on grass surfaces Measurement of the albedo on water surface at different zenith angles. Comparison of the surface albedo on different surfaces Conclusion Surface albedo is the fraction of Sun’s radiation reflected from a surface. Albedo is measured on a scale of 0 to 1 value of zero indicates the surface does not reflect, it absorbs all valueincoming of one means that light . all incoming light is reflected value of one means that all incoming light is reflected from the surface. An ideal white body has an albedo of 1 and an ideal black body has albedo of 0 • Earth receives both short and long wave radiation from the Sun • Some radiation is reflected back to space – Albedo-global mean planetary reflectance • Clouds, air molecules, particles, surface reflection • Earth’s albedo ~ 0.3 • About 30% of the incoming solar flux is reflected back to space • reflection of solar radiation are due to ice, snow, clouds, aerosols, and deserts surfaces. This graph shows the land surface albedo over wavelengths 4001000nm. From this graph we can see that the average albedo is approximately 0.3 or 30% and peaks around 900nm. Liou Xie et .al. 2002 This graph shows the curve of reflection for red ceramics. Values of reflectance were found to be around 9% in the UV range. 33% in the visible range 79% in the infrared(IV) range The average albedo over all wavelengths between 290.0 and 2500.0nm was found to be 67.7% R. T. A. Prado, F. L. Ferreira/ Energy and Buildings 37 (2005) 295-300. Williams et al., 1993. AEROSOL RADIATIVE FORCING Top of Atmosphere Idea S 2 F T (1 N ) [(1 a ) 2 (1 g ) 4a(1 )] 4 Single scattering approximation S = Solar constant (1386 [W/m2]) T = Atmospheric transmission (0.8) N = Cloudiness (0.5) g = Asymmetry parameter (0.7) w = Single scattering albedo (0.75) a = Surface albedo (MODIS) = Aerosol optical depth Chylek and Wong, GRL, 1995 Strong Impacts on Boundary Layer Meteorology and Surface Radiative Forcing. Modified from Dr. Seth Olsen’s AGU Presentation 2006. AEROSOL RADIATIVE FORCING James Hansen, NASA Climatologist Red Tide spectrometer Low cost Small foot print (89.1mm x 63.3 mm) The spectral response from 350nm to 1000nm wavelength Utilizes a detector with 650 active pixel, that is 650 data point in one full spectrum. Integration times as fast as 3 milliseconds Spectrometer help to measure : Absorbance Transmission Reflectance Solar Radiation Visible light (42% of solar energy) Near-infrared light (52%) Ultraviolet light (5%) Albedo is the amount of sunlight that is reflected by a particular surface. Black Asphalt Date: 28th April, 2012 Time: 12:08 pm Black Paper Date: 1st May, 2012 Time: 4:35 pm Zenith Angle = 27.0551° Time: 12:08:03 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.08 – 0.22 Zenith Angle = 27.0551° Time: 12:08:03 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.08 – 0.22 Zenith Angle = 64.5544° Time: 16:35:00 Date: 05/01/2012 Albedo = 0.015 – 0.08 Zenith Angle = 64.5544° Time: 16:35:00 Date: 05/01/2012 Albedo = 0.015 – 0.08 Date : 28th April, 2012 Time : 3:52 pm Zenith Angle = 45.8890° Time: 15:52:15 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.22 – 0.42 (nm) (nm) Date: 28th April, 2012 Time: 11:50 am Date: 28th April, 2012 Time: 12:00 pm Green Grass Zenith Angle = 28.8215° Time: 11:50:02 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.14 – 0.34 Dry grass Zenith Angle =28.001° Time: 12:00:30 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.18 – 0.47 Green Grass Zenith Angle = 28.8215° Time: 11:50:02 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.14 – 0.34 Dry grass Zenith Angle = 28.001° Time: 12:00:30 Date: 4/28/2012 Albedo = 0.18 – 0.47 Date: 29th April, 2012 Time: 1:19 pm and Time : 5:10 pm Zenith Angle = 31.0610° Time: 13:19:03 Date: 4/29/2012 Albedo = 0.1 – 0.27 Zenith Angle = 60.3233° Time: 17:10:20 Date: 4/29/2012 Albedo = 0.31 – 0.76 Zenith Angle = 60.3233° Time: 17:10:20 Date: 4/29/2012 Albedo = 0.31 – 0.76 Zenith Angle = 31.0610° Time: 13:19:03 Date: 4/29/2012 Albedo = 0.1 – 0.27 Gray Concrete Albedo Albedo Grass Surface Water Surface Black Road Wavelength(nm) Wavelength(nm) Liou Xie et .al. 2002 Date: 12th April, 2012 Time: 4:30 pm Date: 5th April, 2012 Time: 5:06 pm Clear day Zenith Angle = 67.5875° Time: 16:30:30 Date: 4/12/2012 Albedo = 0.16 – 0.30 Clear day Zenith Angle = 67.5875° Time: 16:30:30 Date: 4/12/2012 Albedo = 0.16 – 0.30 (nm) Cloudy day Zenith Angle = 75.3181° Time: 17:06:10 Date: 4/05/2012 Albedo = 0.01 – 0.22 (nm) Cloudy day Zenith Angle = 75.3181° Time: 17:06:10 Date: 4/05/2012 Albedo = 0.01 – 0.22 (nm) Measuring and monitoring surface albedo plays an important role in the earths energy balance and climate. The Surfaces which have albedo 1 or close to 1, reflect almost all incoming solar radiation. Most surfaces that have an albedo of 1 or near 1 are white in color. The surfaces which have albedo zero or close to zero, absorb almost all incoming radiation. Our measurements reveal that the albedo of black or dark surfaces was very low, ranging from around zero to approximately 0.2. The albedo of grass varied from around 0.15 to 0.45 depending on the condition of the grass. The albedo of water is dependent on the zenith angle and ranged from 0.1 to 0.76. Concrete was found to have the highest average albedo out of the surfaces we measured, remaining at a fairly constant value of 0.3. Our measurements are consistent with current known surface albedo values for various surfaces.