On an acidification of the Black Sea waters in XX century
advertisement

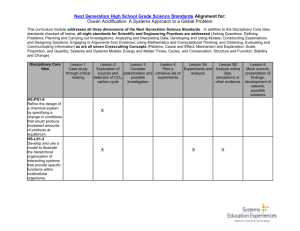
Has been observing the acidification of the Black Sea waters in XX century? Alexander Polonsky Marine Hydrophysical Institute 2011 Sea water acidification: what is it? Keeling curve for monthly atmospheric CO2 concentration at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii demonstrates its rise. Associated pH decreasing is acidification. At the same time pH changes can be due to natural processes. Total yearly CO2 anthropogenic emission is about 10 Gt now (in C equivalent) Science (2009). CO2 + H2O <=> [H]+ + [HCO3]pH is a measure of the acidity. Pure water is neutral, if a pH close to 7.0 (at 25°C). Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline. pH approximately equals to p[H], the negative logarithm (p[H], base 10) of the molar concentration of dissolved hydro ions (Wikipedia). “Ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the pH of the ocean over an extended period, typically decades or longer, which is caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but can also be caused by other chemical additions or subtractions from the ocean. Anthropogenic ocean acidification refers to the component of pH reduction that is caused by human activity” Definition, approved by Surface ocean pH decline vs total carbon emissions and release time. Dangerous level is 0.2 to 0.3 per century (Science, 2008) Variability of air/water pCO2 and pH in the North tropical Pacific: 1988-2008 Time series of (top) atmospheric CO2 and surface ocean pCO2 and (bottom) surface ocean pH at the atmospheric Mauna Loa Observatory (MLO) on the island of Hawai‘i and Station ALOHA in the subtropical North Pacific north of Hawai‘i, 1988–2008. After (Science, 2010) In situ pH trend is about -0.2 per century Recent changes in ocean temperature, acidity, and carbonate ion concentration. (A) Surface temperature anomaly for January 2010 relative to the mean for 1951–1980. (B) The same data presented in (A) as a function of latitude. (C) Estimated change in annual mean sea surface pH between the pre-industrial period (1700s) and the 1990s. (D) Estimated change in annual mean sea surface carbonate ion concentration between the pre-industrial period (1700s) and the 1990s [Science, 2010] Number of pH observations in the Black Sea in XX century Time series of Black Sea pH 8.8 9.2 Surface 10 m 8.6 8.8 8.4 8.4 8.2 8 8 7.6 7.8 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 8.6 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 1960 1980 2000 8.2 100 m 8.4 1000 m 8.1 8 8.2 7.9 8 7.8 7.8 7.7 7.6 7.6 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 1920 1940 Average seasonal pH distribution at 100 m (left) and mean pH profile (right) 8.9 8.8 8.7 8.6 8.5 8.4 8.3 8.2 8.1 8 7.9 7.8 7.7 7.6 7.5 7.4 44 43 42 February -March 30 32 34 36 38 40 0 400 800 1200 1600 44 2000 7.6 42 32 34 36 8 8.2 8.4 8.6 Vertical profile of the average (1924-2000) pH in the Black sea August-September 30 7.8 38 40 Space distribution of Ekman vertical decadal velocity in winter (10-6 m per sec) 1951-1960 1981-1990 Weakening of upward velocity 1961-1970 1991-2000 1971-1980 2000-2007 Intensification of upward velocity The principal reason of interdecadal regional (Black sea) atmospheric variability is Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation ΔP,Δφ 4.0 1 2.0 0.0 2 -2.0 -4.0 1880 1920 1960 2000 Variations of SLP difference in Azores High and Iceland Low (curve 1) and difference of latitudes of these atmospheric centers of action (curve 2) in winter (Polonsky et al, 2004). Frequency of winter Black sea cyclones In fact, this is manifestation of Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (Polonsky, Voskresenskaya, Bardin, 2007) Principal results • The pH decreasing (acidification ?) occurred in the Black Sea between ~1980 and 2000. • The rate of pH decreasing for the last decade of XX century exceed 0.2 pH units per decade in the upper sea layers. • Such high level of pH decreasing is mostly due to intensification of the upward motion in the subsurface layers in 1960-80’s. This leads to pH decreasing in the upper layers because pH is decreasing to the depth.