Earth, sun, moon PPT
advertisement

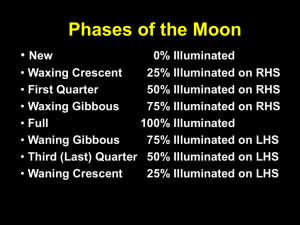
Bringing Astronomy Down to Earth What do we know about Earth – Moon – Sun interactions? Earth’s rotation The Earth rotates on its axis (it makes one complete turn) every 24 hours Earth’s rotation is the cause of our day and night Which way does the Earth rotate? From west to east Earth’s revolution The Earth revolves around the sun (makes one complete circuit) once every 365.26 days This is the cause of our year Leap year Every 4 years we add one day to the calendar year to make up the 1/4th of a day that we miss each year The last leap year was 2008, the next will be _____. Other variations in Earth’s movement Every 100,000 years the Earth’s elliptical orbit varies from more elongated to more circular Every 41,000 years the tilt of the Earth on its axis varies between 21.50 and 24.50 Precession: every 26,000 years the circular motion of the Earth on its axis...causes the Earth to spin like a top on a table Right now the axis points towards Polaris (North Star) In the future will point to the star Vega These are called Milankovitch cycles and they are believed to be one of the causes that the Earth’s climate cycles between ice ages and warm periods What do we mean by latitude and longitude? Latitude = Horizontal (N or S) Longitude = Vertical (E or W) Lines of Latitude 00 to 900 N, 00 to 900 S Important Lines of Latitude What is the latitude of Narragansett, RI? http://www.epodunk.com/cgibin/genInfo.php?locIndex=13438 Aphelion/Perihelion Because of the Earth’s elliptical orbit, the distance between the earth and the sun varies through the year We are closest at perihelion; we are furthest apart at aphelion (apart/aphelion) Aphelion (furthest from sun) occurs on July 4th (152 million km) and Perihelion (closest to sun) occurs on January 3rd (147 million km) Closest in January??? Then why is it coldest??? What causes the seasons?? The tilt of the earth on its axis!! During our summer: Northern hemisphere fully faces the sun During our winter: Southern hemisphere fully faces the sun A: Summer Solstice – June 20 or 21 solstice: means “sun” “stop” – the sun stops getting higher in the sky each day The sun’s rays are directed at the Tropic of Cancer B: Autumnal Equinox – September 22 or 23 Equinox: means “equal nights”; length of day and night are equal all over the world The sun’s rays are directed at the equator C: Winter Solstice – Dec. 21 or 22; sun is lowest in the sky The sun’s rays are directed at the Tropic of Capricorn D: Spring Equinox – March 20 or 21 The sun’s rays are directed at the equator Daylight Change by Latitude Monthly Variation in Daylight in Three Cities 30 25 15 10 5 0 Ja n F uar eb y ru ar y M ar ch A pr il M ay Ju ne Ju A ly S ug ep u te st m b O er ct N ob ov er e D mb ec e em r be r Daylight Hours 20 M onth Narragansett Tromsö Mexico City Can you detect the times of equinox? Can you detect the summer and winter solstices? What is an eclipse? An eclipse occurs when one planetary body passes through the shadow of another. Eclipses are named depending on which body is eclipsed, or blocked Solar Eclipse: (the sun is eclipsed or blocked) The moon is between the sun and earth - the shadow of the moon falls on the earth Within the umbra, you see a total eclipse (smaller area in shadow) Within the penumbra, you see a partial eclipse (larger area in the shadow) Solar eclipses never last > 7 minutes at any location. Why?? Lunar Eclipse: (the moon is eclipsed, or blocked) The earth is between the moon and the sun - the earth’s shadow falls on the lighted half of the moon Total lunar eclipse: moon must pass entirely through the earth’s umbra Partial lunar eclipse: only part of the moon passes through umbra Lunar eclipses may last hours!! The moon looks reddish during a lunar eclipse because the sunlight reflected off the moon is bent in the earth’s atmosphere Moon Phases Phases of the Moon: As Moon revolves around the Earth, different parts of the lighted side of the moon face Earth New moon: moon is between sun and earth – no visible moon Full moon: earth is between sun and moon – fully visible moon Crescent moon: < half of moon visible Gibbous moon: > half of moon visible Waxing: visible part is increasing Waning: visible part is decreasing Moon Phases New moon → waxing crescent → first quarter → waxing gibbous → full moon → waning gibbous → last quarter → waning crescent → back to new moon Phases of the Moon Tides: daily changes in the level of the ocean surface Caused by the gravitational pull of the moon (and the sun) on the Earth’s waters Both Sun and Moon cause the tides Spring tides: S-E-M Neap Tides: S-E M Spring tides: highest high tides of the month; at times of new and full moons Neap tides: lowest high tides of the month; at 1st and last quarters Neap and Spring Tides Tides – 3 tidal patterns diurnal tides: one high, one low every 24 hours semidiurnal tides: two equal high, two equal low every 24 hours semidiurnal mixed tides: 2 highs of different heights, 2 lows of different heights every 24 hours Tidal range: difference in height between the highest high and the lowest low tide Tidal period: time between one high tide and next high tide Tidal day: time between 1st high tide and last high tide in 24 hours What kind of tides in Eastport, ME? Look at the daily tidal range! What kind of tides in Grand Isle, LA? Look at the daily tidal range What kind of tides in Crescent City, CA? What kind of tides in Newport, RI ? Look at the daily tidal range