Faraday Rotation as a Diagnostic of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
advertisement
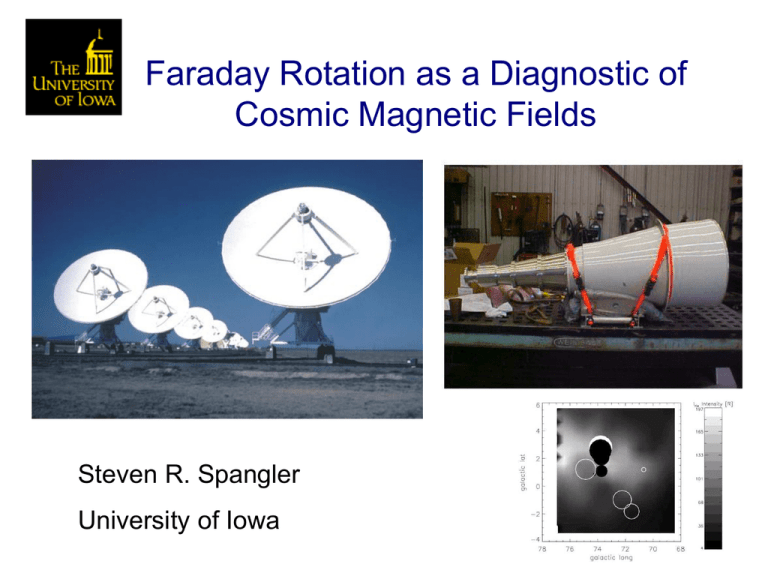
Faraday Rotation as a Diagnostic of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Steven R. Spangler University of Iowa Cosmic magnetic fields here means the solar corona as well as that of the ISM and elsewhere Faraday Rotation in the corona and elsewhere Plasma Contributions to the Faraday Rotation Integral An illustration of Faraday rotation Position angle rotation (1465 MHz) = 14 degrees Coronal RM = 6 rad/sq-m Ingleby, Spangler, Whiting 2007, ApJ 668, 520 Coronal Faraday Rotation Expected level of coronal FR, given independent information Faraday rotation in the Interstellar Medium Minter and Spangler 1996, ApJ 458, 194 The measurement of currents in astrophysical plasmas “Do you have anything to say before we turn on the current?” Differential Faraday Rotation A difference in Rotation Measure between two closely-spaced lines of sight Differential Faraday Rotation and Ampere’s Law Differential Faraday Rotation and Ampere’s Law II Method utilized in Wisconsin Reversed Field Pinch (RFP) by Ding, Brower, et al (PRL 90, 035002, 2003) Observations of Differential Faraday Rotation on August 16, 18 2004 Inferred current of 2.5 GA between lines of sight Total Faraday Differential Faraday Rotation separated by ~ Rotation 35,000 km Are differential Faraday rotation measurements seen through the ISM indications of interstellar currents? A new age of opportunity for cosmic Faraday rotation measurements; the availability of the EVLA • Lower noise receivers • Larger bandwidth • Continuous frequency coverage Why continuous frequency coverage will be a great help in Faraday rotation measurements Old VLA… measurements in Lazio, Spangler, Cordes 1990, ApJ 363, 515 EVLA… continuous frequency coverage from 1.0 to 8.0 GHz (and beyond) Conclusion: Faraday rotation is an excellent diagnostic for magnetic fields (large scale and turbulent) in tenuous, collisionless cosmic plasmas The technique will yield new results in the future, with a new instrument, the EVLA