MS Science - Fair Lawn Public Schools
advertisement

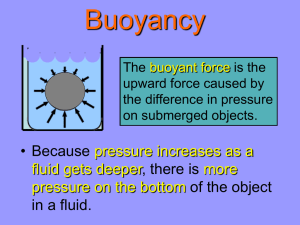
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Pressure and Density of Fluids Lesson 2 The Buoyant Force Lesson 3 Other Effects of Fluid Forces Chapter Wrap-Up In what ways do people use forces in fluids? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you view this presentation, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. Do you agree or disagree? 1. Air is fluid. 2. Pressure is a force acting on a fluid. 3. You can lift a rock easily under water because there is a buoyant force on the rock. Do you agree or disagree? 4. The buoyant force on an object depends on the object’s weight. 5. If you squeeze an unopened plastic ketchup bottle, the pressure on the ketchup changes everywhere in the bottle. 6. Running with an open parachute decreases the drag force on you. Pressure and Density of Fluids • How do force and area affect pressure? • How does pressure change with depth in the atmosphere and under water? • What factors affect the density of a fluid? Pressure and Density of Fluids • fluid • pressure • atmospheric pressure What is a fluid? A fluid is any substance that can flow and take the shape of the container that holds it. fluid from Latin fluidus, means “flowing” What is a fluid? (cont.) • The volume of a liquid is constant, regardless of the container. • The volume of a gas always changes to fill the container. The McGraw-Hill Companies Pressure of Fluids • Pressure is the amount of force per unit area applied to an object’s surface. • All fluids (liquids and gases) apply pressure. • Pressure applied on an object by a fluid is related to the weight of the fluid. Pressure of Fluids (cont.) • In the equation below, P is pressure, f is the force applied to a surface, and a is the surface area over which the force is applied. • The unit measurement for pressure is the pascal (Pa). Pressure of Fluids (cont.) Pressure of Fluids (cont.) A fluid applies pressure perpendicular to all sides of an object in contact with the fluid. Pressure of Fluids (cont.) • Pressure decreases when the surface area over which a force is applied increases. • Pressure increases when the surface area over which a force is applied decreases. Pressure of Fluids (cont.) How does pressure change as surface area changes? Pressure of Fluids (cont.) The ratio of the weight of all the air above you to your surface area is atmospheric pressure. On land, atmospheric pressure depends on your elevation. Under water, the pressure depends on your depth below the water’s surface. Pressure of Fluids (cont.) How does elevation affect atmospheric pressure? Density of Fluids If the volume of two fluids is the same, the fluid that weighs more is denser. dense Science Use a measure of the ratio of mass to volume Common Use slow to learn or understand Density of Fluids (cont.) • You can calculate density with the equation below, where D is density, m is mass, and v is volume. • Density is often measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). Density of Fluids (cont.) • Materials have different densities because of differences in the masses of their molecules and in the distances between them. • Solids are usually denser than liquids or gases. Density of Fluids (cont.) What factors determine the density of fluids? • Pressure is high when a force is applied over a small area. • Atmospheric pressure decreases with elevation. • Fluids form layers depending on their densities. Which term refers to the ratio of the weight of all the air above you to your surface area? A. atmospheric pressure B. density C. elevation D. pascal What happens to pressure applied by a fluid as depth increases? A. decreases B. increases C. fluctuates randomly D. remains the same By what do you divide mass to calculate density? A. volume B. pressure C. force D. area Do you agree or disagree? 1. Air is fluid. 2. Pressure is a force acting on a fluid. The Buoyant Force • How are pressure and the buoyant force related? • How does Archimedes’ principle describe the buoyant force? • What makes an object sink or float in a fluid? The Buoyant Force • buoyant force • Archimedes’ principle What is a buoyant force? A buoyant force is an upward force applied by a fluid on an object in the fluid. buoyant from Spanish boyar, means “to float” What is a buoyant force? (cont.) A buoyant force acts on any object in a liquid. Objects in a gas also experience a buoyant force. Medioimages/Superstock Getty Images/Digital Vision The buoyant force on a diver is the difference between the force from pressure above and below the diver. What is a buoyant force? (cont.) How is pressure related to buoyant force? What is a buoyant force? (cont.) • The depth of an object completely submerged in a fluid has no effect on the buoyant force. • The buoyant force depends on an object’s volume. Archimedes’ Principle • The greater the volume of an object in a fluid, the greater the buoyant force on it. • Archimedes’ principle states that the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces. The buoyant force is greater on the balloon than on the tennis ball or the billiard ball because the balloon displaces more water. Archimedes’ Principle (cont.) What is the buoyant force on you if you displace 400 N of water as you dive under water? Sinking and Floating • When the buoyant force on an object is less than the gravitational force, the object sinks. • An object floats if the buoyant force acting on it is equal to the object’s weight. If the weight of an object is greater than the buoyant force acting on it, the object sinks. Sinking and Floating (cont.) If an object is more dense than the fluid in which it is placed, then the buoyant force on that object will be less than the object’s weight, and the object will sink. If an object weighing 14 N experiences a 12-N buoyant force, will it sink or float? The boat on the left floats because it is filled with air instead of water. As a balloon loses helium, its density increases and its buoyant force decreases. • A buoyant force results from the difference in pressure between the top and the bottom of an object? • Objects that have the same volume in a fluid experience the same buoyant force. • When the density of a balloon becomes greater than the density of air, the balloon sinks. What is the direction of a buoyant force? A. B. C. D. upward horizontal downward diagonal How does increasing the depth of an object in a fluid affect the buoyant force on the fluid? A. It has no effect. B. It decreases the buoyant force. C. It increases the buoyant force. D. The effect depends on the object’s depth. An object floats if the buoyant force is which of these? A. equal to the object’s weight B. greater than the object’s weight C. less than atmospheric pressure D. less than the object’s weight Do you agree or disagree? 3. The buoyant force on an object depends on the object’s weight. 4. You can lift a rock easily under water because there is a buoyant force on the rock. Other Forces in Fluids • How are forces transferred through a fluid? • How does Bernoulli’s principle describe the relationship between pressure and speed? • What affects drag forces? Other Forces in Fluids • Pascal’s principle • Bernoulli’s principle • drag force Fluid Forces—Benefits and Challenges • You produce a force when you squeeze a plastic ketchup bottle. • You make use of a buoyant force when you float on a raft. • Fluid forces from floods, tornadoes, and hurricanes can cause damage. Pascal’s Principle Pascal’s principle states that when pressure is applied to a fluid in a closed container, the pressure increases by the same amount everywhere in the container. Pascal’s Principle (cont.) How does pressure change when force is applied to a fluid in a closed container? Pascal’s Principle (cont.) • A piston uses a small force in one area to apply a larger force in another area. • According to Pascal’s principle, pushing on the piston increases the pressure equally throughout the fluid in the piston. • Car mechanics rely on Pascal’s principle when they raise a car using a hydraulic lift. • Pushing down with a small force in the narrow tube generates a force under the car that is large enough to lift the car. • The piston on the left will have to be pushed down further than the distance the car will be raised. • Since work is force times distance, the work done by the two pistons is equal. Bernoulli’s Principle Bernoulli’s principle states that the pressure of a fluid decreases when the speed of that fluid increases. Bernoulli’s Principle (cont.) What is the relationship between speed and pressure in a fluid? Bernoulli’s Principle (cont.) Bernoulli’s Principle (cont.) How does Bernoulli’s principle explain how wind can take the roof off a house? Because air moves from areas of high to low pressure, the higher pressure on the left side of the soccer ball causes the ball to curve right. Drag Forces Drag force is a force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. drag force from Old Norse draga, means “to draw”; and Latin fortis, means “force” Drag Forces (cont.) • As the speed of an object in a fluid increases, the drag force on that object also increases. • If two objects move in the same direction, the object with the greater surface area toward the direction of the motion has a greater drag force on it. • Drag forces increase when the density of a fluid increases. Drag Forces (cont.) What affects the drag force on an object? • People rely on Pascal’s principle when they use hydraulic lifts. • The imbalance of pressures in fluids can cause a roof to lift off a house in a severe windstorm. • A soccer player who kicks a curved ball makes use of Bernoulli’s principle. Which states that pressure in a closed container is applied equally? A. Archimedes’ principle B. Bernoulli’s principle C. drag force principle D. Pascal’s principle What is the relationship between the amount of work on the two pistons of a closed fluid system? A. More work is done on the larger side. B. More work is done on the smaller side. C. No work is done on either side. D. The amount of work is the same on both sides. Which states that the pressure of a fluid decreases when the speed of that fluid increases? A. Archimedes’ principle B. Bernoulli’s principle C. drag force principle D. Pascal’s principle Do you agree or disagree? 5. If you squeeze an unopened plastic ketchup bottle, the pressure on the ketchup changes everywhere in the bottle. 6. Running with an open parachute decreases the drag force on you. Key Concept Summary Interactive Concept Map Chapter Review Standardized Test Practice People use forces in fluids to float objects on water and in air, to lift objects, and to affect the motions of objects. Lesson 1: Pressure and Density of Fluids • Pressure is the ratio of force to area. • Atmospheric pressure decreases with elevation. Pressure under water increases with depth. • The density of a fluid depends on the mass of the fluid and its volume. Lesson 2: The Buoyant Force • The change in pressure between the top and the bottom of an object results in an upward force called the buoyant force. • Archimedes’ principle states that the weight of the fluid displaced by an object is equal to the buoyant force on that object. • An object sinks if its weight is greater than the buoyant force on it. An object does not sink if the buoyant force on it is equal to its weight. Lesson 3: Other Forces from Fluids • Pascal’s principle states that when pressure is applied to a fluid in a closed container, the pressure increases by the same amount everywhere in the container. • Bernoulli’s principle states that when the speed in a fluid increases, the pressure decreases. • Speed, size, and shape of an object, as well as the density of the fluid in which the object moves, affect the drag force on that object. Which term describes the amount of force per unit area applied to an object’s surface? A. atmospheric pressure B. drag force C. fluid D. pressure By what do you divide force to calculate pressure? A. area B. mass C. volume D. weight Which describes an upward force applied by a fluid on an object in the fluid? A. pressure B. gravity C. density D. buoyant force The buoyant force on a diver is the difference between the upward force from pressure and which of these? A. the depth of the water B. the downward force from pressure C. the density of the diver D. the density of the fluid What happens to the atmospheric pressure as you hike a trail to the top of a mountain? A. it decreases B. it increases C. it first decreases, then increases D. if first increases, then decreases Which term describes any substance that can flow and take the shape of the container that holds it? A. fluid B. gas C. liquid D. solid Which is the unit measurement for pressure? A. grams per cubic centimeter B. joule C. pascal D. newton Archimedes principle states that the buoyant force on an object is equal to what? A. the depth of the object B. the surface area of the object C. the weight of the displaced fluid D. the weight of the object Which describes a force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid? A. atmospheric pressure B. buoyant force C. drag force D. friction What happens to the drag force on an object in a fluid as the speed of the object increases? A. It decreases. B. It depends on the shape of the object. C. It increases. D. It remains constant.