Georgia Institute of Technology
advertisement

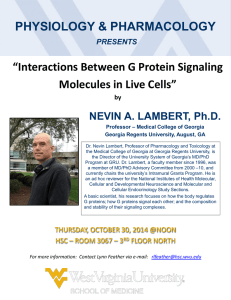
Operational Air Quality and Source Contribution Forecasting in Georgia Yongtao Hu1, M. Talat Odman1, Michael E. Chang2 and Armistead G. Russell1 1School 2Brook of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Byers Institute of Sustainable Systems Georgia Institute of Technology 10th Annual CMAS Conference, October 24th, 2010 Georgia Institute of Technology Outline Local Air Quality Forecasting in Georgia The Hi-Res air quality forecasting system Evolution of Hi-Res during 2006-2011 Met performance and O3 and PM2.5 performance for metro Atlanta New SOA module and its impact on PM2.5 performance Pilot Source Contribution Forecasting Georgia Institute of Technology Local Forecasting: How it works in Georgia A forecasting panel with 5-7 local expert members •air quality researchers, modelers, meteorologists, etc. “Voting” through a decision making online system •the consensus of the panel will be the “ensemble” forecasts Base their “opinion” on multiple available resources •NOAA O3 guidance, Statistical model results, Weather forecasts •Hi-Res O3 and PM2.5 forecasts •Experiences Broadcast to the public •Website: http://www.gaepd.org/air/smogforecast/ and AirNOW •Smog alert through highway traffic information system Georgia Institute of Technology Hi-Res: forecasting ozone and PM2.5 at a 4-km resolution for metro areas in Georgia Hi-Res Modeling Domains Hi-Res Air Quality Forecasting System Serving Metro-Atlanta Area since 2006 Emissions Meteorology Emission Inventory NAM 84-hr Forecast SMOKE WRF Forecast Product CMAQ 4-km (123x123) 12-km (123x138) Air Quality Hi-Res Cycle Cycle 1 00Z 66Z 15Z ramp up Cycle 2 36-12- & 4-km forecasts 27Z 12Z ramp up Operation Forecast Forecast Forecast Day Day 22 Forecast Day Day 11 7pm 0am R& R&S R& 1 F1&R1 36-km (148x112) S2 78Z 7 Forecast Time (UTC) 36-12- & 4-km forecasts Computer Forecast Day 2 Forecast Day 1 0am Time (EST) 0am 0am &S F2 R2&S Georgia Institute of Technology Hi-Res Forecast Products “Single Value” Report: tomorrow’s AQI, ozone and PM2.5 by metro area in Georgia Air Quality Forecasts: AQI, ozone and PM2.5, 48-hrs spatial plots and station profiles Meteorological Forecasts: precipitation, temperature and winds, 48-hrs spatial plots and station profiles Performance Evaluation: time series comparison and scatter plots for the previous day Snapshots from Hi-Res homepage: http://forecast.ce.gatech.edu Georgia Institute of Technology Evolution of Hi-Res during 2006-2011 Updated to latest release of WRF each year before the ozone season. •WRF 2.1, 2.2, 3.0, 3.1, 3.2 and 3.3 CMAQ is typically one version behind. •CMAQ 4.6 with Georgia Tech extensions Projected NEI to current year in the very beginning of each year. Updated forecast products website each year before ozone season. Switched from single-cycle forecasting to two-cycles in 2008. Enlarged 4-km domain to cover the entire state of Georgia in 2009. Introduced Georgia Tech’s new SOA module in 2009. Enlarged 36-km domain to cover the CONUS and enlarged 12-km domain to cover the eastern US in 2011. In 2011 switched landuse data from old USGS data to new MODIS data in WRF, to reflect recent changes in land cover. Enlarged Modeling Domains Current 2006-2010 4-km (99x78) Current 4-km (123x123) 12-km (72x72) 4-km (123x123) 12-km (123x138) 36-km (148x112) 36-km (72x72) Georgia Institute of Technology Ambient Monitoring Sites for Performance Evaluation in Atlanta Metro Kennesaw Gwinnet NE Atlanta Yorkville Atlanta West Atlanta Confederate Ave Douglasville South DeKalb Atlanta Conyers Fayetteville Newnan Walton McDonough Peachtree City SLAMS O3 SLAMS PM2.5 NWS Met Met Performance Overall 2006-2011 Performance (Ozone Season): Atlanta Metro Humidity Temperature 315 20 18 16 Observed Humidity at 2m (g/kg) Observed Daily Hi Temp at 2m (K) 310 305 300 295 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 290 290 0 295 300 305 310 315 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Forecast Humidity at 2m (h/kg) Forecast Daily Hi Temp at 2m (K) MB -0.39K MB -0.68g/kg ME 1.55K ME 1.19g/kg Georgia Institute of Technology 16 18 20 Forecast vs. Observed Temperature 2007 315 310 310 Daily Hi Temp 2m (K) Daily Hi Temp at 2m (K) 2006 315 305 300 MB 0.50K 300 295 295 ME 290 5/1/2006 305 5/31/2006 6/30/2006 1.57K 7/30/2006 8/29/2006 290 5/1/2007 9/28/2006 5/21/2007 6/10/2007 6/30/2007 7/20/2007 8/9/2007 8/29/2007 9/18/2007 310 Daily Hi Temp at 2m (K) 310 Daily Hi Temp at 2m(K) 1.90K 315 315 305 300 MB -0.80K 305 300 MB 295 295 ME 5/21/2008 6/10/2008 6/30/2008 7/20/2008 1.94K 8/9/2008 8/29/2008 9/18/2008 290 5/1/2009 0.37K ME 5/21/2009 6/10/2009 6/30/2009 Date 1.47K 7/20/2009 8/9/2009 8/29/2009 9/18/2009 Date 2011 2010 315 315 310 Daily Hi Temp at 2m (K) 310 Daily Hi Temp at 2m (K) ME 2009 2008 305 300 295 290 05/01/10 -1.16K Date Date 290 5/1/2008 MB 05/21/10 06/10/10 MB -0.19K ME 1.15K 06/30/10 07/20/10 Date 08/09/10 305 300 295 290 MB -0.05K ME 1.29K Georgia Institute of Technology 08/29/10 09/18/10 285 05/01/11 05/21/11 06/10/11 06/30/11 07/20/11 Date 08/09/11 08/29/11 09/18/11 Forecast vs. Observed Humidity 2006 2007 20 20 18 Daily Avg Humidity at 2m (g/kg) Daily Avg Humidity at 2m (g/kg) 18 16 14 12 10 8 MB 6 4 ME 2 -0.74g/kg 1.39g/kg 5/21/2006 6/10/2006 6/30/2006 7/20/2006 8/9/2006 14 12 10 8 MB 6 4 2 0 5/1/2006 16 0 5/1/2007 8/29/2006 9/18/2006 ME 5/21/2007 6/10/2007 Daily Avg Humidity at 2m (g/kg) 18 16 14 12 10 ME 2 0 5/1/2008 5/21/2008 6/10/2008 6/30/2008 7/20/2008 -0.89g/kg 1.33g/kg 8/9/2008 8/29/2008 14 12 10 8 6 2 0 5/1/2009 9/18/2008 MB -0.36g/kg ME 0.96g/kg 4 5/21/2009 6/10/2009 6/30/2009 18 16 16 Daily Avg Humidity at 2m (g/kg) 20 18 14 12 10 8 4 ME 2 0 05/01/10 05/21/10 06/10/10 06/30/10 07/20/10 Date 8/9/2009 8/29/2009 9/18/2009 08/29/11 09/18/11 2011 20 MB 7/20/2009 Date 2010 6 9/18/2007 16 Date Daily Avg Humidity at 2m (g/kg) Daily Avg Humidity at 2m (g/kg) 20 18 4 8/29/2007 2009 20 MB 8/9/2007 Date 2008 6 1.22g/kg 6/30/2007 7/20/2007 Date 8 -0.59g/kg -0.73g/kg 14 12 10 8 6 4 1.03g/kg Georgia Institute of Technology 2 08/09/10 08/29/10 09/18/10 0 05/01/11 05/21/11 MB -0.73g/kg ME 1.22g/kg 06/10/11 06/30/11 07/20/11 Date 08/09/11 Air Quality Performance Metrics Forecast False Alarms Hits NAAQS NAAQS Correct Nonevents Missed Exceedences Observation MNB 1 N N k 1 ck ck m o c o k MNE 1 N N ck ck k 1 ck m o o Overall 2006-2011 Performance (Ozone Season): Atlanta Metro PM2.5 Ozone 150 70.0 146 0 0 4-km 4-km 134 75 35.0 792 58 525 52 0 0.0 150 75 0 0 Obs. 35 70 Obs. MNB 17% MNB -17% MNE 23% MNE 32% Georgia Institute of Technology Ozone Performance Forecast vs. Observed O3 2006 MNB 11% MNE 29% 2007 120.0 100.0 120 MNB 8.5% MNE 19% 100 80 O 3 (p p b ) O3 (ppb) 80.0 60.0 60 40.0 40 20.0 20 0.0 May-01 0 Jun-01 Jul-01 Aug-01 Obs. M a y-0 7 Sep-01 120 100 MNB 17% MNE 23% 2009 120 100 O3 (ppb) O3 (ppb) S e p -0 7 4 -k m MNB 28% MNE 30% 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 Jun-08 Jul-08 Aug-08 Obs 0 May-09 Sep-08 Jun-09 Jul-09 120 Aug-09 Obs 4-km 2010 MNB 14% MNE 18% 120 100 100 80 80 60 Sep-09 4-km 2011 O3 (ppb) O3 (ppb) A ug -0 7 Obs 80 MNB 18% MNE 21% 60 40 40 20 20 0 May-10 J ul-0 7 4-km 2008 0 May-08 J un-0 7 Georgia Institute of Technology Jun-10 Jul-10 Aug-10 Obs 4-km Sep-10 0 May-11 Jun-11 Jul-11 Aug-11 Obs 4-km Sep-11 2009 O3 Performance: Hi-Res vs. GA EPD’s Our 4-km Forecast EPD Ensemble Forecast 150 150 7 75 75 4 108 6 7 EPD 4-km 24 5 125 0 0 0 75 150 0 75 Obs. Obs. MNB 28% MNB 13% MNE 30% MNE 21% 150 2010 O3 Performance: Hi-Res vs. GA EPD’s Our 4-km Forecast EPD Ensemble Forecast 150 150 EPD 4-km 75 75 11 105 10 16 12 14 12 104 0 0 0 75 150 0 75 150 Obs. Obs. MNB 14% MNB 9% MNE 18% MNE 17% 2011 O3 Performance: Hi-Res vs. GA EPD’s Our 4-km Forecast EPD Ensemble Forecast 150 150 EPD 4-km 75 75 10 76 32 13 36 26 12 91 0 0 0 75 150 0 75 150 Obs. Obs. MNB 18% MNB 8% MNE 21% MNE 16% PM2.5 Performance Summer Forecast vs. Observed PM2.5 2006 45.0 -38% MNE 43% 2007 -37% MNE 44% 45 40 35.0 35 30.0 30 O 3 (p p b ) 3 PM 2.5 (mg/m ) 40.0 MNB MNB 25.0 20.0 15 10.0 10 5.0 5 May-01 0 Jun-01 Jul-01 Aug-01 Obs. Sep-01 M a y-0 7 45 40 35 MNB -38% MNE 42% 20 45 40 10 5 0 May-09 Sep-08 Jul-09 MNE 35 Aug-09 Obs MNB 40 4% 25 20 25% 45 40 21% Sep-09 4-km 2011 35 PM2.5 (ug/m3) 30 MNB -2% MNE 25% 30 25 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 May-10 Jun-09 4-km 45 MNE 20 5 2010 8% 25 15 Obs MNB 30 10 Aug-08 S e p -0 7 35 15 Jul-08 A ug -0 7 4 -k m 2009 PM2.5 (ug/m3) 25 Jun-08 J ul-0 7 Obs 30 0 May-08 J un-0 7 4-km 2008 O3 (ppb) 20 15.0 0.0 PM2.5 (ug/m3) 25 Georgia Institute of Technology Jun-10 Jul-10 Aug-10 Obs 4-km Sep-10 0 May-11 Jun-11 Jul-11 Aug-11 Obs 4-km Sep-11 2009 PM2.5 Performance: 4-km vs. GA EPD’s Our 4-km Forecast EPD Ensemble Forecast 70 70 EPD 4-km 0 0 0 0 35 35 129 129 3 3 0 0 0 35 70 0 35 70 Obs. Obs. MNB 8% MNB 11% MNE 25% MNE 24% 2010 PM2.5 Performance: 4-km vs. GA EPD’s Our 4-km Forecast EPD Ensemble Forecast 70 70 0 0 0 EPD 4-km 0 35 138 35 138 0 0 0 0 0 35 70 0 35 Obs. Obs. MNB 4% MNB 14% MNE 21% MNE 30% 70 2011 PM2.5 Performance: 4-km vs. GA EPD’s Our 4-km Forecast EPD Ensemble Forecast 70 70 0 2 1 EPD 4-km 0 35 141 35 141 3 5 0 0 70 35 0 35 0 Obs. Obs. MNB -2% MNB 7% MNE 25% MNE 24% 70 Winter Forecasted vs. Observed PM2.5 2008 45 45 40 40 35 35 30 30 O 3 (ppb) O 3 (p p b ) 2007 25 20 25 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 O ct-0 7 N o v-0 7 D e c-0 7 Ja n-0 8 Obs F e b -0 8 0 Oct-08 M a r-0 8 Nov-08 Dec-08 4 -km 45 45 40 40 35 35 30 30 25 20 20 15 10 10 5 5 Dec-09 Mar-09 25 15 Nov-09 Feb-09 4-km 2010 PM2.5 (ug/m3) PM2.5 (ug/m3) 2009 0 Oct-09 Jan-09 Obs Jan-10 Obs Feb-10 4-km Mar-10 Apr-10 0 Oct-10 Nov-10 Dec-10 Jan-11 Obs Feb-11 4-km Mar-11 Apr-11 A New SOA Module (Baek, J., Georgia Tech, 2009) Included processes: •SOA partitioned from anthropogenic VOCs’ oxidations (8 SVOCs) •From monoterpenes (2 SVOCs) •From isoprene (2 SVOCs added) •From sesquiterpenes (1 SVOC added, gas phase oxidation reactions added for α-caryphyllene, β-humulene, and other sesquiterpenes) •Multigenerational oxidation of all semi-volatile organic carbons (SVOCs) added Multigenerational Oxidation : HSVOC SOA species in CMAQ: •AORGAJ and AORGAI •AORGBJ and AORGBI •AORGBISJ and AORGBISI •AORGBSQJ and AORGBSQI •AORGAGJ and AORGAGI +OH,+O3 LSVOC +OH,+O3 Aerosol Forecast vs. Observed OC at South DeKalb 15 forecast 14 2009 13 Ozone Season May-September obs 12 11 Organic Carbon PM2.5 10 16 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 9 8 7 6 5 4 12 3 1 0 5/1/2009 5/21/2009 6/10/2009 6/30/2009 7/20/2009 8/9/2009 8/29/2009 9/18/2009 Date 8 15 forecast 14 obs 2010 13 12 4 11 10 0 0 4 8 Observed (ug m-3) 12 16 Organic Carbon PM2.5 Forecast (ug m-3) 2 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 5/1/2010 5/21/2010 6/10/2010 6/30/2010 7/20/2010 Date 8/9/2010 8/29/2010 9/18/2010 Source Contribution Forecasting in Pilot Operation Source contribution forecasts for ozone and PM2.5. •Traffic, Power plants and others such as prescribed fires (needs additional efforts). Extra information on top of ozone and PM2.5 concentration forecasts. •Providing quantitative information on specific source contributions •Alerting on specific source impacts •To help public targeting actions to prevent pollution events Using forward sensitivity tool DDM3D in CMAQ to calculate first order sensitivity coefficients •Interpret such sensitivities of ozone and PM2.5 concentrations to total emissions from specific sources as their contributions Challenges in operational forecasting •Computationally expensive, but doable •Instability in calculation Preliminary Source Contribution Forecasts: Traffic and Power Plants Impacts 2009 2010 Summary • 2006-2011 Temperature and humidity performance in May-September are good. – Daily high temperature bias is -0.39K and error is 1.55K – Daily average humidity bias is and error is -0.68g/kg and 1.19g/kg • 2006-2011 Ozone forecasts are good. – Overall bias is +17% and error is 23% • 2006-2011 PM2.5 forecasts are not very accurate. – May-September bias is -17% and error is 32% • The new SOA module helped much better 2009-2011 PM2.5 performances in May-September – Bias is +8% and error is 25% for 2009 – Bias is +4% and error is 21% for 2010 – Bias is -2% and error is 25% for 2011 • Preliminary source contribution forecasting products. Georgia Institute of Technology Acknowledgements We thank Georgia EPD for funding the Hi-Res forecasts, Our former group member Dr. Jaemeen Baek for the new SOA module, and Dr. Carlos Cardelino of Georgia Tech for team forecasts.