origin and evolution of the atmosphere
advertisement
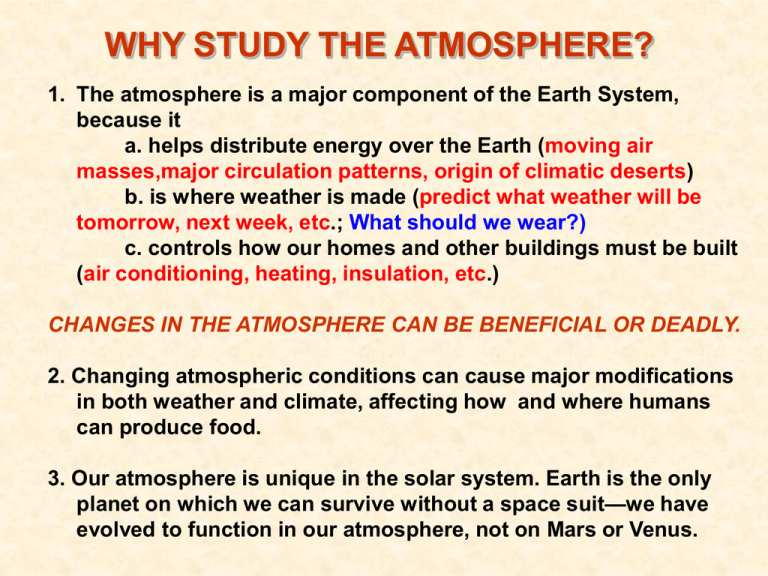
WHY STUDY THE ATMOSPHERE? 1. The atmosphere is a major component of the Earth System, because it a. helps distribute energy over the Earth (moving air masses,major circulation patterns, origin of climatic deserts) b. is where weather is made (predict what weather will be tomorrow, next week, etc.; What should we wear?) c. controls how our homes and other buildings must be built (air conditioning, heating, insulation, etc.) CHANGES IN THE ATMOSPHERE CAN BE BENEFICIAL OR DEADLY. 2. Changing atmospheric conditions can cause major modifications in both weather and climate, affecting how and where humans can produce food. 3. Our atmosphere is unique in the solar system. Earth is the only planet on which we can survive without a space suit—we have evolved to function in our atmosphere, not on Mars or Venus. Commonly Accepted Definitions Weather refers to the current atmospheric conditions (including temperature, precipitation, wind, humidity, barometric pressure) at a particular time and place. Climate refers to the general weather patterns expected in a given area (sometimes based on the 30 year average weather). Climate may also be applied more generally to large-scale weather patterns in time or space (e.g., an Ice Age climate or a tropical climate). Weather is made in the Troposphere 90 80 70 60 Pressure Altitude (km) 50 Density 40 30 20 10 0 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100` 1000 Pressure (mb) .00001 .0001 .001 .01 0.1 3 Density (Kg/m ) 1 10 ORIGIN AND EVOLUTION OF THE ATMOSPHERE ● Early atmosphere [H, He, Ammonia (NH3) and Methane (CH4)] was driven away by solar radiation and lost by their low atomic masses ● Primordial Earth melted completely and gases bubbled out or erupted from early volcanoes. Result was a N-rich atmosphere ● Evolution of blue-green algae changed everything! Photosynthesis by these algae absorbed CO2 from the atmosphere and released O2 ● Most of that oxygen was dissolved in the oceans where it combined with iron and precipitated until about 2.5 billion years ago (2.5 Ga) to form iron oxides in banded iron formation ● At about 2.5 Ga, oceans were saturated with oxygen and free oxygen was added to the atmosphere. Resulting surface oxidation produced first redbeds on the continents. ●At about 1 Ga, reservoirs of oxidizable rock at the surface were saturated and oxygen began to build up in the atmosphere ● Ultraviolet light split O2 molecules forming ozone (O3) that shielded the surface from intense solar radiation. At that point, life could emerge from the ocean and colonize the continents. Cumulative oxygen production EVOLUTION OF ATMOSPHERE OXYGEN CONTENT 100 80 60 40 Little atmospheric O2 Rise of atmospheric O2 20 0 Redbeds Banded Iron formation 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 Billions of years before present Today EVIDENCE FOR ATMOSPHERIC EVOLUTION COMES FROM THE GEOLOGIC RECORD Banded iron formation (3 Ga) Continental redbeds Until about 2.5—2.0Ga, there was not enough oxygen in the atmosphere to oxidize iron minerals. Oxygen dissolved in the oceans oxidized iron to produce marine banded iron formation. At 2.5—2.0 Ga, enough oxygen accumulated in the atmosphere to oxidize iron on the continents and the first redbeds formed. Atmosphere Protocols Cloud type and cover Contrails Precipitation Precipitation pH Digital Max/Min/Current Air & Soil Temperature Surface Temperature Surface Ozone Aerosols Water Vapor Relative Humidity Barometric pressure Atmosphere Measurements Where? Atmosphere Study Site











