Change in supply
advertisement

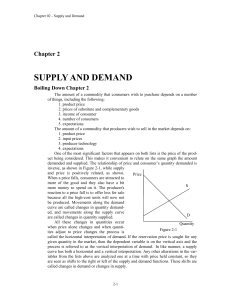
Chapter 3 Demand and Supply Huanren (Warren) Zhang Law of demand • Demand = quantity of a good a consumer is willing and able to purchase at various prices • Law of demand = quantity demanded (Qd) and price (P) are inversely related Change in the quantity demanded • movement from one point to another point on the same demand curve (no shift) Increase in quantity demanded Decrease in quantity demanded B A A B Change in demand • Shift of the entire demand curve Factors causing changes in demand • 1. Income – Normal goods vs. Inferior goods • 2. Prices of related goods – Substitutes vs. Complements • 3. Expectations • 4. # of buyers • 5. Tastes and preferences Law of Supply • Supply = maximum quantity a seller is willing and able to sell at various prices • Law of supply = Price (P) and quantity supplied (Qs) are directly related • Change in the quantity supplied: movement from one point to another point on the same supply curve (no shift) • Change in supply: Shift of the entire supply curve Change in supply Increase in supply Decrease in supply Factors causing changes in supply • 1. Input prices • 2. Price of related goods in production – Substitutes vs. Complements in production • 3. Expectations • 4. # of sellers • 5. Technology Market Equilibrium • Equilibrium in a market occurs when the price balances the plans of buyers and sellers. • When price is greater than equilibrium price, the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded – => there is a surplus and a downward pressure on price • When price is less than equilibrium price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied – => there is a shortage and a upward pressure on price Market equilibrium • Equilibrium price =_____ • Equilibrium quantity= _____ Market equilibrium • Equilibrium price = $6 • Equilibrium quantity= 20 • At P=$4, there is a ____ (surplus/shortage), causing a ____ (increase/decrease) in price • At P=$8, there is a ____ (surplus/shortage), causing a ____ (increase/decrease) in price Market equilibrium • Equilibrium price = $6 • Equilibrium quantity= 20 • At P=$4, there is a shortage, causing a increase in price • At P=$8, there is a surplus, causing a decrease in price Changes in equilibrium • Changes (shifts) in demand • Changes (shifts) in supply • Changes (shifts) in both demand and supply Changes in demand ↑ D → ↑ P and ↑ Q ↓ D → ↓ P and ↓ Q Changes in demand How does an increase in income affect the market for cars (considered as normal goods)? Changes in supply ↑ S → ↓ P and ↑ Q ↓ S → ↑ P and ↓ Q Changes in supply How does an decrease in the price of steel (an input for producing cars) affect the market for cars? Simultaneous shifts in demand and supply • Increase in wages paid to auto workers has raised incomes – Decrease S and increase D • Decrease in S → ↑ P and ↓ Q • Increase in D → ↑ P and ↑ Q • Price rises but change in Q in indeterminate Simultaneous shifts in demand and supply • Anytime both D & S shift, one component of equilibrium will always be indeterminate