Switching losses and snubber circuit
advertisement

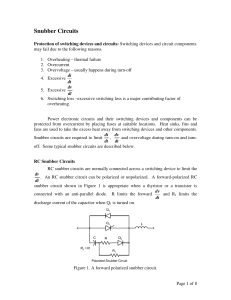
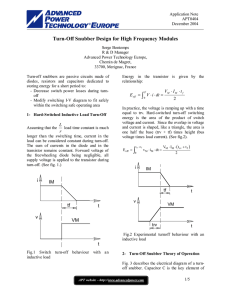
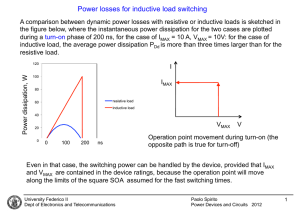
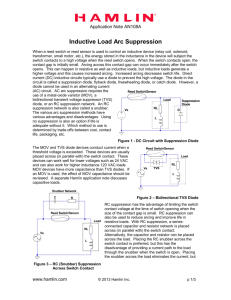
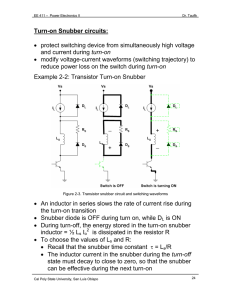
Switching losses & Snubber circuit Ideal switch vs practical switch IDEAL PRACTICAL Block arbitrary large forward and reverse voltages with zero current flow when off Finite blocking voltage with small leakage current during OFF Instantaneous switching from one state to the other Does not instantaneously switch; there is turn-on and turn-off time Conduct arbitrary large current with zero voltage drop when on Finite current conduction capability with small forward voltage drop Negligibly small power required from control source to trigger the switch Some devices required appreciable power to be triggered Ideal switch vs practical switch • In this course, we use ideal switch to describe the power electronic circuits operations – occasionally practical switches will be mentioned. • PE circuit design need to use actual device model in order to analyze power dissipation and efficiency Switching losses Since voltage and current do not change instantaneously, there will be power losses during switching – ‘switching losses’ Switching Power Loss is proportional to: • switching frequency • turn-on and turn-off times Switching losses iT turn-off turn-on Io turn-off turn-on Vd vT The profile must contained within the safe operating area (SOA) of the device Switching losses The profile becomes worse if the stray inductance is considered during the switching vsw = Vd - Ls di dt Switching losses Snubber circuit • In order to reduce the stress and over voltage of the device, a snubber circuit is used to alter the v-i profile of the device • There are various type of snubbers: we will only consider the turn-off and turn-on snubbers Turn-off snubber Turn-on snubber Snubber circuit Turn-off snubber circuit operation • • The switch current can fall immediately since there is a path provided by the capacitor Cs The capacitor voltages increase and stop conducting when Cs=Vd at which diode Df start to conduct Snubber circuit Turn-off snubber circuit operation • • The switch current can fall immediately since there is a path provided by the capacitor Cs The capacitor voltages increase and stop conducting when Cs=Vd at which diode Df start to conduct Snubber circuit Turn-on snubber circuit operation • The stress is reduced by reducing the switch voltage when the switch current increases. Snubber circuit Turn-on snubber circuit operation • The stress is reduced by reducing the switch voltage when the switch current increases.