Chapter 40 Study Guide Answers
advertisement

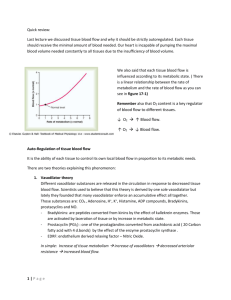
Chapter 40 Study Guide and Notes 1. & 2. How has natural selection/evolution influenced animal body SIZE and FORM? • Physical laws – constrain what natural selection can “invent” – Govern strength, diffusion, movement, heat exchange and therefore limit animal forms Ex. Convergence of body forms in water • Size – thicker skeletons are needed as size increases • Surface area:Volume – regulates size of individual cells – Diffusion across membranes – Thermoregulation of body heat How do the following organisms exchange materials with their environment? How does their structure help this? • Amoeba – Entire surface is in contact with the environment • Hydra – Simple organization where all or nearly all cells are in contact with the environment • A flatworm – Most cells are in direct contact with environment • Whale – Extensively branched or folded surfaces to increase surface area – Interstitial fluid, blood, How are complex body plans advantageous over simple body plans? • Can maintain stable internal environment while living in a variable external environment – External skeleton (protection) – Sensory organs (obtain detailed information) – Internal digestion (control release of stored energy) – Filtration system (adjust composition of interstitial fluid bathing animal’s cells) What is the difference between a Regulator and a Conformer? • Regulator – Uses internal control mechanisms to regulate internal change in the face of external fluctuation. – Mammals • Conformer – Its internal condition conforms to external changes – Reptiles Give an example of negative feedback in detail What is the difference between an endotherm and an ectotherm • Organisms that gain most of their heat from metabolism (cellular respiration) • Mammals and birds • Organisms that gain most of their heat from external sources • Amphibians, reptiles, many fish, most invertebrates List 5 adaptations for thermoregulation • Radiation • Evaporation heat loss • Convection-- Movement of air or liquid past a surface – A breeze to cool organism down – Dilation/constriction of blood vessels • Conduction – direct transfer • Insulation – Controlled seasonally – Amount of hair, feathers, fat or raising the hair/feathers – Oil secretions to waterproof • Circulatory adaptations – Dilation/construction of blood vessels – Countercurrent exchange • Behavioral responses • Adjusting Metabolic heat production – Shivering, nonshivering thermogenesis, brown fat Explain countercurrent exchange • The flow of adjacent fluids in opposing directions that maximizes transfer rates of heat or solutes • Blood vessels are arranged antiparallel to one another • As warm blood passes through arteries, it transfers heat to the colder boold returning from the extremities in the veins • Heat exchange will occur the entire length of the exchanger Basal Metabolic Rate vs. Size Metabolic Rate per kg of body mass vs. body size