Utah*s Biomes
advertisement

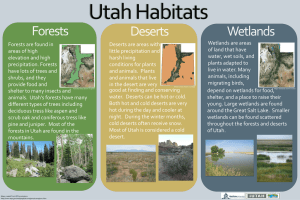
Utah’s Biomes Wetlands Forests Deserts Elevation How does elevation affect: Temperature Precipitation Plants Animals May not always appear wet because of tall plants or low level water. A healthy wetland has a good balance of precipitation and dry weather Wetlands Located between dry land and open water . a low area where the land is soaked with water Wet most of the year because the soil soaks up most of the water and holds it. Wetlands are home for many well-adapted plants and animals. Water enters a wetland by inflow from tributaries or by precipitation. Water can leave a wetland by evaporation (which is the part of the water cycle that includes the movement of water to the air from soil, plants, and water surfaces), by the leaking of water into the soil, or by overflow of water around the edges. Wetlands Wetlands can come in many forms including ponds, swamps, bogs, marshes, lake or river edges, playas, or mudflats. a low area where the land is soaked with water Wetlands are ecosystems in which the soil is saturated with water for at least part of the year (during the growing season). Three things all wetlands have in common 1. Water 2. Wet soil 3. Water loving plants Wetlands a Valuable Resource Help control flooding Clean the water Are rich in natural resources Are the home for more living things than any other habitat Wetlands can benefit us: Wetlands serve as nesting and nursery areas for many kinds of animals. Wetland plants and animals can act like a filter to break down pollution or to trap sediment. Wetlands plants can help to moderate temperatures and also to store carbon. Wetlands can serve as flood control by absorbing water and slowing moving water. Life in the Wetlands Large numbers of fish, insects, birds, and other animals live in the wetlands. They depend upon the wetland habitat to supply them with food, shelter and water. Many animals rely on the protection and security of the large number of plants for raising their young. The wetlands are also used by thousands of migrating birds as nesting and resting places. Coniferous forests Coniferous: evergreen plants that stay green all year and never lose their leaves Forests Deciduous: plants which lose their leaves in the fall and regrow new leaves in the spring an area of land that is covered in trees Deciduous forests The climate in this area has four distinct seasons. The winter in deciduous forests is cold, the summer is hot, and the fall and spring are mild. The average yearly rainfall measures between 75 and 150 cm (30 to 60 in). Deciduous Forests In Utah, the deciduous forests are found on the lower slopes mountains Coniferous Forests Coniferous forest; a forest which is comprised of trees or shrubs that have cones. The winter in this forest is very long and cold. Snowfall is very heavy during the winter season. In the spring the ground often becomes soggy and swampy from the snow melt. Summers are cool and pleasant. Forests a Valuable Resource Forests help reduce gases that are put into the air from cars and factories The trees give out large amounts of oxygen that we breathe Forest help keep our water clean and prevent soil erosion Desert Most of Utah’s natural state is desert land that receives less than 10 inches of rainfall a year Utah is the second driest state in the United States What Plants and Animals do you think live in Utah’s Biomes? Wetlands Deserts Forests