Atmospheric Temperature Controls: Latitude, Altitude & More
advertisement

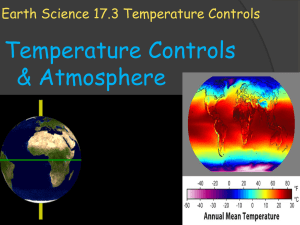
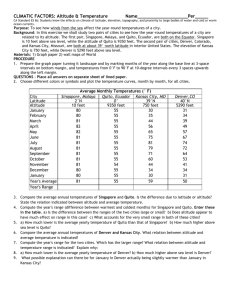
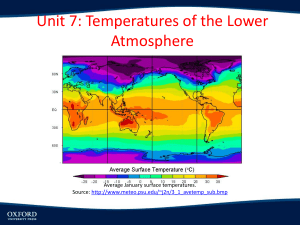
Chapter 17 The Atmosphere: Structure and Temperature Section 17.3 Temperature Controls Temperature Controls Why Temperatures Vary • Temperature is one of the basic elements of weather and climate. • A temperature control is any factor that causes temperature to vary from place to place and from time to time. • Factors that exert a strong influence on temperature are: – Latitude, heating of land and water, altitude, geographic position, cloud cover, and ocean currents. Temperature Controls Why Temperatures Vary • Because variations in the angle of the sun’s rays and length of daylight depend on latitude, they are responsible for warmer temperatures in the tropics and colder temperatures towards the poles. • Seasonal temperature changes happen as the sun’s vertical rays move toward and away from a particular latitude during the year. Question: Which of the following is NOT a factor that controls temperature? A. Longitude B. Cloud cover C. Ocean currents D. Altitude Temperature Controls Land and Water • Land heats more rapidly and to higher temperatures than water. • Land also cools more rapidly and to lower temperatures than water. • Temperature variations are considerably greater over land than over water. – Example: Vancouver has moderate temps compared to Winnipeg due to the proximity to the Pacific Ocean. – Ex: Water accounts for 61% of the Northern Hemisphere and land accounts for the remaining 39%. In the Southern Hemisphere, 81% of the surface is water and only 19% is land. The Southern Hemisphere shows smaller annual temperature variations. Land & Water Mean Monthly Temperatures for Vancouver and Winnipeg Temperature Controls Geographic Position • Geographic settings also play a large role in temperature variations. – A coastal location where prevailing winds blow from the ocean onto shore (windward coast) experience full moderating influence of the ocean – cool summers and mild winters. – A coastal location where the prevailing winds blow from the land to the ocean (leeward coast) will have a more continental temperature pattern. – Example: Eureka, CA is more moderate due to a windward coast compared to NY,NY that has more extreme temps due to the leeward coast. Temperature Controls Mean Monthly Temperatures for Eureka and New York City Temperature Controls Geographic Position • Mountain ranges also effect temperature variations, as they act as barriers. – Mountain ranges cut off the moderating influence of the oceans, thus making those on the windward side of the mountains have more of a marine influence and those on the leeward side a more continental influence. – Example: Spokane has more extreme temp. than Seattle due to the Cascade Mts cutting off the influences of the Pacific Ocean. Temperature Controls Mean Monthly Temperatures for Seattle and Spokane Temperature Controls Altitude • Altitude is another temperature control. • The higher the altitude, the cooler the temperatures. • The lower the altitude, the higher the temperatures. • This is caused by having more or less atmosphere. • Example: Quito, Ecuador is cooler than Guayaquil due to its altitude. Temperature Controls Mean Monthly Temperatures for Guayaquil and Quito Temperature Controls Cloud Cover and Albedo • Cloud cover also greatly effects temperature. • Many clouds have a high albedo, and therefore reflect a significant portion of the sunlight that strikes them back to space. – Albedo: The fraction of total radiation that is reflected by any surface. • By reducing the amount of incoming solar radiation, the maximum temperatures on a cloudy day will be lower than on a cloudless day. • The opposite is true during the night where clouds act as a blanket by absorbing outgoing radiation emitted by the Earth and reradiating it back to the surface. Temperature Controls Clouds Reflect and Absorb Radiation Question: Vancouver, British Columbia, enjoys a moderate year-round climate, which is due to A. The many mountain ranges surrounding the city. B. Its latitude. C. Its relatively high elevation. D. Its close proximity to the Pacific Ocean. Question: The temperature differences seen between Seattle, Washington, and Spokane, Washington, illustrate the effect of A. Cloud cover. B. Geographic position. C. Altitude. D. Ocean currents. Question: The temperature differences between Quito, Ecuador, and Guayaquil, Ecuador, illustrate the effect of A. Cloud cover B. Geographic position. C. Altitude. D. Ocean currents. Question: What causes clouds to reflect a portion of sunlight back to space? A. The amount of oxygen in the atmosphere B. Evaporation from the land C. Temperature differences between the land and the atmosphere D. A characteristic known as albedo Question: Clouds absorb outgoing radiation emitted by Earth and reradiate a portion of it back to the surface during A. Nighttime. B. Daytime. C. Summer. D. Times of heavy rainfall. Temperature Controls World Distribution of Temperature • Isotherms are lines that connect points that have the same temperature. – From hot colors near the equator to cool colors towards the poles. – Isotherms show a general trend of temperatures of land and water, changes in latitude, and ocean currents. – Isotherms generally trend east to west and show a decrease in temperatures from the tropics towards the poles. Question: Which of the following is a general trend on a world isothermal map? A. Temperatures decrease from east to west. B. Isotherms become wider closer to the poles. C. There are more isotherms closer to the equator. D. Temperatures decrease from the tropics toward the poles.