Ch 6 Water Cycle & Weather ppt
advertisement

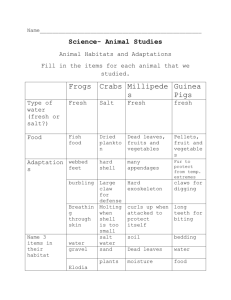
Water Cycle & Weather Chapter 6 L1 Where is Earth’s water? Earth – The water planet – – – – People use water to travel ¾ of surface is covered by water It provides a home & food 3 states of water • Solid (frozen) • Liquid (melted) • Gas (invisible water vapor) Atlantic & Pacific Oceans Arctic & Indian Southern Ocean 97% • Oceans • Seas < 1% • Lakes • Rivers “Water, water, everywhere, Nor any drop to drink” Salt Water Fresh Water Salt v. Fresh • Most of the fresh water is frozen in the polar ice caps and glaciers • You cannot drink salt water • It has dissolved solids in it – Salt from rocks & soil – Rivers carry salt to the ocean – We use ocean salt on food Water table Saltiness MORE • Warm places where water evaporates quickly allows more salt to be quickly left behind (salt does not evaporate) • Red Sea is very salty because there are deserts on three sides • Most of Earth’s water is salty ocean water LESS • Ocean water is less salty near the North and South Poles where the water evaporates less quickly • Fresh water is found in glaciers and ice caps but it is not safe to drink • Safe fresh water is found underground or in lakes, rivers, and streams L2 • • • • Water Cycle Water is recycled No new water is created Water is cleaned through the water cycle Water is always moving – The movement is called the water cycle Water Cycle The Water Cycle • Evaporation – process of changing liquid water to water vapor when it is heated • Condensation – process of water vapor becoming liquid water when it cools • Precipitation any form of water that falls to Earth • Storage (collection) – water from precipitation sinks into soil, or it falls, flows, or seeps into the ocean Sun’s Energy = powers the water cycle Earth’s Atmosphere • The protective blanket that surrounds Earth • It has mass and takes up space • Is a mixture of gases • The layer closest to us has water vapor • Gravity pulls the mass of air to the surface Cumulus Clouds • Thick clouds, white, & puffy, like piles of cotton, they appear in fair/good weather and may reach high in the sky Stratus Clouds • Flat layers of clouds, that form close to Earth’s surface Cirrus Clouds • Feathery clouds that form high in the atmosphere when water vapor turns to tiny crystals of ice L4 meteorologists Ben Tanner, WIS-10 • Study weather conditions, they look at temperature, water, and air movement, data is collected automatically at weather stations barometer • Air pressure affects weather • Air pressure is measured by a tool called a barometer anemometer • Wind affects weather • Wind speed is measured by a tool called an anemometer Wind vane • A wind vane shows the direction from which the wind is blowing • The pointer points into the wind Weather maps • Use symbols to show fronts and weather conditions in different places