Measuring Lung Capacity

Measuring Lung Capacity
Learning Intentions
• Explain the meaning of the terms tidal volume and vital capacity.
• Describe how a spirometer can be used to measure vital capacity, tidal volume, breathing rate and oxygen uptake.
• Analyse and interpret data from a spirometer.
Vital Capacity Is the maximum volume of air that a person can breathe in or out in one breath .
Tidal volume is the volume of air breathed in or out of the lungs in one normal breath at rest .
•
Is a high-tech piece of equipment used to measure vital capacity, tidal volume, breathing rate and oxygen uptake.
Spirometer
Spirometer
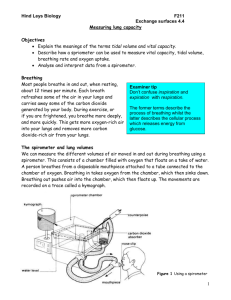
• A spirometer consists of a chamber filled with oxygen on a tank of water.
• A person breaths in the oxygen from the tank causing the lid to sink. Breathing out causes the lid to float up
• The movement of the chamber is recorded using a data logger so that a spirometer trace can be produced.
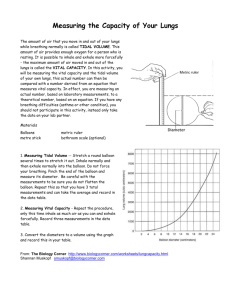
Spirometer Trace
Explanation of the trace
• Residual volume: is the volume of air that always remains in the lungs even after the biggest exhalation
• Dead space: is the air in the bronchioles, bronchi and trachea. There is no gas exchange between this air and the blood.
• Inspiratory reserve volume: is how much more air can be breathed in over and above the normal tidal volume. You use this when exercising.
• Expiratory reserve volume: Is how much more air can be breathed out over and above the normal tidal volume.
Interpreting a spirometer trace
Measurement Male
Tidal Volume
Vital Capacity
Breathing rate
Oxygen uptake dm dm
3
3 breaths/min dm 3 /s
Female
Answer the questions on the worksheet