Plucked strings
advertisement

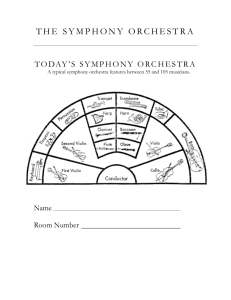
The Orchestra What is an orchestra? The orchestra is made of four families of instruments: •Strings •Brass •Woodwinds •Percussion The string section has been a major part of the orchestra for 200 years. The sound is created by the vibration of strings. There are two types of stringed instruments, bowed and plucked. • Bowed strings are played with a bow, they are the violin, viola, cello and bass. • Plucked strings include the harp, guitar, lute, mandolin, banjo, and others. The strings were originally made out of cat gut, just as tennis racket strings used to be made. The larger the stringed instrument the lower the sound. That’s the case with the String bass. It is sometimes called the double bass or stand-up bass. Large orchestras have 8 to 10 basses. The cello is the second largest of the string section. Of all the strings, the rich, singing sound of the cello make it sound the most like a human voice. Some people believe it is the most expressive instrument in the orchestra. The violin plays an extremely important part in the orchestra, but is the smallest of the string family. It plays the main melody in most orchestral music. The Viola is bigger than the violin, though it looks the same. Its sound is warm, deep and powerful. It is more difficult to play, due to violists having to stretch their fingers further between notes. The plucked strings include the harp, guitar, lute, mandolin and banjo. The strings are plucked to make sweet, delicate music that is softer than most other instruments. The harpsichord also has strings that are plucked. It looks similar to a piano. The piano has strings that are actually hit by small mallets instead of plucked, so it is considered a percussion instrument. All brass instruments are made of long pieces of coiled tubes of metal. Their sound comes from the vibration of air and of the vibration of the musician's lips as they make a buzzing noise. The sound coming out of a brass instrument can be changed when the player changes his lip tension. Members of the brass section include: •French horn •Tuba •Trumpet •Trombone French horns are the leaders of the brass section in the orchestra. They don't have valves. Instead they have keys. Tubas are the largest brass instruments. The first tuba was made in Germany by a composer named Richard Wagner. The trumpet also belongs to the Brass family. • Long ago trumpets were used during battles. • The soldiers would listen for their special trumpet calls to know what to do on the battlefield. • Kings like trumpets to play at their royal celebrations because they sound so important and special. The trombone is another member of the brass family. You play the trombone by sliding tubing back and forth to make the tube longer or shorter. This changes the sound. A woodwind is an instrument that you blow into or over. The woodwinds include flutes, oboes, clarinets, bassoons, and saxophones. The sound is created by the vibration of air and the reed that the musician attaches to the mouthpiece. They are called woodwinds because they used to be made of wood, though saxophones are included because they use a reed. A Reed is a thin piece of cane, which is attached to the mouthpiece of a woodwind instrument to produce sound by vibrating when the player blows into the instrument. There are two types of reeds: Single and Double The clarinet is the most important woodwind in the orchestra. It has a very wide range. A single reed is used on this instrument. It has 18 holes, six of which are covered by fingers and the remainder by keys. The highest woodwind is the flute. Opening and closing holes in the body of the instrument controls the pitch of the tones. This woodwind does not need a reed. The vibration is created by the air blowing over the mouthpiece. Flutes were once made of wood. Today, they can be made of all types of metal, including silver, gold or platinum, or a combination. They are a descendant from another woodwind which does not need a reed called a recorder. The oboe is the soprano of the double-reeded woodwinds. The sound is produced by forcing a column of air and the double reed to vibrate. The bassoon is the lowest and largest of the woodwinds. This sound is also produced by forcing a column of air and a double reed to vibrate. The saxophone is considered a woodwind because even though it is made of brass, it is played in a very similar way to the clarinet and uses a single reed. It is the only woodwind that has never been made of wood. It is made of a long, bent tube with holes in it, which are covered by pads called keys. The saxophone has three parts: the body, the neck and the mouthpiece. The percussion section of the orchestra has many different instruments in it. It is usually in the back of the orchestra. It is made up of instruments that use a mallet, or other device, to strike, shake or rattle to produce the sound. The Tympani is a definite pitched drum in the percussion family. It can be tuned to many different pitches. These drums are often called “Kettle” drums. Another is the snare drum which comes is different types and sizes. They have an upper head which is played by striking and an underneath head which has little strips of gut or metal stretched across it. These strips vibrate to make a rattling sound. Drums are probably the oldest type of percussion instrument. People in the Middle East used to put drums on either side of their camels. The drummer sat on top and played them. These percussion instruments are smaller, hand held instruments. Even though they are very different from other percussion instruments and even from each other, you still play them by hitting, shaking or scraping. Can you name them? The xylophone and glockenspiel are tuned percussion instruments. They hold their tune better that any of the other percussion instruments. The marimba is a larger, deeper, more mellow-sounding type of xylophone. Can you name at least two instruments from each family of the orchestra? Can you recognize the distinct sound of Each family?