File
advertisement

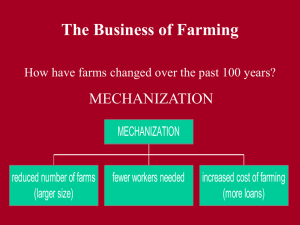
Starter Task: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Zk1nd_dY8 1. Finish your poster (for HW if not enough class time) 2. Fill out the Fish Reflections Worksheet and attach it to your poster. Starter Task You know oranges grow in Florida (Thanks Tropicana commercials!) but can oranges grow in Canada? Explain your answer. Agriculture – The Business of Farming Learning Objective: To explore another primary industry - Agriculture. Activation Task: FILL IN THE ________________. Agriculture depends on the interaction of four natural systems: 1. Climate 2. Soil 3. Biology 4. Topography Two variables in climate contribute to the success of farming: Solar heat Knowing the amount of heat in an area helps farmers determine what type of crop to grow and how long it will take Amount of heat may be measured in growing degree-days (GDD) Farmers also consider the growing season ◦ the number of days during which crops can ripen They also consider the frost-free period ◦ the number of days between the last The second variable farmers consider is moisture Farmers need to know not only how much precipitation they get, but also how much evapotranspiration takes place in their location Warm areas experience more evaportranspiration than cool areas, and will therefore require higher levels of precipitation (or irrigation) for good plant growth Soil is a complex substance composed of minerals, water, air, bacteria, and humus (decaying organic material such as leaves, twigs, grass, and pine cones) Humus is the most important factor determining a soil’s fertility The amount of humus is determined by the amount of moisture and plant growth Some organisms are highly beneficial to farming such as earthworms (improves the movement of air through the soil) and bees (plant pollination) Other organisms are highly destructive (weed and insect pests reduce productivity) Land features have an effect on agricultural productivity as well. Level, well-drained land is generally best for farming (i.e. Fraser River delta, Annapolis Valley) Mountainous or hilly areas that tend to lose topsoil through erosion are less productive Flat, sandy areas with high water tables are also less productive because they are too wet for farming Land is a renewable resource when it can support new crops year after year, if properly used. Land can be classified as a nonrenewable resource because there is a limited amount of it available, especially land that is suitable for farming. 60s-70s federal and provincial governments surveyed parts of Canada to determine the land’s suitability, or land capability, for agriculture. As part of the Canada Land Inventory (CLI), the survey divided Canada’s land into seven classes to form a classification system that is helpful in landuse planning. Canadian Land Inventory - the amount of Class 1 land in all of Canada is less than the size of New Brunswick (0.5% of Canada’s land surface – 4.2 million hectares) - only 11% of Canada’s land surface is capable of agriculture of some kind - 50% of the Class 1 land in Canada is located in Ontario BUT Ontario also has the greatest degree of urbanization in Canada There are five major agricultural production sectors in Canada. a) b) c) d) e) grains & oilseeds (wheat, oats, rye, flax seed, canola, soybeans, and corn ) 34% red meats (beef, hog, veal, lamb) 27% dairy 12 % horticulture 9% poultry and eggs 8% Horticulture, poultry & eggs, and dairy are all produced with a domestic orientation – they stay in Canada Grain and oilseeds & red meat both have a domestic and export orientation – sometimes they stay and sometimes they go In 1867, about 82% of Canadians lived in rural areas In 2000, almost 80% of Canadians live in urban areas, and farmers account for about 3% of Canada’s labour force. What has caused this staggering change? In the 1880s, farmers were able to manage only small farms of about 50 hectare in size Farm work was accomplished by horses pulling plows and wagons, and by human muscle power for most other chores Today, one or two people can operate a farm over 200 hectares in size with the help of modern equipment Increased mechanization has brought about an increase in the size of farms and a decline in their numbers The type of farming is determined not only by natural factors such as soil and climate but also by economic factors: I. Cost and value of land – expensive farmland means the farmer will produce products that earn a high profit. The farmer will use the profit to pay for the mortgage, or to pay higher taxes usually associated with land of higher value II. Proximity to market – If farms are close to their markets, farmers will most likely produce perishable products such as vegetables, milk, and eggs. If they are far from markets, they will produce less perishable products such as grain and oilseeds. III. Competition – If there is an oversupply of a particular product, its price will drop, and farm incomes will diminish. The farmer will then choose to grow another product for which there is a greater demand and higher returns. Intensive Farming ◦ In densely populated areas such as ON, PQ ◦ Farms are small because land is so expensive ◦ Requires large investment in equipment and labour for high profits per hectare ◦ Needs to be processed and transported quickly Extensive Farming ◦ Where population densities are lower ◦ Land is plentiful and not as costly ◦ The profits per hectare are lower, but the larger area makes up for this ◦ It requires less workers and is highly mechanized ◦ Beef cattle, grain, oil seed Demonstration Task: Read page 300. Answer p. 391 #1, 3, 6, 7 The UMM Game: 5 minutes THE FISHING INDUSTRY Talking points: Bycatch, Sustainability, Reasons why the fishing industry is in Crisis, etc. Reflection Task: 1. Did I achieve my learning objective? 1. Can I improve or should I give myself a high-five?