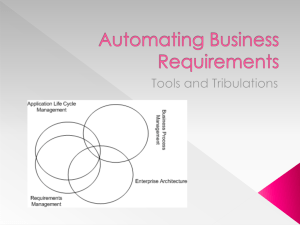
Performance Management
advertisement

April 2012 Agenda 9:00 Arrive 9:15 Officer Announcements Chicago chapter updates 9:30 Guest Speaker: Bryan Rogers Performance Management 10:30 Networking Break 11:00 Group Round Table Discussion 12:00 Adjourn International ABPMP Updates New Registries Available: CBOK Update International Needs Volunteers: Independent Consultant Training Providers Development around Training Provider program CBPP study sessions CBPP exams through the Chapters Improve process for tracking certification / continuing education Renew Certification Chicago Chapter Updates Chicago chapter meeting changes: update your calendars NOW MEETING SECOND FRIDAY OF EVERY OTHER MONTH 8:30-12:30 AM Webinar links will be provided Interested in happy hour events? BrainStorm Chicago May 7-8: http://www.bpminstitute.org/events/brainstormchicago TEK systems – IT trends in industry Achieve Success With BPM Applying BPM to Transform Your Business Managing Processes and Decisions for Better Business Outcomes Using Business Decision Management to Revolutionize Business Requirements and Processes Next Meeting: June 8, 2012 Welcome to new members Name Title, Company What do you want to learn about Performance Management and/or Process Management Presented to Agenda What is Business Process Management? What is Business Performance Management? • What are common themes or issues in Business Performance Management? SEG & Bryan Rogers introduction • What aspects are common between both BPM's and how can they be leveraged together? Summary & Closing remarks 6 Business Process Management Business process management (BPM) is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. Business process management (BPM) is a systematic approach to making an organization's workflow more effective, more efficient and more capable of adapting to an ever-changing environment. A business process is an activity or set of activities that will accomplish a specific organizational goal. The goal of BPM is to reduce human error and miscommunication and focus stakeholders on the requirements of their roles. 7 Business Performance Management Business performance management is a set of management and analytic processes that enable the management of an organization's performance to achieve one or more pre-selected goals. Business performance management is contained within approaches to business process management. Business performance management has three main activities: 1. Selection of goals, 2. Consolidation of measurement information relevant to an organization’s progress against these goals, and 3. Interventions made by managers in light of this information with a view to improving future performance against these goals. 8 Commonalities between Business Process Management and Business Performance Management Alignment of processes with needs of clients and goals of organizations Measurement & Monitoring of processes and results Consolidation of Information Best Practices Solution Decision 9 Bryan Rogers, MBA, CPA Principal, BPM Practice Career Highlights Financial Executive with over 20 years experience FP&A positions with multi-billion dollar companies Former VP of Finance for $300 million business SME for Planning & Reporting BPM Expertise Implementation & Design of Budgeting Solutions BPM Process Redesign Monthly, Quarterly Executive Management Reporting Business Intelligence Solutions Pre & Post Merger & Acquisition Planning Incentive Compensation Reporting & Design Capital Project ROI Analysis 10 BPM – Selection of Goals Stakeholders / Investors Board of Directors / Senior Management Line of Business Management NonManagement Employees Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) 11 BPM – Consolidation of Information Dashboards HRIS Metrics Reports CRM Business Distributed via Intelligence • Handhelds ERP • iPads • Web-access • e-mail CPM 12 • PDF Best Practices: Business Performance Management Process Effective integration of people, processes & systems Involve all department managers Create complete organizational integrity Enhance accountability Improve execution Leverage individual skills Business Performance Management Planning Process Before Best Practice Implementation 15 Best Practices: Business Performance Management Process Effective integration of people, processes & systems People are your most important resource . . . Do they spend their time . . . re-keying in data or providing business insight? making requests to IT or developing their own reports? tying out financial results or developing scenarios? performing manual tasks or reviewing exceptions? What is the cost of underutilized human resources? BPM Best Practices: Planning & Forecasting 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Drive Collaboration Align Strategic and Operating Plans Create Driver-Based Plans Provide Real-Time Visibility into Financial Performance Evaluate Cause and Effect Relationships Deliver Timely and Accurate Reports Perform Continuous Rolling Forecasts Perform What-if Analysis 17 Planning Process After Best Practice Implementation 18 BPM – SaaS solutions Business Process Management (BPM) Software-as-a-service (SaaS), or “software on-demand”, is business management software that is typically deployed offsite by the vendor, and is accessed via the internet. The software may also be installed on a company’s own internal servers and accessed via an intranet or internet. SaaS uses cloud technology whereby multiple end-users, management, and IT access shared resources, software and information. Vendors offering SaaS often provide both shared and dedicated resources (hardware and software), and support a multi-tenant architecture. Licenses are administered on a pay-as-you-go, or per user, basis. 19 Cloud-Based CPM Solution Spreadsheets Manual Inefficient Error-Prone Non-collaborative Cloud-Based CPM Enterprise Apps Difficult to Deploy Fast to deploy Low User-Adoption Easy to use Expensive, Poor ROI Affordable IT-Intensive No IT required 20 On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Solutions 21 Decision Criteria for Solution Maturity Data Participants Integration Frequency Reporting Process Expert Type Number Source How Often Beginner 22 T Complexity & Maturity of Planning and Reporting Maturity Data Participants Integration Frequency Reporting Process Expert Metrics / KPIs All Mgrs with KPI Impact Connector- Other Ops Data Rolling Forecasts XBRL Scenario Analysis Functional Mgrs Import Other Ops Data SEC Reporting Collaborative Online Dialogue Monthly Forecasts Dashboards Alerting Divisional Mgr Connector GL Data Board Packs Workflow Operational Data BS / Cash Flow Inc. Statement Sales Capital Senior Execs Personnel Expense Beginner Finance Import GL Data Quarterly Forecast Mgmt Reporting Export AP to GL Semi-Annual Revision Variance Reports No integration Annual Budget Budget Summary Annotations Email Foundation for Successful Business Process or Performance Management Implementation 1) Get Executive sponsorship early 2) Establish quick wins . . . Relieve the pain 3) Maintain project momentum 4) Create a baseline and define desired improvement in key metric 5) Build culture of continuous improvement 6) Transfer knowledge throughout organization 24 Roundtable Discussions 1) What strategies have you found to work well when implementing a new BPM process? What has not worked well? 2) Have you established Key Performance Indicators or Metrics for your process? 3) How are these KPIs and Metrics communicated to the organization? 4) Does your process include established Best Practices and what are they? 5) What are your future plans for your BPM process and desired objectives? 25 Questions & Answers Please reach out for further information: Bryan Rogers, Principal brogers@solomonedwards.com 26 Overall Trends in BPerfM More enterprises move to cloud Vendors wake up to virtualization Performance benchmarks shift to competition Introduction of new choices Round Table Discussion Points Best Practices in BPerfM and BProcM Create inventory: External organizations on KPI: Identify 6-10 high level “core” processes (order to cash, idea to launch, etc) Identify executives involved in managing these today Ask what are they measuring today and how are they using it? What decisions do they want to make but don’t have metrics today for it? Try to show whether the metrics are aligned to a single process goal or compete against each other? KPI Library APQC HIMMS (Healthcare Info Mgmt) Group consensus building – what is goal of process, then find KPI that support it – use template to rank everyone’s first, second, third priority to show team consensus Round Table Discussion Points Creating a Process Framework: Facilitated discussion Use of industry frameworks: APQC Process Framework Value-Chain.org BPM incubator Need to continual draft, present, communicate concept of framework – everyone has different perspective of process start/end, level of detail, etc. Only map a process if you want to improve it.. Which ones are a priority? Process has to be end-to-end and not functional or task level