Tools of Modern Astronomy
advertisement

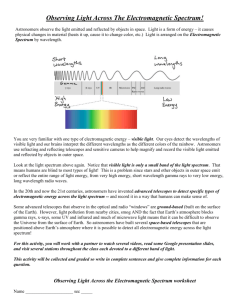
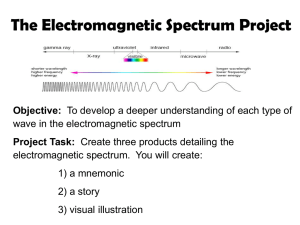
Chapter 21 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Introduction How do we study other stars in our galaxy if they are so far away? We study the radiation that stars emit to find out more about them. Energy that can travel through space Electrois called electromagnetic radiation. magnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic radiation can travel through empty space and travels in waves. Electromagnetic radiation travels the speed of light. Electromagnetic Spectrum Picture From: http://www.astronomynotes.com/light/s3.htm The electromagnetic spectrum is Electrothe full range of wavelengths of magnetic Spectrum electromagnetic radiation. Diagram From: saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/nav-uplink.cfm Diagram From: http://zebu.uoregon.edu/~imamura/122/images/electromagnetic-spectrum.jpg RADIO WAVES Electromagnetic Longest waves and less frequent Spectrum than other waves. Used for communication. Radio telescopes used to collect radio waves. Size of wave ranges from the size of a football field to the size of a football. MICROWAVES Electromagnetic Used in communication, weather Spectrum maps, and as a heat source. Size of wave ranges from 1 foot to 1 centimeter. INFRARED WAVES Electromagnetic Used as a source of heat. Spectrum Infrared telescopes used to detect infrared waves. Size of wave ranges from a few centimeters to a few millimeters. VISIBLE LIGHT Electromagnetic Only energy we can see with the Spectrum naked eye. Refracting and reflecting telescopes use visible light. Size of wave is microscopic. VISIBLE LIGHT Electromagnetic White light can be separated into the Spectrum 7 different colors of light. ROYGBIV Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet Spectroscopes used to break white light down into different colors. ULTRAVIOLET WAVES Electromagnetic Energy that is partially blocked by Spectrum our atmosphere. Common uses are tanning beds, disinfection, and black lights. A large amount of UV light is harmful for living things. UV cameras and telescopes use UV rays. Size of wave is a few molecules. X-RAYS Electromagnetic Atmosphere reflects all X-rays back into space. Spectrum Commonly used to take pictures of bones. Very harmful to living things. X-ray telescopes use X-rays. Size of wave is one molecule. GAMMA WAVES Electromagnetic Shortest wave with the most energy. Spectrum Atmosphere blocks all gamma rays from entering. Deadly to living things. Used for medical treatment. Gamma telescopes study deep space, black holes, stars, etc. Size of wave is smaller than an atom. Telescopes Most telescopes collect and focus different types of electromagnetic radiation. Two main types of telescopes: reflecting and refracting telescopes. Refracting telescopes use lenses that bend light to focus onto a small area. Reflecting telescopes use mirrors instead of lenses but still focuses light onto a small area. The Keck Telescopes: Located in Mauna Kea, Hawaii Hale 200-inch Reflector: Located in Mt. Palomar, California Observat- A building that contains one or more telescopes is an observatory. ories Most observatories are on mountaintops where images are less blurred because of the Earth’s atmosphere. A giant telescope relies on multiple dishes - Located in Socorro, New Mexico Satellites The shorter electromagnetic radiation is blocked by the Earth’s atmosphere. Telescopes are placed on satellites to detect these short, high energy waves. Hubble Space Telescope – reflecting telescope that detects visible light, infrared, and UV radiation. Hubble Space Telescope Compton Gamma Ray Observatory Chandra X-ray Observatory A telescope penetrates space with X-ray vision Spitzer Space Telescope It will spend 2 ½ to 5 years studying infrared light. Spectrographs Most large telescopes have spectrographs. A spectrograph breaks the light up into colors. Spectrographs reveal information about stars like their composition and temperatures. Electromagnetic Spectrum Video Clip: http://lgfl.skoool.co.uk/keystage4.aspx?id=318 Electromagnetic Spectrum Video Clip