Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic Waves
advertisement

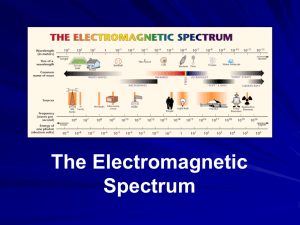
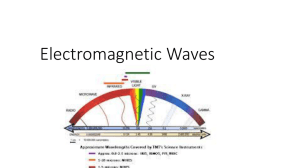
Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic Waves Mechanical Waves • Waves that require a material medium • Examples include water, sound, and waves along a spring or rope • These materials carry the energy of the wave Electromagnetic Waves • Waves that DO NOT require a medium for motion • Examples include light waves, radio waves, and X-rays • All electromagnetic waves travel through space at the speed of light • Since these waves can’t be observed, we study mechanical waves Electromagnetic Waves Transverse Waves Mechanical Waves Longitudinal Waves Electromagnetic Waves Surface Waves Waves Transverse Waves • Particles of medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the motion of the wave • Examples include guitar strings, waves in piano strings Longitudinal Wave • Particles of medium to move parallel to the direction of the wave • Examples include sound waves, waves through fluids, liquids, gases or plasma Surface Waves • Mixture of transverse and longitudinal waves • Example: At the surface of the water, particles move parallel and perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Earthworm Examination • Grab an earthworm from the vermicompost. Study the movement and decide whether an earthworm moves by longitudinal, transverse, or surface waves... Types of Waves • Using materials around the classroom, set up a demonstration showing a: – Transverse Wave – Longitudinal Wave – Surface Wave