energy - City of Cape Town
advertisement
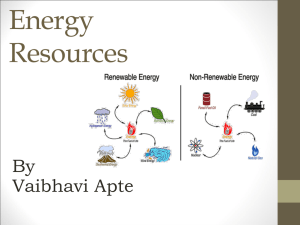
ENERGY Global Warming The atmosphere is like an insulator keeping in greenhouse gasses such as CO2, methane, etc. The sun is our primary energy source Greenhouse gasses trap heat and leads to global warming / climate change. Climate change Greenhouse gases are increasing. Average global temperatures are rising. Climate changes are happening. An inconvenient truth Ancient Sunlight Fossil Fuels SA relies heavily on crude oil imported from the Middle East. • Crude oil is shipped to Saldanha Bay, north of CT • Pumped 120km to the refinery in Milnerton • Refined into liquid fuels like petrol, diesel, paraffin and gas • Distributed to fuel suppliers Power plant to plug • Most of the electricity in SA is generated near the coal fields of Mpumalanga. • Transmission occurs through huge power lines along Eskom’s national grid. Other fuel types Paraffin Wood LPG Carbon Footprint • Burning coal releases harmful gases into the atmosphere. • SO2 + water = acid rain. • CO2 = highest contributing global warming greenhouse gas. • Methane and other gasses are however much stronger • Most of SAs energy comes from burning coal, a fossil fuel Carbon Footprint We produce on average 8 tons of CO2 per person each year in South Africa • Coal based electricity • “Cheap” electricity • Inefficient systems 8 4 1 Do you know your carbon footprint? For on-line carbon calculators visit www.trees.co.za or www.bp.com Renewable Energy Renewable or not? • Fossil fuels cannot be reproduced or regenerated on a scale that can sustain consumption patterns indefinitely and mostly exist in a fixed amount, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas • Renewable energy is energy that comes from renewable resources, such as wind, solar, geothermal, biofuels Potential energy sources Wind 870 TW Geothermal 32 TW Hydro 7,2 TW Solar / Sun 86 000 TW Global human energy consumption 15 TW Solar Power • The average home in SA receives 600kWh of sunshine per day • The average home uses 774kWh of electricity per month Solar Water Heating Solar water heaters • Electric hot water geysers use 60% of the energy in a home • The sun heats water directly and does not create electricity • Solar water heaters are costly, but save huge amounts over time Solar Power (PV) Solar power generation • Photovoltaic (PV) cells convert sunlight into electricity • This electricity can be stored in batteries and used when required • It is however still relatively expensive Alternative Energy Consider alternative cooking options Alternative Options Induction stove top Alternative Options Heat Pump • Not renewable, but very efficient for heating and cooling water or air • Air-to-water • Air-to-air • Eskom is currently giving rebates • Cheaper than a SWH Wind Turbines • Wind farms produce clean sustainable electricity, but it is an expensive option • No pollution • No natural resources depleted Renewable Energy • Biofuels can be produced from wheat, corn, potato, sugar cane, etc • Spent oil or algae can also be used and has no impact on food security • Be aware of concerns around food security Nuclear Power Nuclear Power Is nuclear power an option? • Koeberg is the only nuclear power station in Africa • Power is relatively clean – minimal CO2 emissions • Output is high – one uranium pebble (size of cricket ball) produces as much electricity as (a truck load) 7,6 tons of coal • SA is rich in uranium, the core of nuclear fuel, although most of the uranium needed is imported Nuclear Power • Uranium is a non-renewable resource • Radioactive waste is highly dangerous • It must be buried far underground as it remains active for 1000s of years. Remember to tell your grandchildren's children to tell their grandchildren's children, to tell their grandchildren's children, to tell their grandchildren's, grandchildren's, •children Uranium is ato non-renewable how deal with the resource • Radioactive is highly dangerous nuclearwaste waste... • It must be buried far underground as it remains active for 1000s of years. Nuclear Power Transport in our City Over 50% of all energy used in Cape Town is spent on transportation - cars, buses, trains and taxis. Transport in our City How can we reduce our fuel consumption? •Lift clubs / car share • Use public transport • Drive our cars efficiently • Buy smaller & efficient cars • Consider a hybrid vehicle • Cycle or walk Eco Driving • Service your vehicle regularly • Check your tyre pressure monthly • Remove unnecessary weight from your vehicle • Close your windows at higher speeds • Use air conditioning sparingly • Reduce idling • Avoid speeding and drive smoothly • When accelerating, change gears as early as possible Bus Rapid Transport (BRT) The City aims to provide better public transport services Energy Efficiency The energy efficient house p58 Energy efficient homes Electricity Safety • Check that all electrical wiring is correct and safe • Check for gas leaks • Make sure your home is well ventilated BLue is Left BRown is Right Energy saving tips Energy saving tips Energy saving tips WASTE WASTE ENERGY ENERGY The challenge: What are you going to do differently? WATER WATER BIODIVERSITY BIODIVERSITY